Neural Score Matching for High-Dimensional Causal Inference
Paper and Code
Mar 01, 2022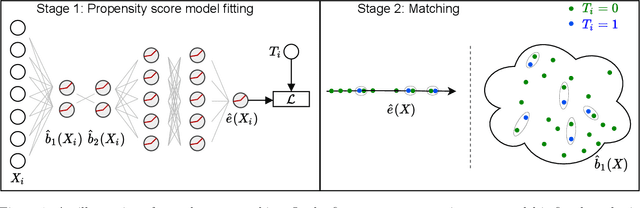
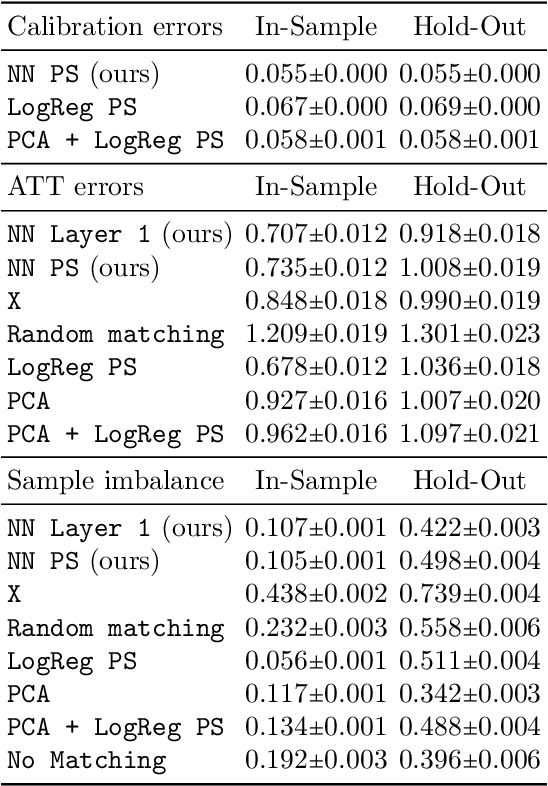


Traditional methods for matching in causal inference are impractical for high-dimensional datasets. They suffer from the curse of dimensionality: exact matching and coarsened exact matching find exponentially fewer matches as the input dimension grows, and propensity score matching may match highly unrelated units together. To overcome this problem, we develop theoretical results which motivate the use of neural networks to obtain non-trivial, multivariate balancing scores of a chosen level of coarseness, in contrast to the classical, scalar propensity score. We leverage these balancing scores to perform matching for high-dimensional causal inference and call this procedure neural score matching. We show that our method is competitive against other matching approaches on semi-synthetic high-dimensional datasets, both in terms of treatment effect estimation and reducing imbalance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge