Pedro M. Gordaliza
From 100,000+ images to winning the first brain MRI foundation model challenges: Sharing lessons and models
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Developing Foundation Models for medical image analysis is essential to overcome the unique challenges of radiological tasks. The first challenges of this kind for 3D brain MRI, SSL3D and FOMO25, were held at MICCAI 2025. Our solution ranked first in tracks of both contests. It relies on a U-Net CNN architecture combined with strategies leveraging anatomical priors and neuroimaging domain knowledge. Notably, our models trained 1-2 orders of magnitude faster and were 10 times smaller than competing transformer-based approaches. Models are available here: https://github.com/jbanusco/BrainFM4Challenges.
Causal Attribution of Model Performance Gaps in Medical Imaging Under Distribution Shifts
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Deep learning models for medical image segmentation suffer significant performance drops due to distribution shifts, but the causal mechanisms behind these drops remain poorly understood. We extend causal attribution frameworks to high-dimensional segmentation tasks, quantifying how acquisition protocols and annotation variability independently contribute to performance degradation. We model the data-generating process through a causal graph and employ Shapley values to fairly attribute performance changes to individual mechanisms. Our framework addresses unique challenges in medical imaging: high-dimensional outputs, limited samples, and complex mechanism interactions. Validation on multiple sclerosis (MS) lesion segmentation across 4 centers and 7 annotators reveals context-dependent failure modes: annotation protocol shifts dominate when crossing annotators (7.4% $\pm$ 8.9% DSC attribution), while acquisition shifts dominate when crossing imaging centers (6.5% $\pm$ 9.1%). This mechanism-specific quantification enables practitioners to prioritize targeted interventions based on deployment context.
Benchmarking and Explaining Deep Learning Cortical Lesion MRI Segmentation in Multiple Sclerosis
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Cortical lesions (CLs) have emerged as valuable biomarkers in multiple sclerosis (MS), offering high diagnostic specificity and prognostic relevance. However, their routine clinical integration remains limited due to subtle magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance, challenges in expert annotation, and a lack of standardized automated methods. We propose a comprehensive multi-centric benchmark of CL detection and segmentation in MRI. A total of 656 MRI scans, including clinical trial and research data from four institutions, were acquired at 3T and 7T using MP2RAGE and MPRAGE sequences with expert-consensus annotations. We rely on the self-configuring nnU-Net framework, designed for medical imaging segmentation, and propose adaptations tailored to the improved CL detection. We evaluated model generalization through out-of-distribution testing, demonstrating strong lesion detection capabilities with an F1-score of 0.64 and 0.5 in and out of the domain, respectively. We also analyze internal model features and model errors for a better understanding of AI decision-making. Our study examines how data variability, lesion ambiguity, and protocol differences impact model performance, offering future recommendations to address these barriers to clinical adoption. To reinforce the reproducibility, the implementation and models will be publicly accessible and ready to use at https://github.com/Medical-Image-Analysis-Laboratory/ and https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15911797.
ConfLUNet: Multiple sclerosis lesion instance segmentation in presence of confluent lesions
May 28, 2025Abstract:Accurate lesion-level segmentation on MRI is critical for multiple sclerosis (MS) diagnosis, prognosis, and disease monitoring. However, current evaluation practices largely rely on semantic segmentation post-processed with connected components (CC), which cannot separate confluent lesions (aggregates of confluent lesion units, CLUs) due to reliance on spatial connectivity. To address this misalignment with clinical needs, we introduce formal definitions of CLUs and associated CLU-aware detection metrics, and include them in an exhaustive instance segmentation evaluation framework. Within this framework, we systematically evaluate CC and post-processing-based Automated Confluent Splitting (ACLS), the only existing methods for lesion instance segmentation in MS. Our analysis reveals that CC consistently underestimates CLU counts, while ACLS tends to oversplit lesions, leading to overestimated lesion counts and reduced precision. To overcome these limitations, we propose ConfLUNet, the first end-to-end instance segmentation framework for MS lesions. ConfLUNet jointly optimizes lesion detection and delineation from a single FLAIR image. Trained on 50 patients, ConfLUNet significantly outperforms CC and ACLS on the held-out test set (n=13) in instance segmentation (Panoptic Quality: 42.0% vs. 37.5%/36.8%; p = 0.017/0.005) and lesion detection (F1: 67.3% vs. 61.6%/59.9%; p = 0.028/0.013). For CLU detection, ConfLUNet achieves the highest F1[CLU] (81.5%), improving recall over CC (+12.5%, p = 0.015) and precision over ACLS (+31.2%, p = 0.003). By combining rigorous definitions, new CLU-aware metrics, a reproducible evaluation framework, and the first dedicated end-to-end model, this work lays the foundation for lesion instance segmentation in MS.
Explainability of AI Uncertainty: Application to Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation on MRI
Apr 07, 2025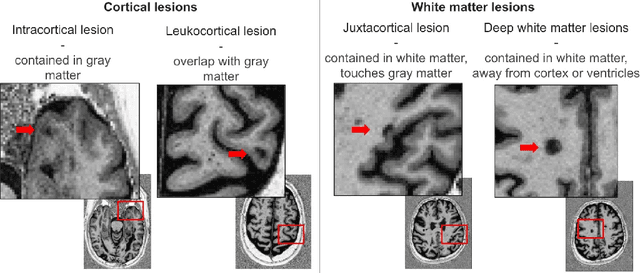



Abstract:Trustworthy artificial intelligence (AI) is essential in healthcare, particularly for high-stakes tasks like medical image segmentation. Explainable AI and uncertainty quantification significantly enhance AI reliability by addressing key attributes such as robustness, usability, and explainability. Despite extensive technical advances in uncertainty quantification for medical imaging, understanding the clinical informativeness and interpretability of uncertainty remains limited. This study introduces a novel framework to explain the potential sources of predictive uncertainty, specifically in cortical lesion segmentation in multiple sclerosis using deep ensembles. The proposed analysis shifts the focus from the uncertainty-error relationship towards relevant medical and engineering factors. Our findings reveal that instance-wise uncertainty is strongly related to lesion size, shape, and cortical involvement. Expert rater feedback confirms that similar factors impede annotator confidence. Evaluations conducted on two datasets (206 patients, almost 2000 lesions) under both in-domain and distribution-shift conditions highlight the utility of the framework in different scenarios.
Interpretability of Uncertainty: Exploring Cortical Lesion Segmentation in Multiple Sclerosis
Jul 08, 2024


Abstract:Uncertainty quantification (UQ) has become critical for evaluating the reliability of artificial intelligence systems, especially in medical image segmentation. This study addresses the interpretability of instance-wise uncertainty values in deep learning models for focal lesion segmentation in magnetic resonance imaging, specifically cortical lesion (CL) segmentation in multiple sclerosis. CL segmentation presents several challenges, including the complexity of manual segmentation, high variability in annotation, data scarcity, and class imbalance, all of which contribute to aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty. We explore how UQ can be used not only to assess prediction reliability but also to provide insights into model behavior, detect biases, and verify the accuracy of UQ methods. Our research demonstrates the potential of instance-wise uncertainty values to offer post hoc global model explanations, serving as a sanity check for the model. The implementation is available at https://github.com/NataliiaMolch/interpret-lesion-unc.
PhD Thesis. Computer-Aided Assessment of Tuberculosis with Radiological Imaging: From rule-based methods to Deep Learning
May 31, 2022
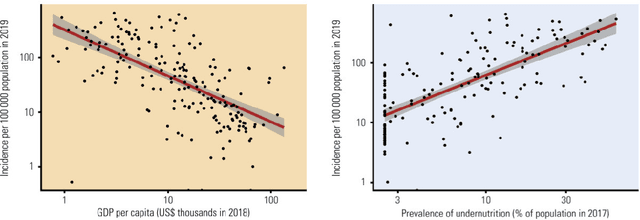
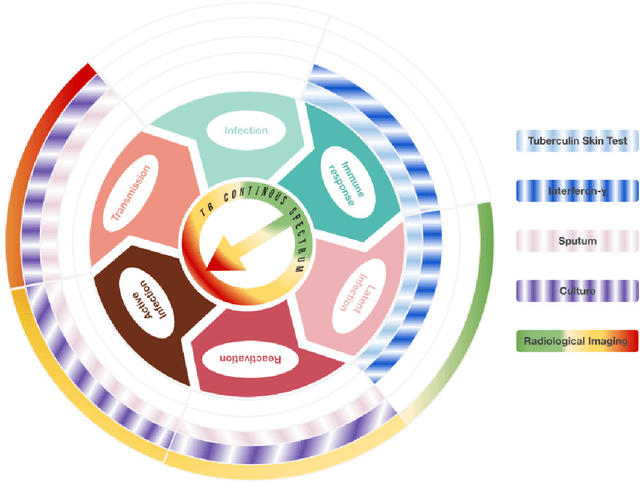

Abstract:Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb.) that produces pulmonary damage due to its airborne nature. This fact facilitates the disease fast-spreading, which, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2021 caused 1.2 million deaths and 9.9 million new cases. Fortunately, X-Ray Computed Tomography (CT) images enable capturing specific manifestations of TB that are undetectable using regular diagnostic tests. However, this procedure is unfeasible to process the thousands of volume images belonging to the different TB animal models and humans required for a suitable (pre-)clinical trial. To achieve suitable results, automatization of different image analysis processes is a must to quantify TB. Thus, in this thesis, we introduce a set of novel methods based on the state of the art Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Computer Vision (CV). Initially, we present an algorithm to assess Pathological Lung Segmentation (PLS). Next, a Gaussian Mixture Model ruled by an Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm is employed to automatically. Chapter 3 introduces a model to automate the identification of TB lesions and the characterization of disease progression. Chapter 4 extends the classification of TB lesions. Namely, we introduce a computational model to infer TB manifestations present in each lung lobe of CT scans by employing the associated radiologist reports as ground truth. In Chapter 5, we present a DL model capable of extracting disentangled information from images of different animal models, as well as information of the mechanisms that generate the CT volumes. To sum up, the thesis presents a collection of valuable tools to automate the quantification of pathological lungs. Chapter 6 elaborates on these conclusions.
Translational Lung Imaging Analysis Through Disentangled Representations
Mar 03, 2022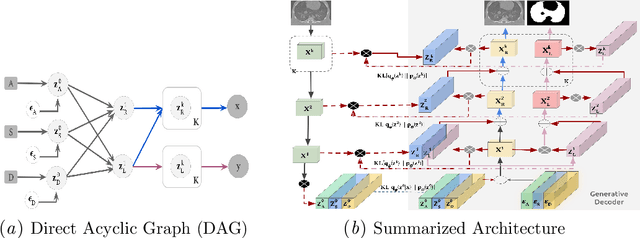
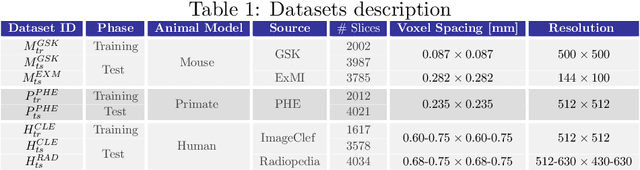
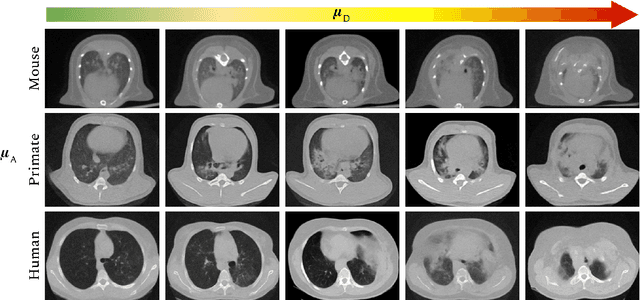

Abstract:The development of new treatments often requires clinical trials with translational animal models using (pre)-clinical imaging to characterize inter-species pathological processes. Deep Learning (DL) models are commonly used to automate retrieving relevant information from the images. Nevertheless, they typically suffer from low generability and explainability as a product of their entangled design, resulting in a specific DL model per animal model. Consequently, it is not possible to take advantage of the high capacity of DL to discover statistical relationships from inter-species images. To alleviate this problem, in this work, we present a model capable of extracting disentangled information from images of different animal models and the mechanisms that generate the images. Our method is located at the intersection between deep generative models, disentanglement and causal representation learning. It is optimized from images of pathological lung infected by Tuberculosis and is able: a) from an input slice, infer its position in a volume, the animal model to which it belongs, the damage present and even more, generate a mask covering the whole lung (similar overlap measures to the nnU-Net), b) generate realistic lung images by setting the above variables and c) generate counterfactual images, namely, healthy versions of a damaged input slice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge