Oscar Clivio
Learning to Defer for Causal Discovery with Imperfect Experts
Feb 18, 2025
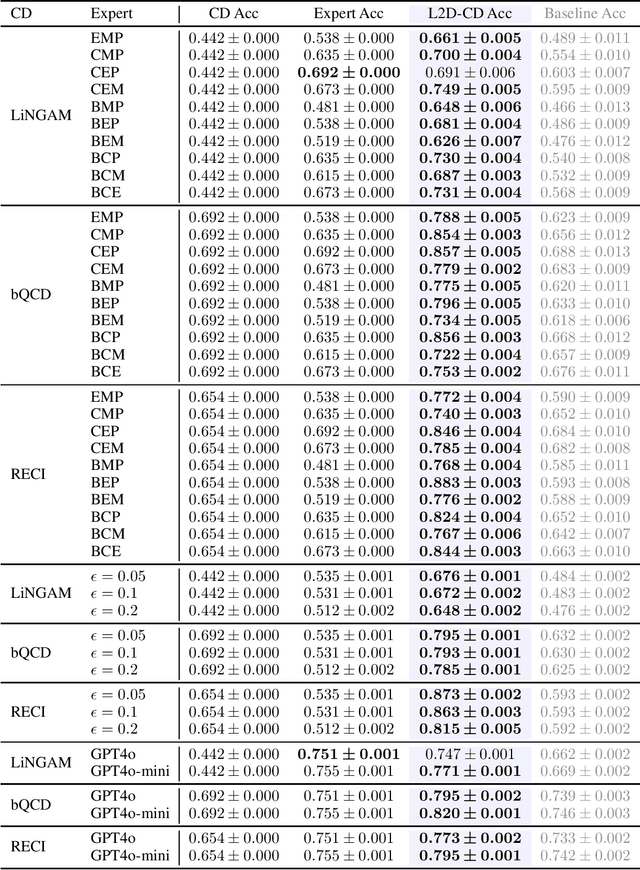
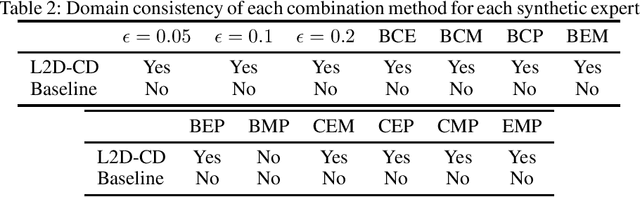
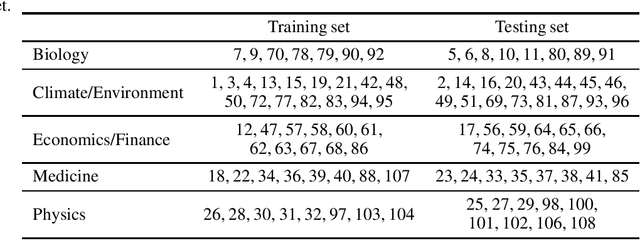
Abstract:Integrating expert knowledge, e.g. from large language models, into causal discovery algorithms can be challenging when the knowledge is not guaranteed to be correct. Expert recommendations may contradict data-driven results, and their reliability can vary significantly depending on the domain or specific query. Existing methods based on soft constraints or inconsistencies in predicted causal relationships fail to account for these variations in expertise. To remedy this, we propose L2D-CD, a method for gauging the correctness of expert recommendations and optimally combining them with data-driven causal discovery results. By adapting learning-to-defer (L2D) algorithms for pairwise causal discovery (CD), we learn a deferral function that selects whether to rely on classical causal discovery methods using numerical data or expert recommendations based on textual meta-data. We evaluate L2D-CD on the canonical T\"ubingen pairs dataset and demonstrate its superior performance compared to both the causal discovery method and the expert used in isolation. Moreover, our approach identifies domains where the expert's performance is strong or weak. Finally, we outline a strategy for generalizing this approach to causal discovery on graphs with more than two variables, paving the way for further research in this area.
Towards Representation Learning for Weighting Problems in Design-Based Causal Inference
Sep 24, 2024Abstract:Reweighting a distribution to minimize a distance to a target distribution is a powerful and flexible strategy for estimating a wide range of causal effects, but can be challenging in practice because optimal weights typically depend on knowledge of the underlying data generating process. In this paper, we focus on design-based weights, which do not incorporate outcome information; prominent examples include prospective cohort studies, survey weighting, and the weighting portion of augmented weighting estimators. In such applications, we explore the central role of representation learning in finding desirable weights in practice. Unlike the common approach of assuming a well-specified representation, we highlight the error due to the choice of a representation and outline a general framework for finding suitable representations that minimize this error. Building on recent work that combines balancing weights and neural networks, we propose an end-to-end estimation procedure that learns a flexible representation, while retaining promising theoretical properties. We show that this approach is competitive in a range of common causal inference tasks.
A Critical Review of Causal Reasoning Benchmarks for Large Language Models
Jul 10, 2024


Abstract:Numerous benchmarks aim to evaluate the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) for causal inference and reasoning. However, many of them can likely be solved through the retrieval of domain knowledge, questioning whether they achieve their purpose. In this review, we present a comprehensive overview of LLM benchmarks for causality. We highlight how recent benchmarks move towards a more thorough definition of causal reasoning by incorporating interventional or counterfactual reasoning. We derive a set of criteria that a useful benchmark or set of benchmarks should aim to satisfy. We hope this work will pave the way towards a general framework for the assessment of causal understanding in LLMs and the design of novel benchmarks.
PWSHAP: A Path-Wise Explanation Model for Targeted Variables
Jun 26, 2023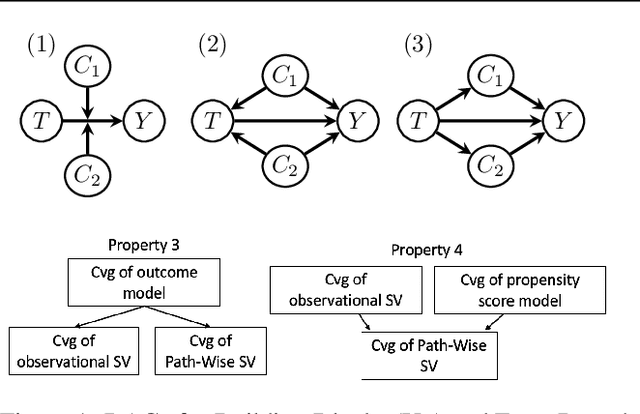
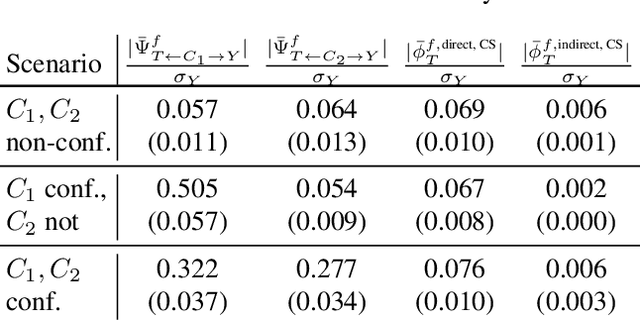
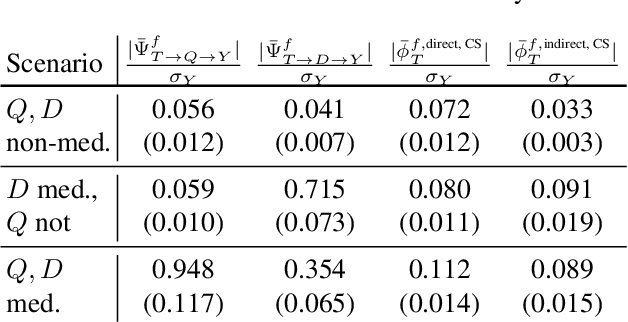
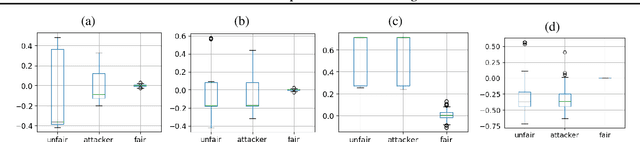
Abstract:Predictive black-box models can exhibit high accuracy but their opaque nature hinders their uptake in safety-critical deployment environments. Explanation methods (XAI) can provide confidence for decision-making through increased transparency. However, existing XAI methods are not tailored towards models in sensitive domains where one predictor is of special interest, such as a treatment effect in a clinical model, or ethnicity in policy models. We introduce Path-Wise Shapley effects (PWSHAP), a framework for assessing the targeted effect of a binary (e.g.~treatment) variable from a complex outcome model. Our approach augments the predictive model with a user-defined directed acyclic graph (DAG). The method then uses the graph alongside on-manifold Shapley values to identify effects along causal pathways whilst maintaining robustness to adversarial attacks. We establish error bounds for the identified path-wise Shapley effects and for Shapley values. We show PWSHAP can perform local bias and mediation analyses with faithfulness to the model. Further, if the targeted variable is randomised we can quantify local effect modification. We demonstrate the resolution, interpretability, and true locality of our approach on examples and a real-world experiment.
Neural Score Matching for High-Dimensional Causal Inference
Mar 01, 2022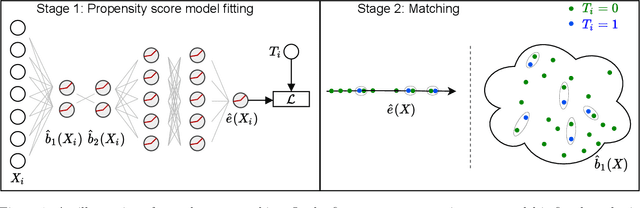
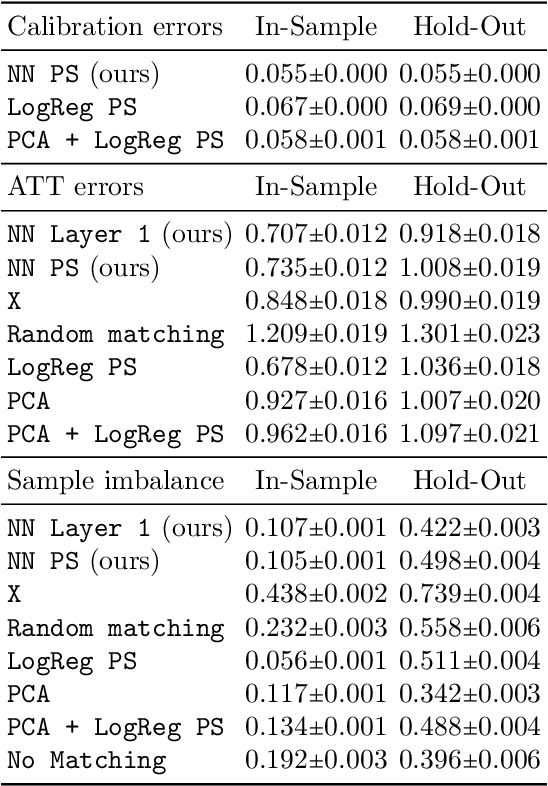


Abstract:Traditional methods for matching in causal inference are impractical for high-dimensional datasets. They suffer from the curse of dimensionality: exact matching and coarsened exact matching find exponentially fewer matches as the input dimension grows, and propensity score matching may match highly unrelated units together. To overcome this problem, we develop theoretical results which motivate the use of neural networks to obtain non-trivial, multivariate balancing scores of a chosen level of coarseness, in contrast to the classical, scalar propensity score. We leverage these balancing scores to perform matching for high-dimensional causal inference and call this procedure neural score matching. We show that our method is competitive against other matching approaches on semi-synthetic high-dimensional datasets, both in terms of treatment effect estimation and reducing imbalance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge