Po-Jui Lu
Benchmarking and Explaining Deep Learning Cortical Lesion MRI Segmentation in Multiple Sclerosis
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Cortical lesions (CLs) have emerged as valuable biomarkers in multiple sclerosis (MS), offering high diagnostic specificity and prognostic relevance. However, their routine clinical integration remains limited due to subtle magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance, challenges in expert annotation, and a lack of standardized automated methods. We propose a comprehensive multi-centric benchmark of CL detection and segmentation in MRI. A total of 656 MRI scans, including clinical trial and research data from four institutions, were acquired at 3T and 7T using MP2RAGE and MPRAGE sequences with expert-consensus annotations. We rely on the self-configuring nnU-Net framework, designed for medical imaging segmentation, and propose adaptations tailored to the improved CL detection. We evaluated model generalization through out-of-distribution testing, demonstrating strong lesion detection capabilities with an F1-score of 0.64 and 0.5 in and out of the domain, respectively. We also analyze internal model features and model errors for a better understanding of AI decision-making. Our study examines how data variability, lesion ambiguity, and protocol differences impact model performance, offering future recommendations to address these barriers to clinical adoption. To reinforce the reproducibility, the implementation and models will be publicly accessible and ready to use at https://github.com/Medical-Image-Analysis-Laboratory/ and https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15911797.
Interpretability of Uncertainty: Exploring Cortical Lesion Segmentation in Multiple Sclerosis
Jul 08, 2024


Abstract:Uncertainty quantification (UQ) has become critical for evaluating the reliability of artificial intelligence systems, especially in medical image segmentation. This study addresses the interpretability of instance-wise uncertainty values in deep learning models for focal lesion segmentation in magnetic resonance imaging, specifically cortical lesion (CL) segmentation in multiple sclerosis. CL segmentation presents several challenges, including the complexity of manual segmentation, high variability in annotation, data scarcity, and class imbalance, all of which contribute to aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty. We explore how UQ can be used not only to assess prediction reliability but also to provide insights into model behavior, detect biases, and verify the accuracy of UQ methods. Our research demonstrates the potential of instance-wise uncertainty values to offer post hoc global model explanations, serving as a sanity check for the model. The implementation is available at https://github.com/NataliiaMolch/interpret-lesion-unc.
GAMER-MRIL identifies Disability-Related Brain Changes in Multiple Sclerosis
Aug 15, 2023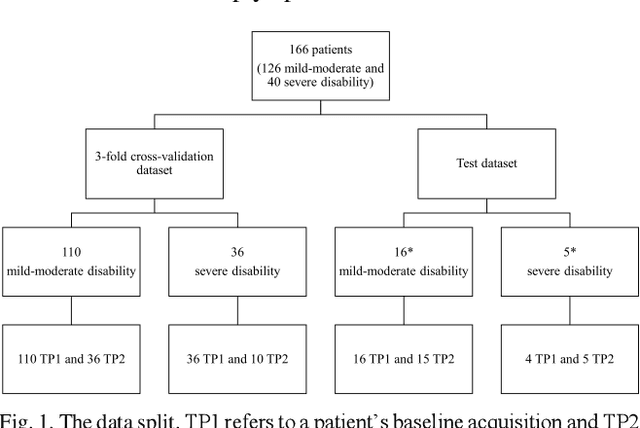
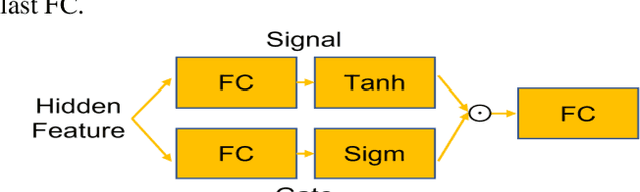
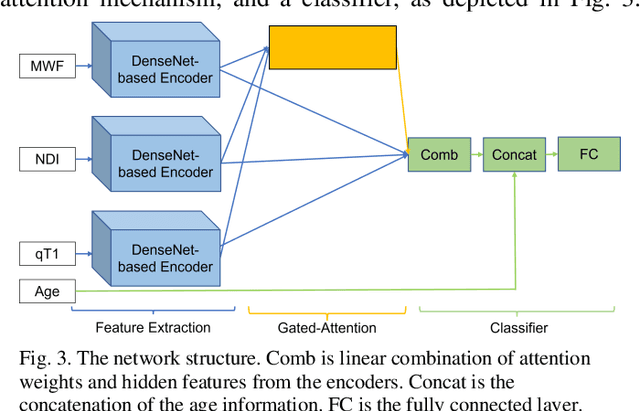
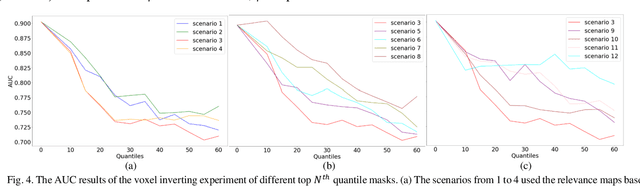
Abstract:Objective: Identifying disability-related brain changes is important for multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. Currently, there is no clear understanding about which pathological features drive disability in single MS patients. In this work, we propose a novel comprehensive approach, GAMER-MRIL, leveraging whole-brain quantitative MRI (qMRI), convolutional neural network (CNN), and an interpretability method from classifying MS patients with severe disability to investigating relevant pathological brain changes. Methods: One-hundred-sixty-six MS patients underwent 3T MRI acquisitions. qMRI informative of microstructural brain properties was reconstructed, including quantitative T1 (qT1), myelin water fraction (MWF), and neurite density index (NDI). To fully utilize the qMRI, GAMER-MRIL extended a gated-attention-based CNN (GAMER-MRI), which was developed to select patch-based qMRI important for a given task/question, to the whole-brain image. To find out disability-related brain regions, GAMER-MRIL modified a structure-aware interpretability method, Layer-wise Relevance Propagation (LRP), to incorporate qMRI. Results: The test performance was AUC=0.885. qT1 was the most sensitive measure related to disability, followed by NDI. The proposed LRP approach obtained more specifically relevant regions than other interpretability methods, including the saliency map, the integrated gradients, and the original LRP. The relevant regions included the corticospinal tract, where average qT1 and NDI significantly correlated with patients' disability scores ($\rho$=-0.37 and 0.44). Conclusion: These results demonstrated that GAMER-MRIL can classify patients with severe disability using qMRI and subsequently identify brain regions potentially important to the integrity of the mobile function. Significance: GAMER-MRIL holds promise for developing biomarkers and increasing clinicians' trust in NN.
Shifts 2.0: Extending The Dataset of Real Distributional Shifts
Jun 30, 2022



Abstract:Distributional shift, or the mismatch between training and deployment data, is a significant obstacle to the usage of machine learning in high-stakes industrial applications, such as autonomous driving and medicine. This creates a need to be able to assess how robustly ML models generalize as well as the quality of their uncertainty estimates. Standard ML baseline datasets do not allow these properties to be assessed, as the training, validation and test data are often identically distributed. Recently, a range of dedicated benchmarks have appeared, featuring both distributionally matched and shifted data. Among these benchmarks, the Shifts dataset stands out in terms of the diversity of tasks as well as the data modalities it features. While most of the benchmarks are heavily dominated by 2D image classification tasks, Shifts contains tabular weather forecasting, machine translation, and vehicle motion prediction tasks. This enables the robustness properties of models to be assessed on a diverse set of industrial-scale tasks and either universal or directly applicable task-specific conclusions to be reached. In this paper, we extend the Shifts Dataset with two datasets sourced from industrial, high-risk applications of high societal importance. Specifically, we consider the tasks of segmentation of white matter Multiple Sclerosis lesions in 3D magnetic resonance brain images and the estimation of power consumption in marine cargo vessels. Both tasks feature ubiquitous distributional shifts and a strict safety requirement due to the high cost of errors. These new datasets will allow researchers to further explore robust generalization and uncertainty estimation in new situations. In this work, we provide a description of the dataset and baseline results for both tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge