Qingpeng Li
Back to Fundamentals: Low-Level Visual Features Guided Progressive Token Pruning
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) excel in semantic segmentation but demand significant computation, posing challenges for deployment on resource-constrained devices. Existing token pruning methods often overlook fundamental visual data characteristics. This study introduces 'LVTP', a progressive token pruning framework guided by multi-scale Tsallis entropy and low-level visual features with twice clustering. It integrates high-level semantics and basic visual attributes for precise segmentation. A novel dynamic scoring mechanism using multi-scale Tsallis entropy weighting overcomes limitations of traditional single-parameter entropy. The framework also incorporates low-level feature analysis to preserve critical edge information while optimizing computational cost. As a plug-and-play module, it requires no architectural changes or additional training. Evaluations across multiple datasets show 20%-45% computational reductions with negligible performance loss, outperforming existing methods in balancing cost and accuracy, especially in complex edge regions.
DREB-Net: Dual-stream Restoration Embedding Blur-feature Fusion Network for High-mobility UAV Object Detection
Oct 23, 2024Abstract:Object detection algorithms are pivotal components of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imaging systems, extensively employed in complex fields. However, images captured by high-mobility UAVs often suffer from motion blur cases, which significantly impedes the performance of advanced object detection algorithms. To address these challenges, we propose an innovative object detection algorithm specifically designed for blurry images, named DREB-Net (Dual-stream Restoration Embedding Blur-feature Fusion Network). First, DREB-Net addresses the particularities of blurry image object detection problem by incorporating a Blurry image Restoration Auxiliary Branch (BRAB) during the training phase. Second, it fuses the extracted shallow features via Multi-level Attention-Guided Feature Fusion (MAGFF) module, to extract richer features. Here, the MAGFF module comprises local attention modules and global attention modules, which assign different weights to the branches. Then, during the inference phase, the deep feature extraction of the BRAB can be removed to reduce computational complexity and improve detection speed. In loss function, a combined loss of MSE and SSIM is added to the BRAB to restore blurry images. Finally, DREB-Net introduces Fast Fourier Transform in the early stages of feature extraction, via a Learnable Frequency domain Amplitude Modulation Module (LFAMM), to adjust feature amplitude and enhance feature processing capability. Experimental results indicate that DREB-Net can still effectively perform object detection tasks under motion blur in captured images, showcasing excellent performance and broad application prospects. Our source code will be available at https://github.com/EEIC-Lab/DREB-Net.git.
SurANet: Surrounding-Aware Network for Concealed Object Detection via Highly-Efficient Interactive Contrastive Learning Strategy
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:Concealed object detection (COD) in cluttered scenes is significant for various image processing applications. However, due to that concealed objects are always similar to their background, it is extremely hard to distinguish them. Here, the major obstacle is the tiny feature differences between the inside and outside object boundary region, which makes it trouble for existing COD methods to achieve accurate results. In this paper, considering that the surrounding environment information can be well utilized to identify the concealed objects, and thus, we propose a novel deep Surrounding-Aware Network, namely SurANet, for COD tasks, which introduces surrounding information into feature extraction and loss function to improve the discrimination. First, we enhance the semantics of feature maps using differential fusion of surrounding features to highlight concealed objects. Next, a Surrounding-Aware Contrastive Loss is applied to identify the concealed object via learning surrounding feature maps contrastively. Then, SurANet can be trained end-to-end with high efficiency via our proposed Spatial-Compressed Correlation Transmission strategy after our investigation of feature dynamics, and extensive experiments improve that such features can be well reserved respectively. Finally, experimental results demonstrate that the proposed SurANet outperforms state-of-the-art COD methods on multiple real datasets. Our source code will be available at https://github.com/kyh433/SurANet.
R$^3$-Net: A Deep Network for Multi-oriented Vehicle Detection in Aerial Images and Videos
Aug 16, 2018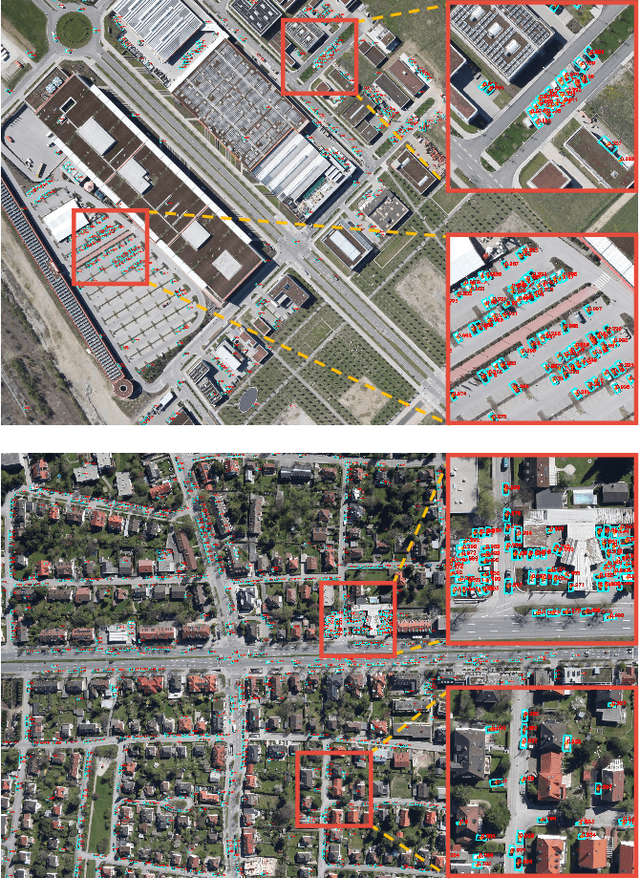
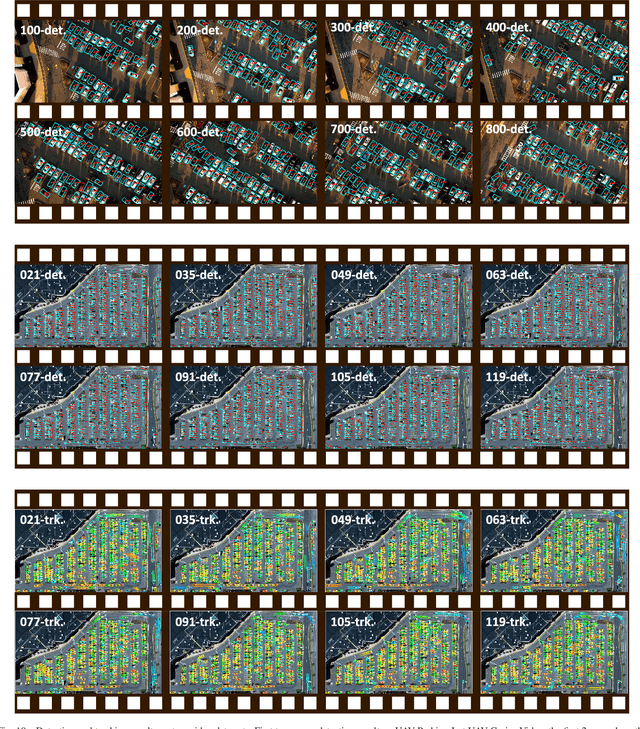
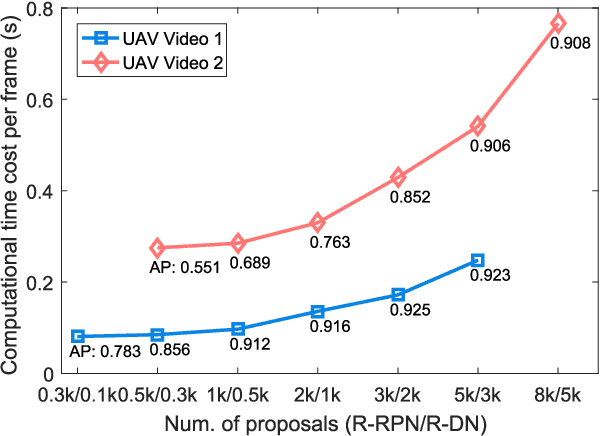
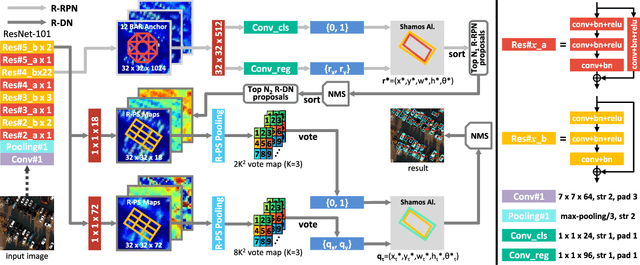
Abstract:Vehicle detection is a significant and challenging task in aerial remote sensing applications. Most existing methods detect vehicles with regular rectangle boxes and fail to offer the orientation of vehicles. However, the orientation information is crucial for several practical applications, such as the trajectory and motion estimation of vehicles. In this paper, we propose a novel deep network, called rotatable region-based residual network (R$^3$-Net), to detect multi-oriented vehicles in aerial images and videos. More specially, R$^3$-Net is utilized to generate rotatable rectangular target boxes in a half coordinate system. First, we use a rotatable region proposal network (R-RPN) to generate rotatable region of interests (R-RoIs) from feature maps produced by a deep convolutional neural network. Here, a proposed batch averaging rotatable anchor (BAR anchor) strategy is applied to initialize the shape of vehicle candidates. Next, we propose a rotatable detection network (R-DN) for the final classification and regression of the R-RoIs. In R-DN, a novel rotatable position sensitive pooling (R-PS pooling) is designed to keep the position and orientation information simultaneously while downsampling the feature maps of R-RoIs. In our model, R-RPN and R-DN can be trained jointly. We test our network on two open vehicle detection image datasets, namely DLR 3K Munich Dataset and VEDAI Dataset, demonstrating the high precision and robustness of our method. In addition, further experiments on aerial videos show the good generalization capability of the proposed method and its potential for vehicle tracking in aerial videos. The demo video is available at https://youtu.be/xCYD-tYudN0.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge