Nitya Kasturi
Looper: An end-to-end ML platform for product decisions
Nov 10, 2021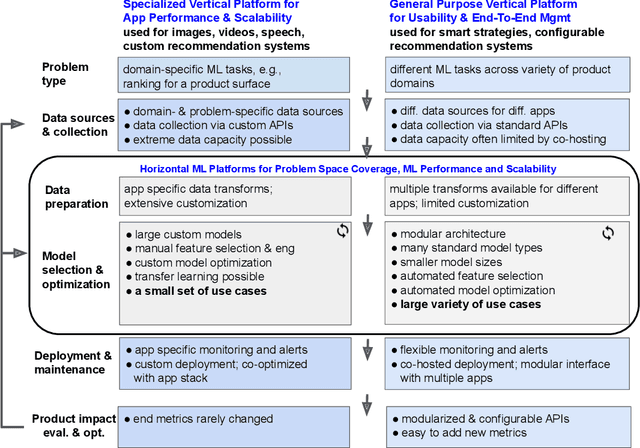
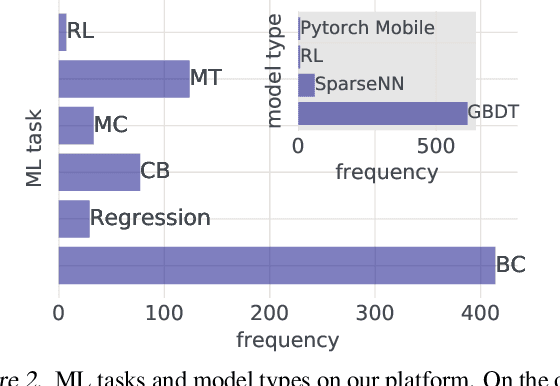
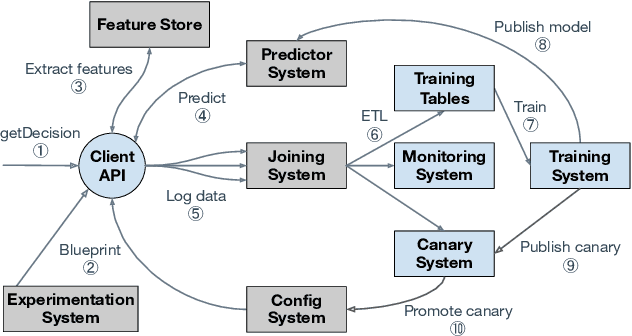
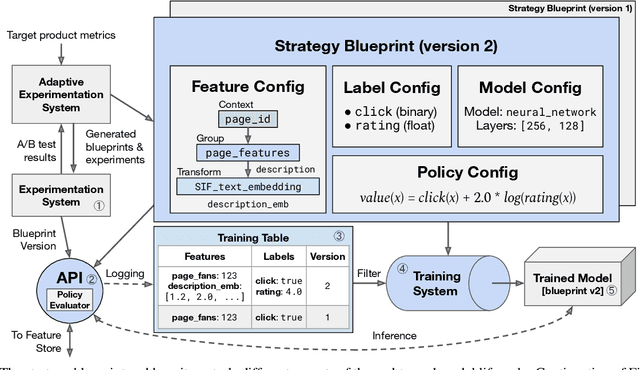
Abstract:Modern software systems and products increasingly rely on machine learning models to make data-driven decisions based on interactions with users and systems, e.g., compute infrastructure. For broader adoption, this practice must (i) accommodate software engineers without ML backgrounds, and (ii) provide mechanisms to optimize for product goals. In this work, we describe general principles and a specific end-to-end ML platform, Looper, which offers easy-to-use APIs for decision-making and feedback collection. Looper supports the full end-to-end ML lifecycle from online data collection to model training, deployment, inference, and extends support to evaluation and tuning against product goals. We outline the platform architecture and overall impact of production deployment -- Looper currently hosts 700 ML models and makes 6 million decisions per second. We also describe the learning curve and summarize experiences of platform adopters.
Text Ranking and Classification using Data Compression
Sep 23, 2021
Abstract:A well-known but rarely used approach to text categorization uses conditional entropy estimates computed using data compression tools. Text affinity scores derived from compressed sizes can be used for classification and ranking tasks, but their success depends on the compression tools used. We use the Zstandard compressor and strengthen these ideas in several ways, calling the resulting language-agnostic technique Zest. In applications, this approach simplifies configuration, avoiding careful feature extraction and large ML models. Our ablation studies confirm the value of individual enhancements we introduce. We show that Zest complements and can compete with language-specific multidimensional content embeddings in production, but cannot outperform other counting methods on public datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge