Pengzhan Sun
Visual Intention Grounding for Egocentric Assistants
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Visual grounding associates textual descriptions with objects in an image. Conventional methods target third-person image inputs and named object queries. In applications such as AI assistants, the perspective shifts -- inputs are egocentric, and objects may be referred to implicitly through needs and intentions. To bridge this gap, we introduce EgoIntention, the first dataset for egocentric visual intention grounding. EgoIntention challenges multimodal LLMs to 1) understand and ignore unintended contextual objects and 2) reason about uncommon object functionalities. Benchmark results show that current models misidentify context objects and lack affordance understanding in egocentric views. We also propose Reason-to-Ground (RoG) instruction tuning; it enables hybrid training with normal descriptions and egocentric intentions with a chained intention reasoning and object grounding mechanism. RoG significantly outperforms naive finetuning and hybrid training on EgoIntention, while maintaining or slightly improving naive description grounding. This advancement enables unified visual grounding for egocentric and exocentric visual inputs while handling explicit object queries and implicit human intentions.
Analyzing the Synthetic-to-Real Domain Gap in 3D Hand Pose Estimation
Mar 25, 2025



Abstract:Recent synthetic 3D human datasets for the face, body, and hands have pushed the limits on photorealism. Face recognition and body pose estimation have achieved state-of-the-art performance using synthetic training data alone, but for the hand, there is still a large synthetic-to-real gap. This paper presents the first systematic study of the synthetic-to-real gap of 3D hand pose estimation. We analyze the gap and identify key components such as the forearm, image frequency statistics, hand pose, and object occlusions. To facilitate our analysis, we propose a data synthesis pipeline to synthesize high-quality data. We demonstrate that synthetic hand data can achieve the same level of accuracy as real data when integrating our identified components, paving the path to use synthetic data alone for hand pose estimation. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/delaprada/HandSynthesis.git.
Simultaneous Detection and Interaction Reasoning for Object-Centric Action Recognition
Apr 18, 2024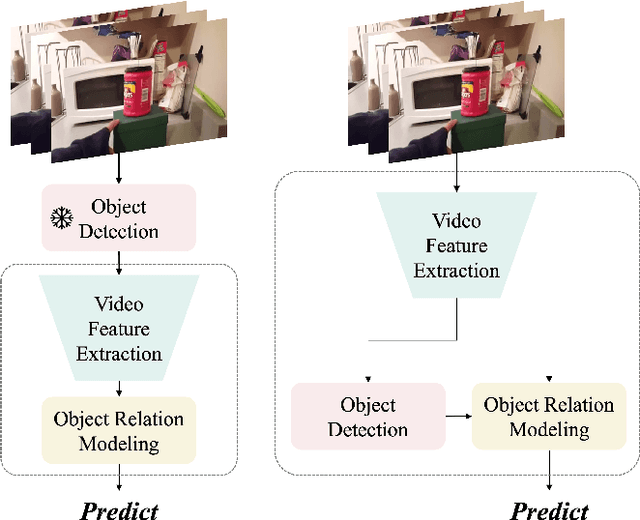
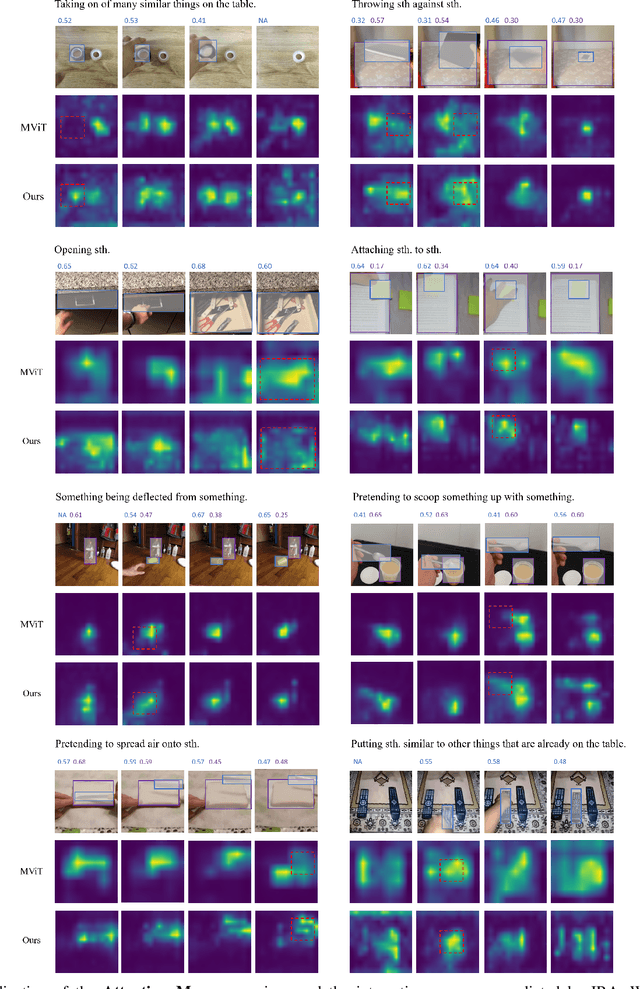
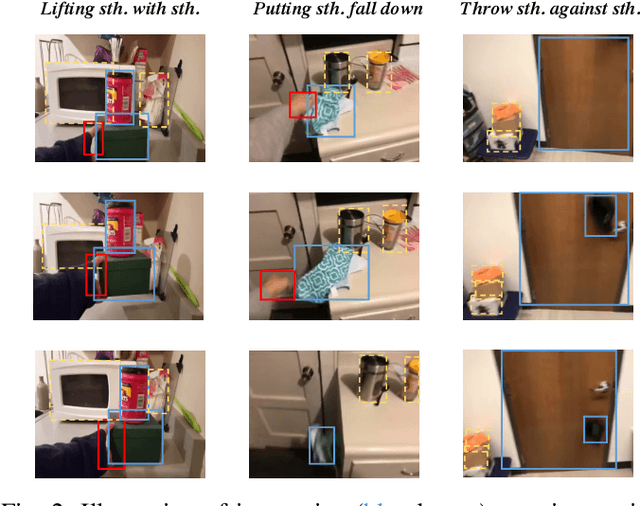
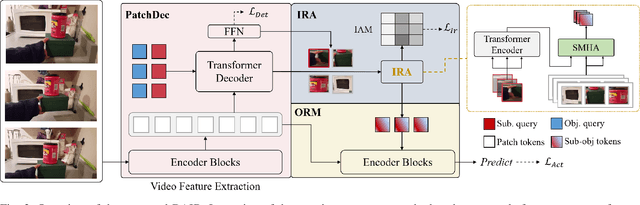

Abstract:The interactions between human and objects are important for recognizing object-centric actions. Existing methods usually adopt a two-stage pipeline, where object proposals are first detected using a pretrained detector, and then are fed to an action recognition model for extracting video features and learning the object relations for action recognition. However, since the action prior is unknown in the object detection stage, important objects could be easily overlooked, leading to inferior action recognition performance. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end object-centric action recognition framework that simultaneously performs Detection And Interaction Reasoning in one stage. Particularly, after extracting video features with a base network, we create three modules for concurrent object detection and interaction reasoning. First, a Patch-based Object Decoder generates proposals from video patch tokens. Then, an Interactive Object Refining and Aggregation identifies important objects for action recognition, adjusts proposal scores based on position and appearance, and aggregates object-level info into a global video representation. Lastly, an Object Relation Modeling module encodes object relations. These three modules together with the video feature extractor can be trained jointly in an end-to-end fashion, thus avoiding the heavy reliance on an off-the-shelf object detector, and reducing the multi-stage training burden. We conduct experiments on two datasets, Something-Else and Ikea-Assembly, to evaluate the performance of our proposed approach on conventional, compositional, and few-shot action recognition tasks. Through in-depth experimental analysis, we show the crucial role of interactive objects in learning for action recognition, and we can outperform state-of-the-art methods on both datasets.
HRS-Bench: Holistic, Reliable and Scalable Benchmark for Text-to-Image Models
Apr 11, 2023



Abstract:In recent years, Text-to-Image (T2I) models have been extensively studied, especially with the emergence of diffusion models that achieve state-of-the-art results on T2I synthesis tasks. However, existing benchmarks heavily rely on subjective human evaluation, limiting their ability to holistically assess the model's capabilities. Furthermore, there is a significant gap between efforts in developing new T2I architectures and those in evaluation. To address this, we introduce HRS-Bench, a concrete evaluation benchmark for T2I models that is Holistic, Reliable, and Scalable. Unlike existing bench-marks that focus on limited aspects, HRS-Bench measures 13 skills that can be categorized into five major categories: accuracy, robustness, generalization, fairness, and bias. In addition, HRS-Bench covers 50 scenarios, including fashion, animals, transportation, food, and clothes. We evaluate nine recent large-scale T2I models using metrics that cover a wide range of skills. A human evaluation aligned with 95% of our evaluations on average was conducted to probe the effectiveness of HRS-Bench. Our experiments demonstrate that existing models often struggle to generate images with the desired count of objects, visual text, or grounded emotions. We hope that our benchmark help ease future text-to-image generation research. The code and data are available at https://eslambakr.github.io/hrsbench.github.io
ImageCaptioner$^2$: Image Captioner for Image Captioning Bias Amplification Assessment
Apr 10, 2023



Abstract:Most pre-trained learning systems are known to suffer from bias, which typically emerges from the data, the model, or both. Measuring and quantifying bias and its sources is a challenging task and has been extensively studied in image captioning. Despite the significant effort in this direction, we observed that existing metrics lack consistency in the inclusion of the visual signal. In this paper, we introduce a new bias assessment metric, dubbed $ImageCaptioner^2$, for image captioning. Instead of measuring the absolute bias in the model or the data, $ImageCaptioner^2$ pay more attention to the bias introduced by the model w.r.t the data bias, termed bias amplification. Unlike the existing methods, which only evaluate the image captioning algorithms based on the generated captions only, $ImageCaptioner^2$ incorporates the image while measuring the bias. In addition, we design a formulation for measuring the bias of generated captions as prompt-based image captioning instead of using language classifiers. Finally, we apply our $ImageCaptioner^2$ metric across 11 different image captioning architectures on three different datasets, i.e., MS-COCO caption dataset, Artemis V1, and Artemis V2, and on three different protected attributes, i.e., gender, race, and emotions. Consequently, we verify the effectiveness of our $ImageCaptioner^2$ metric by proposing AnonymousBench, which is a novel human evaluation paradigm for bias metrics. Our metric shows significant superiority over the recent bias metric; LIC, in terms of human alignment, where the correlation scores are 80% and 54% for our metric and LIC, respectively. The code is available at https://eslambakr.github.io/imagecaptioner2.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge