Robert Haase
Efficient MedSAMs: Segment Anything in Medical Images on Laptop
Dec 20, 2024


Abstract:Promptable segmentation foundation models have emerged as a transformative approach to addressing the diverse needs in medical images, but most existing models require expensive computing, posing a big barrier to their adoption in clinical practice. In this work, we organized the first international competition dedicated to promptable medical image segmentation, featuring a large-scale dataset spanning nine common imaging modalities from over 20 different institutions. The top teams developed lightweight segmentation foundation models and implemented an efficient inference pipeline that substantially reduced computational requirements while maintaining state-of-the-art segmentation accuracy. Moreover, the post-challenge phase advanced the algorithms through the design of performance booster and reproducibility tasks, resulting in improved algorithms and validated reproducibility of the winning solution. Furthermore, the best-performing algorithms have been incorporated into the open-source software with a user-friendly interface to facilitate clinical adoption. The data and code are publicly available to foster the further development of medical image segmentation foundation models and pave the way for impactful real-world applications.
Gadolinium dose reduction for brain MRI using conditional deep learning
Mar 06, 2024



Abstract:Recently, deep learning (DL)-based methods have been proposed for the computational reduction of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) to mitigate adverse side effects while preserving diagnostic value. Currently, the two main challenges for these approaches are the accurate prediction of contrast enhancement and the synthesis of realistic images. In this work, we address both challenges by utilizing the contrast signal encoded in the subtraction images of pre-contrast and post-contrast image pairs. To avoid the synthesis of any noise or artifacts and solely focus on contrast signal extraction and enhancement from low-dose subtraction images, we train our DL model using noise-free standard-dose subtraction images as targets. As a result, our model predicts the contrast enhancement signal only; thereby enabling synthesization of images beyond the standard dose. Furthermore, we adapt the embedding idea of recent diffusion-based models to condition our model on physical parameters affecting the contrast enhancement behavior. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on synthetic and real datasets using various scanners, field strengths, and contrast agents.
Faithful Synthesis of Low-dose Contrast-enhanced Brain MRI Scans using Noise-preserving Conditional GANs
Jun 26, 2023Abstract:Today Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) are indispensable in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for diagnosing various diseases. However, GBCAs are expensive and may accumulate in patients with potential side effects, thus dose-reduction is recommended. Still, it is unclear to which extent the GBCA dose can be reduced while preserving the diagnostic value -- especially in pathological regions. To address this issue, we collected brain MRI scans at numerous non-standard GBCA dosages and developed a conditional GAN model for synthesizing corresponding images at fractional dose levels. Along with the adversarial loss, we advocate a novel content loss function based on the Wasserstein distance of locally paired patch statistics for the faithful preservation of noise. Our numerical experiments show that conditional GANs are suitable for generating images at different GBCA dose levels and can be used to augment datasets for virtual contrast models. Moreover, our model can be transferred to openly available datasets such as BraTS, where non-standard GBCA dosage images do not exist.
Understanding metric-related pitfalls in image analysis validation
Feb 09, 2023Abstract:Validation metrics are key for the reliable tracking of scientific progress and for bridging the current chasm between artificial intelligence (AI) research and its translation into practice. However, increasing evidence shows that particularly in image analysis, metrics are often chosen inadequately in relation to the underlying research problem. This could be attributed to a lack of accessibility of metric-related knowledge: While taking into account the individual strengths, weaknesses, and limitations of validation metrics is a critical prerequisite to making educated choices, the relevant knowledge is currently scattered and poorly accessible to individual researchers. Based on a multi-stage Delphi process conducted by a multidisciplinary expert consortium as well as extensive community feedback, the present work provides the first reliable and comprehensive common point of access to information on pitfalls related to validation metrics in image analysis. Focusing on biomedical image analysis but with the potential of transfer to other fields, the addressed pitfalls generalize across application domains and are categorized according to a newly created, domain-agnostic taxonomy. To facilitate comprehension, illustrations and specific examples accompany each pitfall. As a structured body of information accessible to researchers of all levels of expertise, this work enhances global comprehension of a key topic in image analysis validation.
A Hitchhiker`s Guide through the Bio-image Analysis Software Universe
Apr 15, 2022
Abstract:Modern research in the life sciences is unthinkable without computational methods for extracting, quantifying and visualizing information derived from biological microscopy imaging data. In the past decade, we observed a dramatic increase in available software packages for these purposes. As it is increasingly difficult to keep track of the number of available image analysis platforms, tool collections, components and emerging technologies, we provide a conservative overview of software we use in daily routine and give insights into emerging new tools. We give guidance on which aspects to consider when choosing the right platform, including aspects such as image data type, skills of the team, infrastructure and community at the institute and availability of time and budget.
Star-convex Polyhedra for 3D Object Detection and Segmentation in Microscopy
Aug 09, 2019


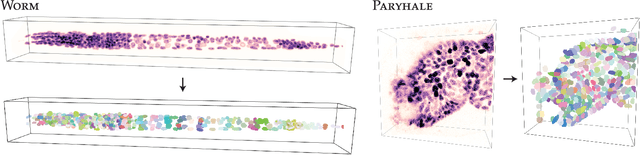
Abstract:Accurate detection and segmentation of cell nuclei in volumetric (3D) fluorescence microscopy datasets is an important step in many biomedical research projects. Although many automated methods for these tasks exist, they often struggle for images with low signal-to-noise ratios and/or dense packing of nuclei. It was recently shown for 2D microscopy images that these issues can be alleviated by training a neural network to directly predict a suitable shape representation (star-convex polygon) for cell nuclei. In this paper, we adopt and extend this approach to 3D volumes by using star-convex polyhedra to represent cell nuclei and similar shapes. To that end, we overcome the challenges of 1) finding parameter-efficient star-convex polyhedra representations that can faithfully describe cell nuclei shapes, 2) adapting to anisotropic voxel sizes often found in fluorescence microscopy datasets, and 3) efficiently computing intersections between pairs of star-convex polyhedra (required for non-maximum suppression). Although our approach is quite general, since star-convex polyhedra subsume common shapes like bounding boxes and spheres as special cases, our focus is on accurate detection and segmentation of cell nuclei. That that end, we demonstrate on two challenging datasets that our approach (StarDist-3D) leads to superior results when compared to classical and deep-learning based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge