Norm Zhou
Practical Policy Optimization with Personalized Experimentation
Mar 30, 2023

Abstract:Many organizations measure treatment effects via an experimentation platform to evaluate the casual effect of product variations prior to full-scale deployment. However, standard experimentation platforms do not perform optimally for end user populations that exhibit heterogeneous treatment effects (HTEs). Here we present a personalized experimentation framework, Personalized Experiments (PEX), which optimizes treatment group assignment at the user level via HTE modeling and sequential decision policy optimization to optimize multiple short-term and long-term outcomes simultaneously. We describe an end-to-end workflow that has proven to be successful in practice and can be readily implemented using open-source software.
Scalable End-to-End ML Platforms: from AutoML to Self-serve
Mar 04, 2023


Abstract:ML platforms help enable intelligent data-driven applications and maintain them with limited engineering effort. Upon sufficiently broad adoption, such platforms reach economies of scale that bring greater component reuse while improving efficiency of system development and maintenance. For an end-to-end ML platform with broad adoption, scaling relies on pervasive ML automation and system integration to reach the quality we term self-serve that we define with ten requirements and six optional capabilities. With this in mind, we identify long-term goals for platform development, discuss related tradeoffs and future work. Our reasoning is illustrated on two commercially-deployed end-to-end ML platforms that host hundreds of real-time use cases -- one general-purpose and one specialized.
Looper: An end-to-end ML platform for product decisions
Nov 10, 2021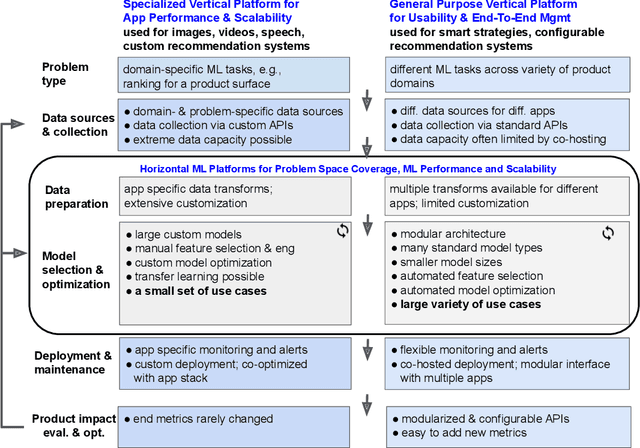
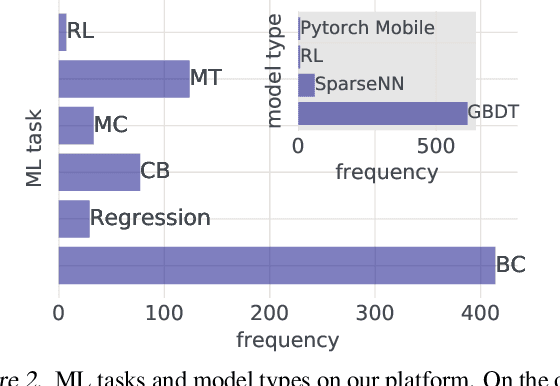
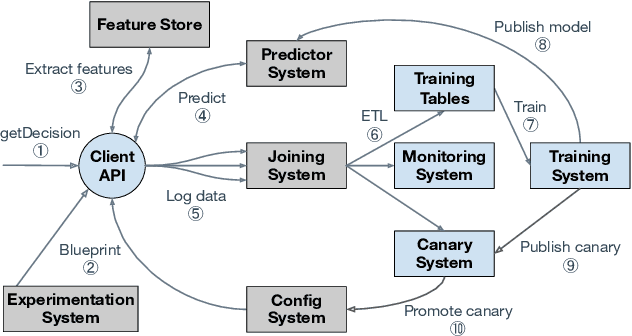
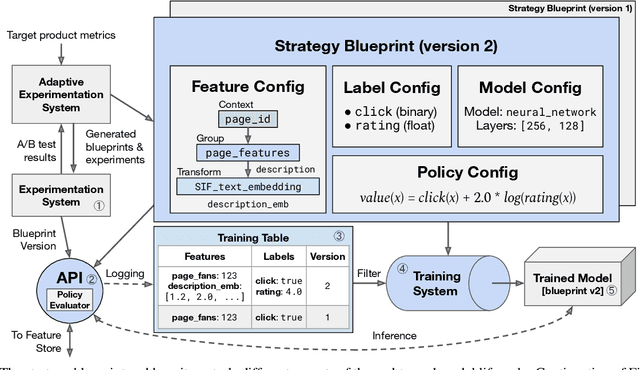
Abstract:Modern software systems and products increasingly rely on machine learning models to make data-driven decisions based on interactions with users and systems, e.g., compute infrastructure. For broader adoption, this practice must (i) accommodate software engineers without ML backgrounds, and (ii) provide mechanisms to optimize for product goals. In this work, we describe general principles and a specific end-to-end ML platform, Looper, which offers easy-to-use APIs for decision-making and feedback collection. Looper supports the full end-to-end ML lifecycle from online data collection to model training, deployment, inference, and extends support to evaluation and tuning against product goals. We outline the platform architecture and overall impact of production deployment -- Looper currently hosts 700 ML models and makes 6 million decisions per second. We also describe the learning curve and summarize experiences of platform adopters.
Personalization for Web-based Services using Offline Reinforcement Learning
Feb 10, 2021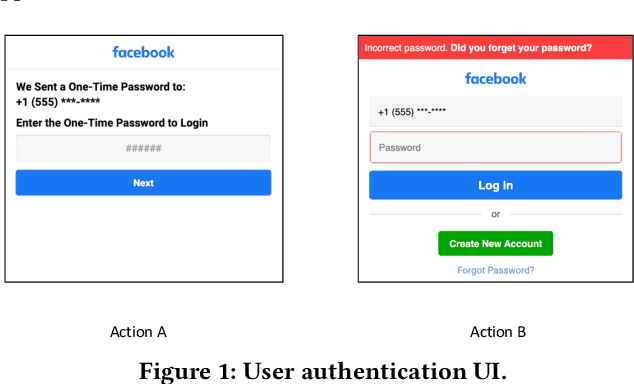
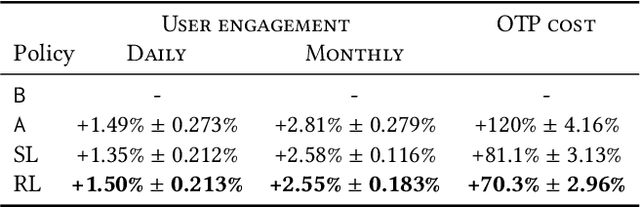
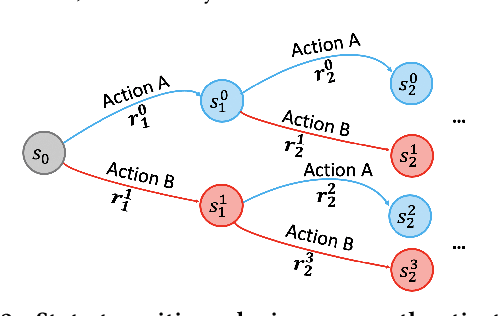
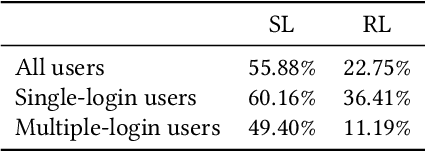
Abstract:Large-scale Web-based services present opportunities for improving UI policies based on observed user interactions. We address challenges of learning such policies through model-free offline Reinforcement Learning (RL) with off-policy training. Deployed in a production system for user authentication in a major social network, it significantly improves long-term objectives. We articulate practical challenges, compare several ML techniques, provide insights on training and evaluation of RL models, and discuss generalizations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge