Rohan Rao
HybridRAG: Integrating Knowledge Graphs and Vector Retrieval Augmented Generation for Efficient Information Extraction
Aug 09, 2024



Abstract:Extraction and interpretation of intricate information from unstructured text data arising in financial applications, such as earnings call transcripts, present substantial challenges to large language models (LLMs) even using the current best practices to use Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) (referred to as VectorRAG techniques which utilize vector databases for information retrieval) due to challenges such as domain specific terminology and complex formats of the documents. We introduce a novel approach based on a combination, called HybridRAG, of the Knowledge Graphs (KGs) based RAG techniques (called GraphRAG) and VectorRAG techniques to enhance question-answer (Q&A) systems for information extraction from financial documents that is shown to be capable of generating accurate and contextually relevant answers. Using experiments on a set of financial earning call transcripts documents which come in the form of Q&A format, and hence provide a natural set of pairs of ground-truth Q&As, we show that HybridRAG which retrieves context from both vector database and KG outperforms both traditional VectorRAG and GraphRAG individually when evaluated at both the retrieval and generation stages in terms of retrieval accuracy and answer generation. The proposed technique has applications beyond the financial domain
3D Human Reconstruction in the Wild with Collaborative Aerial Cameras
Aug 09, 2021
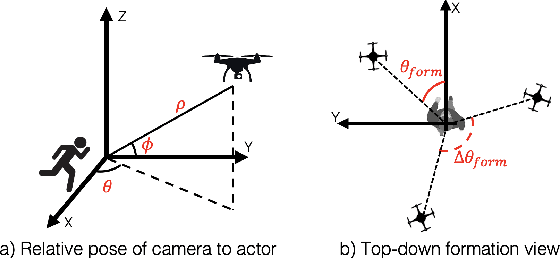
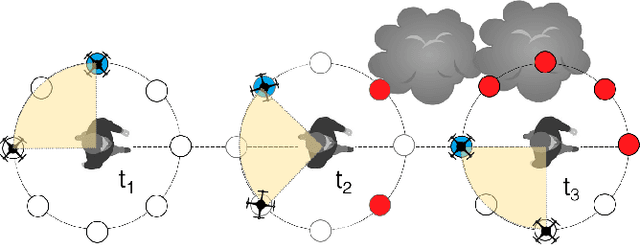

Abstract:Aerial vehicles are revolutionizing applications that require capturing the 3D structure of dynamic targets in the wild, such as sports, medicine, and entertainment. The core challenges in developing a motion-capture system that operates in outdoors environments are: (1) 3D inference requires multiple simultaneous viewpoints of the target, (2) occlusion caused by obstacles is frequent when tracking moving targets, and (3) the camera and vehicle state estimation is noisy. We present a real-time aerial system for multi-camera control that can reconstruct human motions in natural environments without the use of special-purpose markers. We develop a multi-robot coordination scheme that maintains the optimal flight formation for target reconstruction quality amongst obstacles. We provide studies evaluating system performance in simulation, and validate real-world performance using two drones while a target performs activities such as jogging and playing soccer. Supplementary video: https://youtu.be/jxt91vx0cns
Wasserstein K-Means for Clustering Tomographic Projections
Oct 20, 2020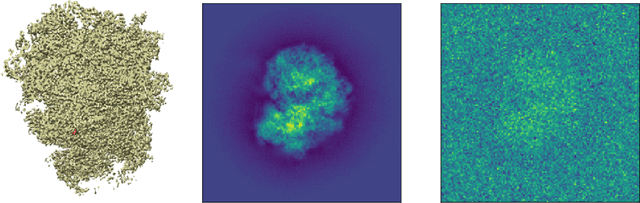
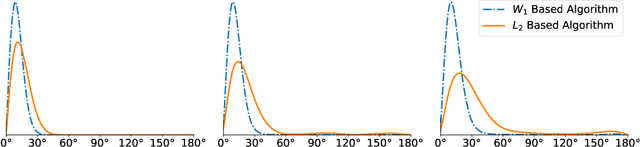
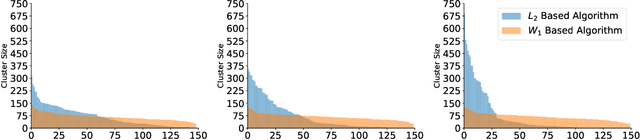
Abstract:Motivated by the 2D class averaging problem in single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), we present a k-means algorithm based on a rotationally-invariant Wasserstein metric for images. Unlike existing methods that are based on Euclidean ($L_2$) distances, we prove that the Wasserstein metric better accommodates for the out-of-plane angular differences between different particle views. We demonstrate on a synthetic dataset that our method gives superior results compared to an $L_2$ baseline. Furthermore, there is little computational overhead, thanks to the use of a fast linear-time approximation to the Wasserstein-1 metric, also known as the Earthmover's distance.
Keep CALM and Explore: Language Models for Action Generation in Text-based Games
Oct 06, 2020



Abstract:Text-based games present a unique challenge for autonomous agents to operate in natural language and handle enormous action spaces. In this paper, we propose the Contextual Action Language Model (CALM) to generate a compact set of action candidates at each game state. Our key insight is to train language models on human gameplay, where people demonstrate linguistic priors and a general game sense for promising actions conditioned on game history. We combine CALM with a reinforcement learning agent which re-ranks the generated action candidates to maximize in-game rewards. We evaluate our approach using the Jericho benchmark, on games unseen by CALM during training. Our method obtains a 69% relative improvement in average game score over the previous state-of-the-art model. Surprisingly, on half of these games, CALM is competitive with or better than other models that have access to ground truth admissible actions. Code and data are available at https://github.com/princeton-nlp/calm-textgame.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge