Rebecca Kramer-Bottiglio
Yale University
An Open-Source, Reproducible Tensegrity Robot that can Navigate Among Obstacles
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Tensegrity robots, composed of rigid struts and elastic tendons, provide impact resistance, low mass, and adaptability to unstructured terrain. Their compliance and complex, coupled dynamics, however, present modeling and control challenges, hindering path planning and obstacle avoidance. This paper presents a complete, open-source, and reproducible system that enables navigation for a 3-bar tensegrity robot. The system comprises: (i) an inexpensive, open-source hardware design, and (ii) an integrated, open-source software stack for physics-based modeling, system identification, state estimation, path planning, and control. All hardware and software are publicly available at https://sites.google.com/view/tensegrity-navigation/. The proposed system tracks the robot's pose and executes collision-free paths to a specified goal among known obstacle locations. System robustness is demonstrated through experiments involving unmodeled environmental challenges, including a vertical drop, an incline, and granular media, culminating in an outdoor field demonstration. To validate reproducibility, experiments were conducted using robot instances at two different laboratories. This work provides the robotics community with a complete navigation system for a compliant, impact-resistant, and shape-morphing robot. This system is intended to serve as a springboard for advancing the navigation capabilities of other unconventional robotic platforms.
Impact-resistant, autonomous robots inspired by tensegrity architecture
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:Future robots will navigate perilous, remote environments with resilience and autonomy. Researchers have proposed building robots with compliant bodies to enhance robustness, but this approach often sacrifices the autonomous capabilities expected of rigid robots. Inspired by tensegrity architecture, we introduce a tensegrity robot -- a hybrid robot made from rigid struts and elastic tendons -- that demonstrates the advantages of compliance and the autonomy necessary for task performance. This robot boasts impact resistance and autonomy in a field environment and additional advances in the state of the art, including surviving harsh impacts from drops (at least 5.7 m), accurately reconstructing its shape and orientation using on-board sensors, achieving high locomotion speeds (18 bar lengths per minute), and climbing the steepest incline of any tensegrity robot (28 degrees). We characterize the robot's locomotion on unstructured terrain, showcase its autonomous capabilities in navigation tasks, and demonstrate its robustness by rolling it off a cliff.
Learning Differentiable Tensegrity Dynamics using Graph Neural Networks
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:Tensegrity robots are composed of rigid struts and flexible cables. They constitute an emerging class of hybrid rigid-soft robotic systems and are promising systems for a wide array of applications, ranging from locomotion to assembly. They are difficult to control and model accurately, however, due to their compliance and high number of degrees of freedom. To address this issue, prior work has introduced a differentiable physics engine designed for tensegrity robots based on first principles. In contrast, this work proposes the use of graph neural networks to model contact dynamics over a graph representation of tensegrity robots, which leverages their natural graph-like cable connectivity between end caps of rigid rods. This learned simulator can accurately model 3-bar and 6-bar tensegrity robot dynamics in simulation-to-simulation experiments where MuJoCo is used as the ground truth. It can also achieve higher accuracy than the previous differentiable engine for a real 3-bar tensegrity robot, for which the robot state is only partially observable. When compared against direct applications of recent mesh-based graph neural network simulators, the proposed approach is computationally more efficient, both for training and inference, while achieving higher accuracy. Code and data are available at https://github.com/nchen9191/tensegrity_gnn_simulator_public
Stretchable Arduinos embedded in soft robots
Sep 16, 2024Abstract:To achieve real-world functionality, robots must have the ability to carry out decision-making computations. However, soft robots stretch and therefore need a solution other than rigid computers. Examples of embedding computing capacity into soft robots currently include appending rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs) to the robot, integrating soft logic gates, and exploiting material responses for material-embedded computation. Although promising, these approaches introduce limitations such as rigidity, tethers, or low logic gate density. The field of stretchable electronics has sought to solve these challenges, but a complete pipeline for direct integration of single-board computers, microcontrollers, and other complex circuitry into soft robots has remained elusive. We present a generalized method to translate any complex two-layer circuit into a soft, stretchable form. This enabled the creation of stretchable single-board microcontrollers (including Arduinos) and other commercial circuits (including Sparkfun circuits), without design simplifications. As demonstrations of the method's utility, we embed highly stretchable (>300% strain) Arduino Pro Minis into the bodies of multiple soft robots. This makes use of otherwise inert structural material, fulfilling the promise of the stretchable electronics field to integrate state-of-the-art computational power into robust, stretchable systems during active use.
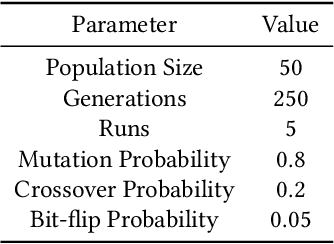
* 45 pages, 19 figures total. Main text is 28 pages with 6 figures. The rest is supplementary
Gradient-based Design of Computational Granular Crystals
Apr 07, 2024Abstract:There is growing interest in engineering unconventional computing devices that leverage the intrinsic dynamics of physical substrates to perform fast and energy-efficient computations. Granular metamaterials are one such substrate that has emerged as a promising platform for building wave-based information processing devices with the potential to integrate sensing, actuation, and computation. Their high-dimensional and nonlinear dynamics result in nontrivial and sometimes counter-intuitive wave responses that can be shaped by the material properties, geometry, and configuration of individual grains. Such highly tunable rich dynamics can be utilized for mechanical computing in special-purpose applications. However, there are currently no general frameworks for the inverse design of large-scale granular materials. Here, we build upon the similarity between the spatiotemporal dynamics of wave propagation in material and the computational dynamics of Recurrent Neural Networks to develop a gradient-based optimization framework for harmonically driven granular crystals. We showcase how our framework can be utilized to design basic logic gates where mechanical vibrations carry the information at predetermined frequencies. We compare our design methodology with classic gradient-free methods and find that our approach discovers higher-performing configurations with less computational effort. Our findings show that a gradient-based optimization method can greatly expand the design space of metamaterials and provide the opportunity to systematically traverse the parameter space to find materials with the desired functionalities.
Universal Mechanical Polycomputation in Granular Matter
May 29, 2023Abstract:Unconventional computing devices are increasingly of interest as they can operate in environments hostile to silicon-based electronics, or compute in ways that traditional electronics cannot. Mechanical computers, wherein information processing is a material property emerging from the interaction of components with the environment, are one such class of devices. This information processing can be manifested in various physical substrates, one of which is granular matter. In a granular assembly, vibration can be treated as the information-bearing mode. This can be exploited to realize "polycomputing": materials can be evolved such that a single grain within them can report the result of multiple logical operations simultaneously at different frequencies, without recourse to quantum effects. Here, we demonstrate the evolution of a material in which one grain acts simultaneously as two different NAND gates at two different frequencies. NAND gates are of interest as any logical operations can be built from them. Moreover, they are nonlinear thus demonstrating a step toward general-purpose, computationally dense mechanical computers. Polycomputation was found to be distributed across each evolved material, suggesting the material's robustness. With recent advances in material sciences, hardware realization of these materials may eventually provide devices that challenge the computational density of traditional computers.
Real2Sim2Real Transfer for Control of Cable-driven Robots via a Differentiable Physics Engine
Sep 20, 2022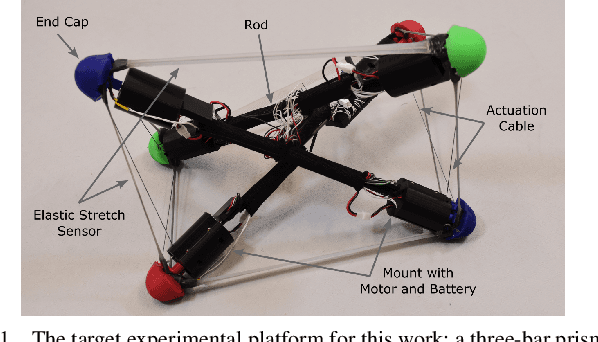
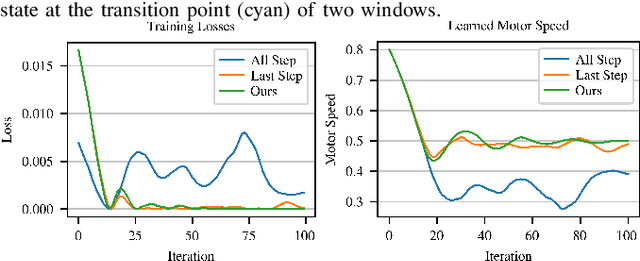
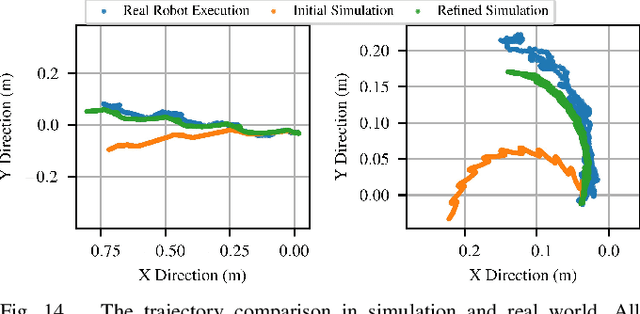
Abstract:Tensegrity robots, composed of rigid rods and flexible cables, exhibit high strength-to-weight ratios and extreme deformations, enabling them to navigate unstructured terrain and even survive harsh impacts. However, they are hard to control due to their high dimensionality, complex dynamics, and coupled architecture. Physics-based simulation is one avenue for developing locomotion policies that can then be transferred to real robots, but modeling tensegrity robots is a complex task, so simulations experience a substantial sim2real gap. To address this issue, this paper describes a Real2Sim2Real strategy for tensegrity robots. This strategy is based on a differential physics engine that can be trained given limited data from a real robot (i.e. offline measurements and one random trajectory) and achieve a high enough accuracy to discover transferable locomotion policies. Beyond the overall pipeline, key contributions of this work include computing non-zero gradients at contact points, a loss function, and a trajectory segmentation technique that avoid conflicts in gradient evaluation during training. The proposed pipeline is demonstrated and evaluated on a real 3-bar tensegrity robot.
6N-DoF Pose Tracking for Tensegrity Robots
May 29, 2022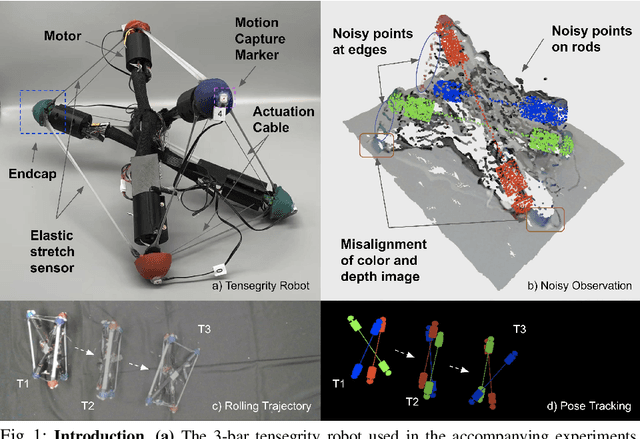
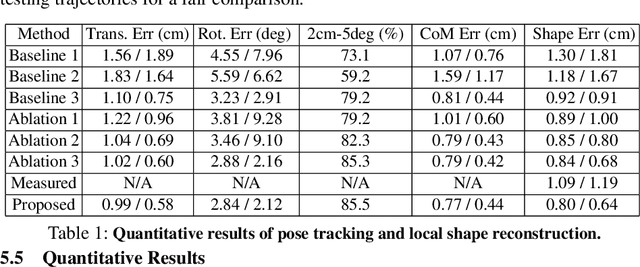


Abstract:Tensegrity robots, which are composed of rigid compressive elements (rods) and flexible tensile elements (e.g., cables), have a variety of advantages, including flexibility, light weight, and resistance to mechanical impact. Nevertheless, the hybrid soft-rigid nature of these robots also complicates the ability to localize and track their state. This work aims to address what has been recognized as a grand challenge in this domain, i.e., the pose tracking of tensegrity robots through a markerless, vision-based method, as well as novel, onboard sensors that can measure the length of the robot's cables. In particular, an iterative optimization process is proposed to estimate the 6-DoF poses of each rigid element of a tensegrity robot from an RGB-D video as well as endcap distance measurements from the cable sensors. To ensure the pose estimates of rigid elements are physically feasible, i.e., they are not resulting in collisions between rods or with the environment, physical constraints are introduced during the optimization. Real-world experiments are performed with a 3-bar tensegrity robot, which performs locomotion gaits. Given ground truth data from a motion capture system, the proposed method achieves less than 1 cm translation error and 3 degrees rotation error, which significantly outperforms alternatives. At the same time, the approach can provide pose estimates throughout the robot's motion, while motion capture often fails due to occlusions.
Evolving Programmable Computational Metamaterials
Apr 19, 2022
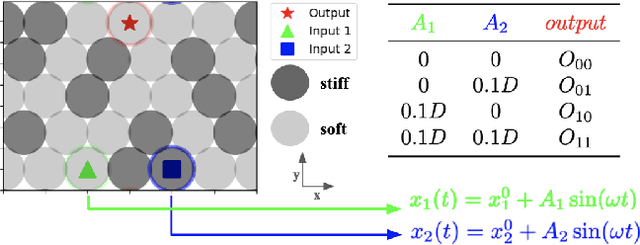
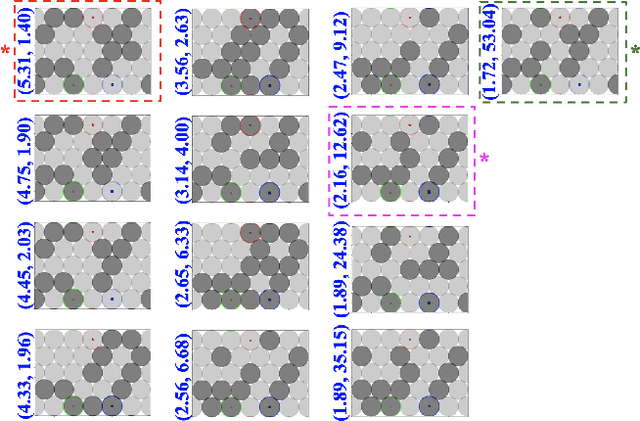
Abstract:Granular metamaterials are a promising choice for the realization of mechanical computing devices. As preliminary evidence of this, we demonstrate here how to embed Boolean logic gates (AND and XOR) into a granular metamaterial by evolving where particular grains are placed in the material. Our results confirm the existence of gradients of increasing "AND-ness" and "XOR-ness" within the space of possible materials that can be followed by evolutionary search. We measure the computational functionality of a material by probing how it transforms bits encoded as vibrations with zero or non-zero amplitude. We compared the evolution of materials built from mass-contrasting particles and materials built from stiffness-contrasting particles, and found that the latter were more evolvable. We believe this work may pave the way toward evolutionary design of increasingly sophisticated, programmable, and computationally dense metamaterials with certain advantages over more traditional computational substrates.
Soft Lattice Modules that Behave Independently and Collectively
Oct 21, 2021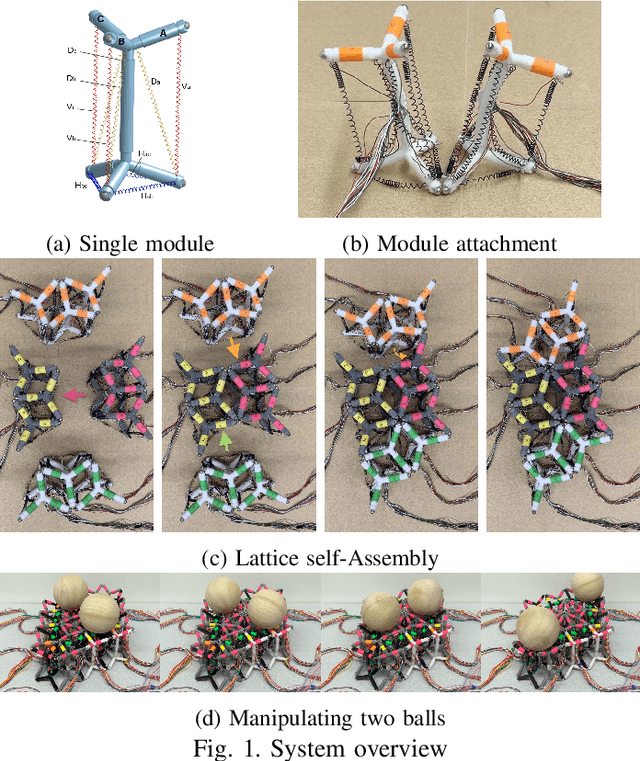

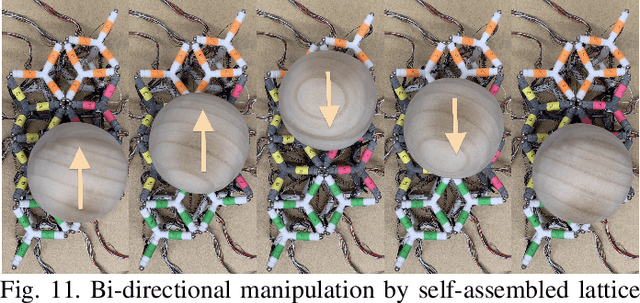
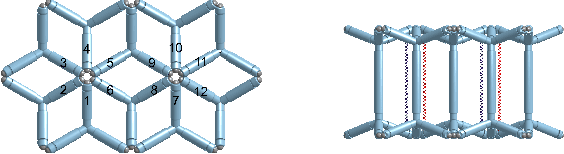
Abstract:Natural systems integrate the work of many sub-units (cells) toward a large-scale unified goal (morphological and behavioral), which can counteract the effects of unexpected experiences, damage, or simply changes in tasks demands. In this paper, we exploit the opportunities presented by soft, modular, and tensegrity robots to introduce soft lattice modules that parallel the sub-units seen in biological systems. The soft lattice modules are comprised of 3D printed plastic "skeletons", linear contracting shape memory alloy spring actuators, and permanent magnets that enable adhesion between modules. The soft lattice modules are capable of independent locomotion, and can also join with other modules to achieve collective, self-assembled, larger scale tasks such as collective locomotion and moving an object across the surface of the lattice assembly. This work represents a preliminary step toward soft modular systems capable of independent and collective behaviors, and provide a platform for future studies on distributed control.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge