Nupur Kumari
Learning an Image Editing Model without Image Editing Pairs
Oct 16, 2025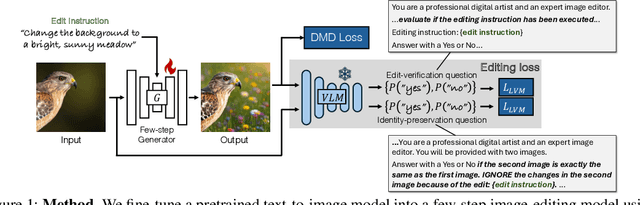
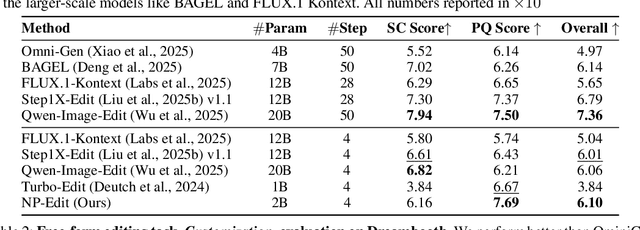

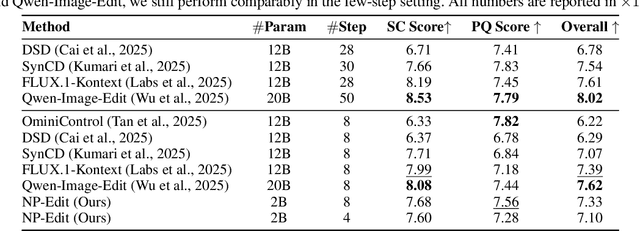
Abstract:Recent image editing models have achieved impressive results while following natural language editing instructions, but they rely on supervised fine-tuning with large datasets of input-target pairs. This is a critical bottleneck, as such naturally occurring pairs are hard to curate at scale. Current workarounds use synthetic training pairs that leverage the zero-shot capabilities of existing models. However, this can propagate and magnify the artifacts of the pretrained model into the final trained model. In this work, we present a new training paradigm that eliminates the need for paired data entirely. Our approach directly optimizes a few-step diffusion model by unrolling it during training and leveraging feedback from vision-language models (VLMs). For each input and editing instruction, the VLM evaluates if an edit follows the instruction and preserves unchanged content, providing direct gradients for end-to-end optimization. To ensure visual fidelity, we incorporate distribution matching loss (DMD), which constrains generated images to remain within the image manifold learned by pretrained models. We evaluate our method on standard benchmarks and include an extensive ablation study. Without any paired data, our method performs on par with various image editing diffusion models trained on extensive supervised paired data, under the few-step setting. Given the same VLM as the reward model, we also outperform RL-based techniques like Flow-GRPO.
Generating Multi-Image Synthetic Data for Text-to-Image Customization
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:Customization of text-to-image models enables users to insert custom concepts and generate the concepts in unseen settings. Existing methods either rely on costly test-time optimization or train encoders on single-image training datasets without multi-image supervision, leading to worse image quality. We propose a simple approach that addresses both limitations. We first leverage existing text-to-image models and 3D datasets to create a high-quality Synthetic Customization Dataset (SynCD) consisting of multiple images of the same object in different lighting, backgrounds, and poses. We then propose a new encoder architecture based on shared attention mechanisms that better incorporate fine-grained visual details from input images. Finally, we propose a new inference technique that mitigates overexposure issues during inference by normalizing the text and image guidance vectors. Through extensive experiments, we show that our model, trained on the synthetic dataset with the proposed encoder and inference algorithm, outperforms existing tuning-free methods on standard customization benchmarks.
Generative Photomontage
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:Text-to-image models are powerful tools for image creation. However, the generation process is akin to a dice roll and makes it difficult to achieve a single image that captures everything a user wants. In this paper, we propose a framework for creating the desired image by compositing it from various parts of generated images, in essence forming a Generative Photomontage. Given a stack of images generated by ControlNet using the same input condition and different seeds, we let users select desired parts from the generated results using a brush stroke interface. We introduce a novel technique that takes in the user's brush strokes, segments the generated images using a graph-based optimization in diffusion feature space, and then composites the segmented regions via a new feature-space blending method. Our method faithfully preserves the user-selected regions while compositing them harmoniously. We demonstrate that our flexible framework can be used for many applications, including generating new appearance combinations, fixing incorrect shapes and artifacts, and improving prompt alignment. We show compelling results for each application and demonstrate that our method outperforms existing image blending methods and various baselines.
Customizing Text-to-Image Models with a Single Image Pair
May 02, 2024Abstract:Art reinterpretation is the practice of creating a variation of a reference work, making a paired artwork that exhibits a distinct artistic style. We ask if such an image pair can be used to customize a generative model to capture the demonstrated stylistic difference. We propose Pair Customization, a new customization method that learns stylistic difference from a single image pair and then applies the acquired style to the generation process. Unlike existing methods that learn to mimic a single concept from a collection of images, our method captures the stylistic difference between paired images. This allows us to apply a stylistic change without overfitting to the specific image content in the examples. To address this new task, we employ a joint optimization method that explicitly separates the style and content into distinct LoRA weight spaces. We optimize these style and content weights to reproduce the style and content images while encouraging their orthogonality. During inference, we modify the diffusion process via a new style guidance based on our learned weights. Both qualitative and quantitative experiments show that our method can effectively learn style while avoiding overfitting to image content, highlighting the potential of modeling such stylistic differences from a single image pair.
Customizing Text-to-Image Diffusion with Camera Viewpoint Control
Apr 18, 2024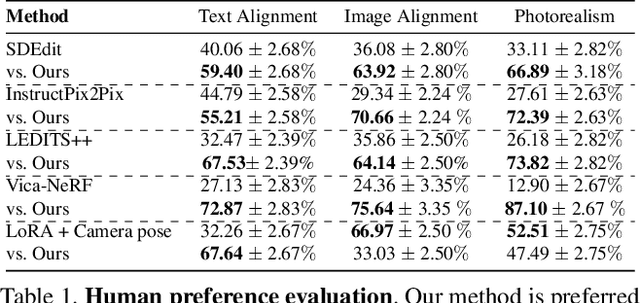


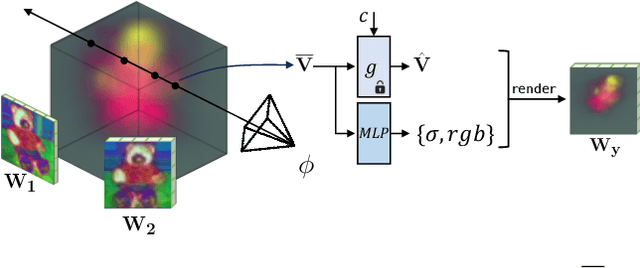
Abstract:Model customization introduces new concepts to existing text-to-image models, enabling the generation of the new concept in novel contexts. However, such methods lack accurate camera view control w.r.t the object, and users must resort to prompt engineering (e.g., adding "top-view") to achieve coarse view control. In this work, we introduce a new task -- enabling explicit control of camera viewpoint for model customization. This allows us to modify object properties amongst various background scenes via text prompts, all while incorporating the target camera pose as additional control. This new task presents significant challenges in merging a 3D representation from the multi-view images of the new concept with a general, 2D text-to-image model. To bridge this gap, we propose to condition the 2D diffusion process on rendered, view-dependent features of the new object. During training, we jointly adapt the 2D diffusion modules and 3D feature predictions to reconstruct the object's appearance and geometry while reducing overfitting to the input multi-view images. Our method outperforms existing image editing and model personalization baselines in preserving the custom object's identity while following the input text prompt and the object's camera pose.
Ablating Concepts in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Mar 23, 2023


Abstract:Large-scale text-to-image diffusion models can generate high-fidelity images with powerful compositional ability. However, these models are typically trained on an enormous amount of Internet data, often containing copyrighted material, licensed images, and personal photos. Furthermore, they have been found to replicate the style of various living artists or memorize exact training samples. How can we remove such copyrighted concepts or images without retraining the model from scratch? To achieve this goal, we propose an efficient method of ablating concepts in the pretrained model, i.e., preventing the generation of a target concept. Our algorithm learns to match the image distribution for a target style, instance, or text prompt we wish to ablate to the distribution corresponding to an anchor concept. This prevents the model from generating target concepts given its text condition. Extensive experiments show that our method can successfully prevent the generation of the ablated concept while preserving closely related concepts in the model.
Multi-Concept Customization of Text-to-Image Diffusion
Dec 08, 2022
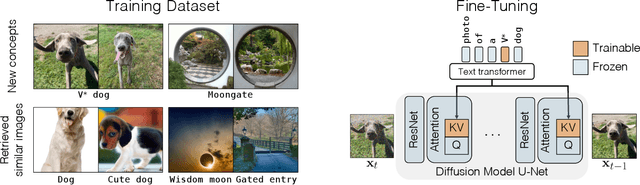
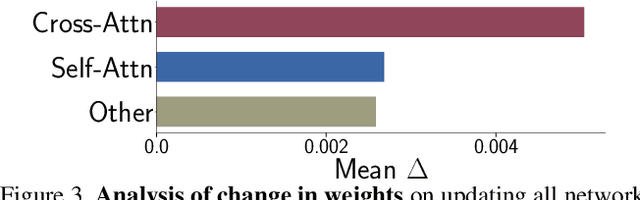
Abstract:While generative models produce high-quality images of concepts learned from a large-scale database, a user often wishes to synthesize instantiations of their own concepts (for example, their family, pets, or items). Can we teach a model to quickly acquire a new concept, given a few examples? Furthermore, can we compose multiple new concepts together? We propose Custom Diffusion, an efficient method for augmenting existing text-to-image models. We find that only optimizing a few parameters in the text-to-image conditioning mechanism is sufficiently powerful to represent new concepts while enabling fast tuning (~6 minutes). Additionally, we can jointly train for multiple concepts or combine multiple fine-tuned models into one via closed-form constrained optimization. Our fine-tuned model generates variations of multiple, new concepts and seamlessly composes them with existing concepts in novel settings. Our method outperforms several baselines and concurrent works, regarding both qualitative and quantitative evaluations, while being memory and computationally efficient.
Content-Based Search for Deep Generative Models
Oct 06, 2022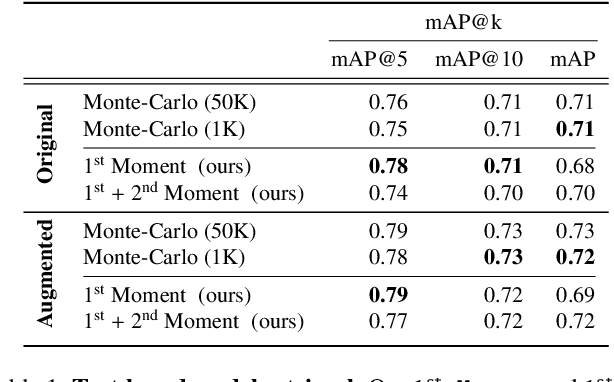
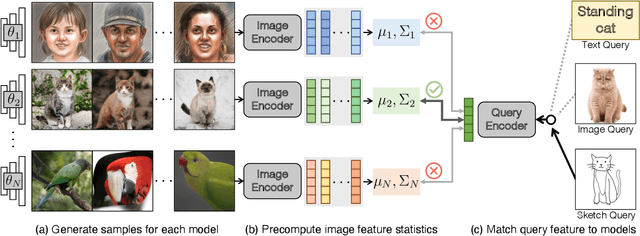
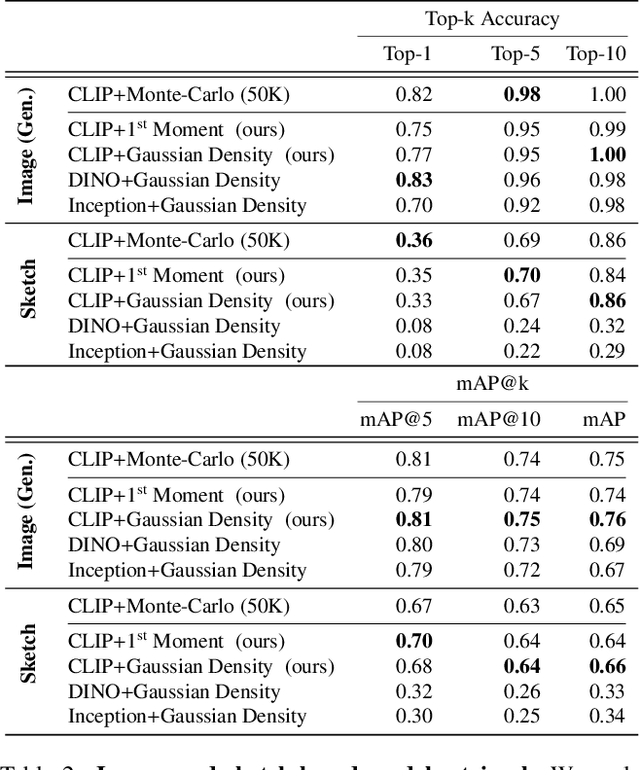
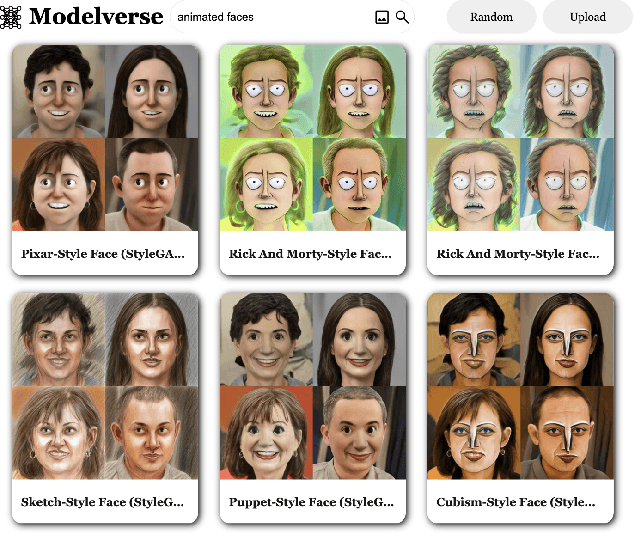
Abstract:The growing proliferation of pretrained generative models has made it infeasible for a user to be fully cognizant of every model in existence. To address this need, we introduce the task of content-based model search: given a query and a large set of generative models, find the models that best match the query. Because each generative model produces a distribution of images, we formulate the search problem as an optimization to maximize the probability of generating a query match given a model. We develop approximations to make this problem tractable when the query is an image, a sketch, a text description, another generative model, or a combination of the above. We benchmark our method in both accuracy and speed over a set of generative models. We demonstrate that our model search retrieves suitable models for image editing and reconstruction, few-shot transfer learning, and latent space interpolation. Finally, we deploy our search algorithm to our online generative model-sharing platform at https://modelverse.cs.cmu.edu.
Ensembling Off-the-shelf Models for GAN Training
Jan 18, 2022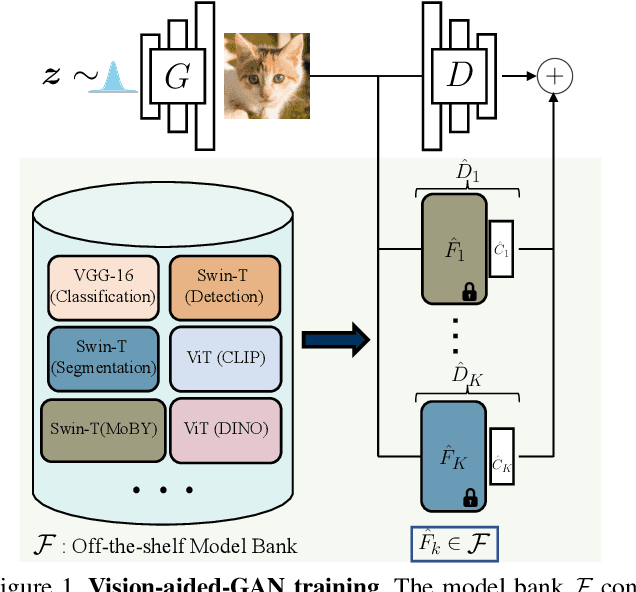
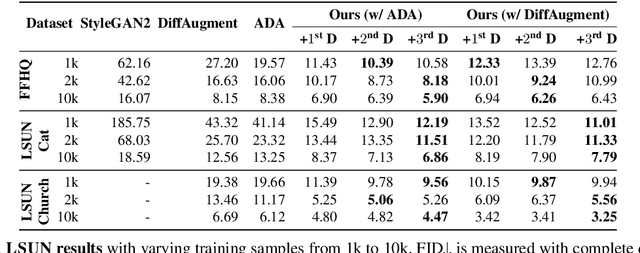
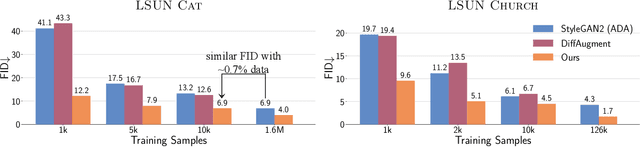
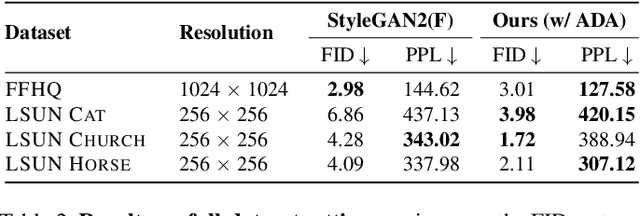
Abstract:The advent of large-scale training has produced a cornucopia of powerful visual recognition models. However, generative models, such as GANs, have traditionally been trained from scratch in an unsupervised manner. Can the collective "knowledge" from a large bank of pretrained vision models be leveraged to improve GAN training? If so, with so many models to choose from, which one(s) should be selected, and in what manner are they most effective? We find that pretrained computer vision models can significantly improve performance when used in an ensemble of discriminators. Notably, the particular subset of selected models greatly affects performance. We propose an effective selection mechanism, by probing the linear separability between real and fake samples in pretrained model embeddings, choosing the most accurate model, and progressively adding it to the discriminator ensemble. Interestingly, our method can improve GAN training in both limited data and large-scale settings. Given only 10k training samples, our FID on LSUN Cat matches the StyleGAN2 trained on 1.6M images. On the full dataset, our method improves FID by 1.5x to 2x on cat, church, and horse categories of LSUN.
Data Instance Prior for Transfer Learning in GANs
Dec 08, 2020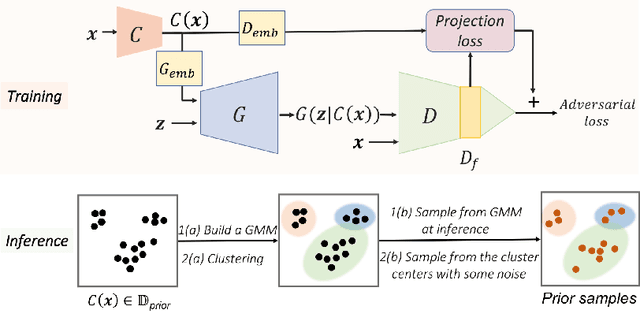
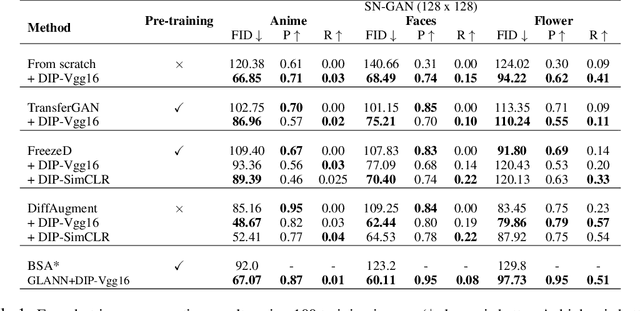
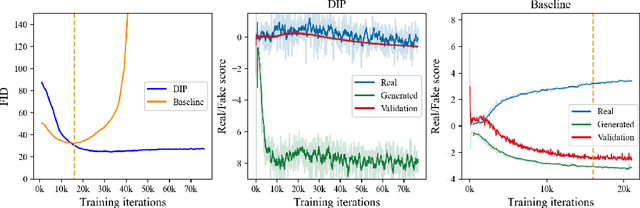
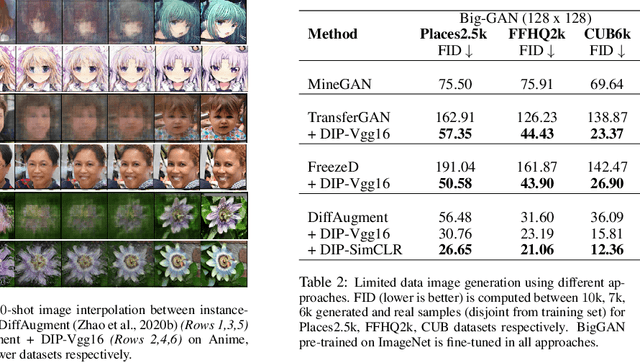
Abstract:Recent advances in generative adversarial networks (GANs) have shown remarkable progress in generating high-quality images. However, this gain in performance depends on the availability of a large amount of training data. In limited data regimes, training typically diverges, and therefore the generated samples are of low quality and lack diversity. Previous works have addressed training in low data setting by leveraging transfer learning and data augmentation techniques. We propose a novel transfer learning method for GANs in the limited data domain by leveraging informative data prior derived from self-supervised/supervised pre-trained networks trained on a diverse source domain. We perform experiments on several standard vision datasets using various GAN architectures (BigGAN, SNGAN, StyleGAN2) to demonstrate that the proposed method effectively transfers knowledge to domains with few target images, outperforming existing state-of-the-art techniques in terms of image quality and diversity. We also show the utility of data instance prior in large-scale unconditional image generation and image editing tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge