Amir Mohammadi Nasab
Scale invariant robot behavior with fractals
Mar 08, 2021



Abstract:Robots deployed at orders of magnitude different size scales, and that retain the same desired behavior at any of those scales, would greatly expand the environments in which the robots could operate. However it is currently not known whether such robots exist, and, if they do, how to design them. Since self similar structures in nature often exhibit self similar behavior at different scales, we hypothesize that there may exist robot designs that have the same property. Here we demonstrate that this is indeed the case for some, but not all, modular soft robots: there are robot designs that exhibit a desired behavior at a small size scale, and if copies of that robot are attached together to realize the same design at higher scales, those larger robots exhibit similar behavior. We show how to find such designs in simulation using an evolutionary algorithm. Further, when fractal attachment is not assumed and attachment geometries must thus be evolved along with the design of the base robot unit, scale invariant behavior is not achieved, demonstrating that structural self similarity, when combined with appropriate designs, is a useful path to realizing scale invariant robot behavior. We validate our findings by demonstrating successful transferal of self similar structure and behavior to pneumatically-controlled soft robots. Finally, we show that biobots can spontaneously exhibit self similar attachment geometries, thereby suggesting that self similar behavior via self similar structure may be realizable across a wide range of robot platforms in future.
Scalable sim-to-real transfer of soft robot designs
Nov 23, 2019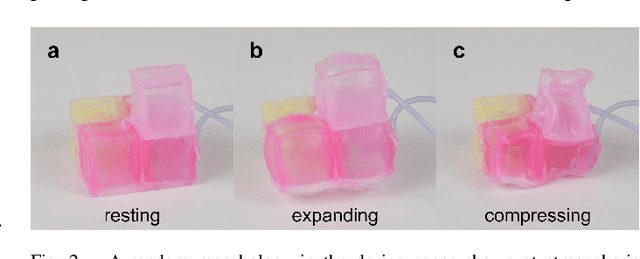
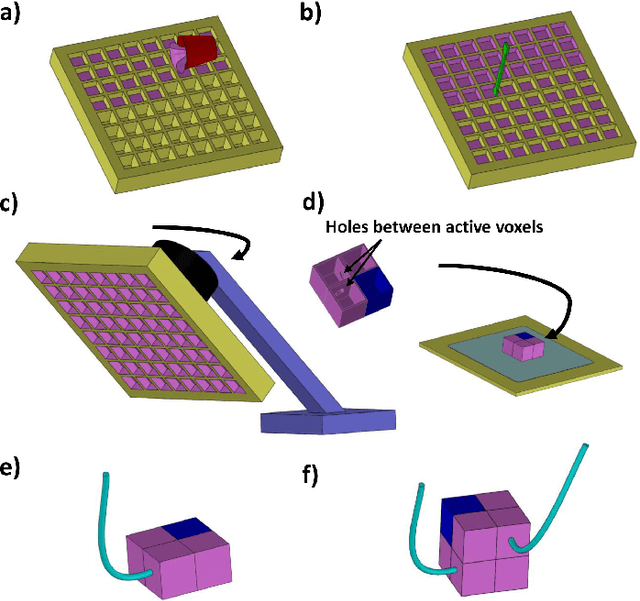
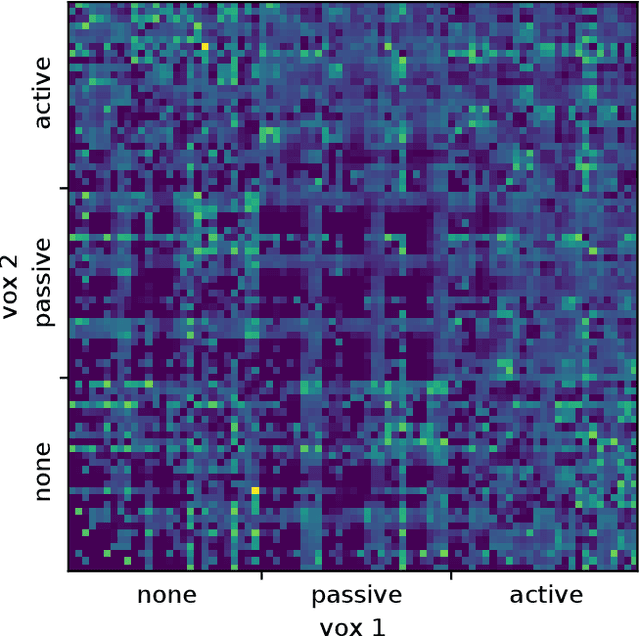
Abstract:The manual design of soft robots and their controllers is notoriously challenging, but it could be augmented---or, in some cases, entirely replaced---by automated design tools. Machine learning algorithms can automatically propose, test, and refine designs in simulation, and the most promising ones can then be manufactured in reality (sim2real). However, it is currently not known how to guarantee that behavior generated in simulation can be preserved when deployed in reality. Although many previous studies have devised training protocols that facilitate sim2real transfer of control polices, little to no work has investigated the simulation-reality gap as a function of morphology. This is due in part to an overall lack of tools capable of systematically designing and rapidly manufacturing robots. Here we introduce a low cost, open source, and modular soft robot design and construction kit, and use it to simulate, fabricate, and measure the simulation-reality gap of minimally complex yet soft, locomoting machines. We prove the scalability of this approach by transferring an order of magnitude more robot designs from simulation to reality than any other method. The kit and its instructions can be found here: https://github.com/skriegman/sim2real4designs
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge