Nitin J. Sanket
AsterNav: Autonomous Aerial Robot Navigation In Darkness Using Passive Computation
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Autonomous aerial navigation in absolute darkness is crucial for post-disaster search and rescue operations, which often occur from disaster-zone power outages. Yet, due to resource constraints, tiny aerial robots, perfectly suited for these operations, are unable to navigate in the darkness to find survivors safely. In this paper, we present an autonomous aerial robot for navigation in the dark by combining an Infra-Red (IR) monocular camera with a large-aperture coded lens and structured light without external infrastructure like GPS or motion-capture. Our approach obtains depth-dependent defocus cues (each structured light point appears as a pattern that is depth dependent), which acts as a strong prior for our AsterNet deep depth estimation model. The model is trained in simulation by generating data using a simple optical model and transfers directly to the real world without any fine-tuning or retraining. AsterNet runs onboard the robot at 20 Hz on an NVIDIA Jetson Orin$^\text{TM}$ Nano. Furthermore, our network is robust to changes in the structured light pattern and relative placement of the pattern emitter and IR camera, leading to simplified and cost-effective construction. We successfully evaluate and demonstrate our proposed depth navigation approach AsterNav using depth from AsterNet in many real-world experiments using only onboard sensing and computation, including dark matte obstacles and thin ropes (diameter 6.25mm), achieving an overall success rate of 95.5% with unknown object shapes, locations and materials. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work on monocular, structured-light-based quadrotor navigation in absolute darkness.
VizFlyt: Perception-centric Pedagogical Framework For Autonomous Aerial Robots
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Autonomous aerial robots are becoming commonplace in our lives. Hands-on aerial robotics courses are pivotal in training the next-generation workforce to meet the growing market demands. Such an efficient and compelling course depends on a reliable testbed. In this paper, we present VizFlyt, an open-source perception-centric Hardware-In-The-Loop (HITL) photorealistic testing framework for aerial robotics courses. We utilize pose from an external localization system to hallucinate real-time and photorealistic visual sensors using 3D Gaussian Splatting. This enables stress-free testing of autonomy algorithms on aerial robots without the risk of crashing into obstacles. We achieve over 100Hz of system update rate. Lastly, we build upon our past experiences of offering hands-on aerial robotics courses and propose a new open-source and open-hardware curriculum based on VizFlyt for the future. We test our framework on various course projects in real-world HITL experiments and present the results showing the efficacy of such a system and its large potential use cases. Code, datasets, hardware guides and demo videos are available at https://pear.wpi.edu/research/vizflyt.html
EdgeFlowNet: 100FPS@1W Dense Optical Flow For Tiny Mobile Robots
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:Optical flow estimation is a critical task for tiny mobile robotics to enable safe and accurate navigation, obstacle avoidance, and other functionalities. However, optical flow estimation on tiny robots is challenging due to limited onboard sensing and computation capabilities. In this paper, we propose EdgeFlowNet , a high-speed, low-latency dense optical flow approach for tiny autonomous mobile robots by harnessing the power of edge computing. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach by deploying EdgeFlowNet on a tiny quadrotor to perform static obstacle avoidance, flight through unknown gaps and dynamic obstacle dodging. EdgeFlowNet is about 20 faster than the previous state-of-the-art approaches while improving accuracy by over 20% and using only 1.08W of power enabling advanced autonomy on palm-sized tiny mobile robots.
Detecting Olives with Synthetic or Real Data? Olive the Above
Aug 16, 2023



Abstract:Modern robotics has enabled the advancement in yield estimation for precision agriculture. However, when applied to the olive industry, the high variation of olive colors and their similarity to the background leaf canopy presents a challenge. Labeling several thousands of very dense olive grove images for segmentation is a labor-intensive task. This paper presents a novel approach to detecting olives without the need to manually label data. In this work, we present the world's first olive detection dataset comprised of synthetic and real olive tree images. This is accomplished by generating an auto-labeled photorealistic 3D model of an olive tree. Its geometry is then simplified for lightweight rendering purposes. In addition, experiments are conducted with a mix of synthetically generated and real images, yielding an improvement of up to 66% compared to when only using a small sample of real data. When access to real, human-labeled data is limited, a combination of mostly synthetic data and a small amount of real data can enhance olive detection.
WorldGen: A Large Scale Generative Simulator
Oct 03, 2022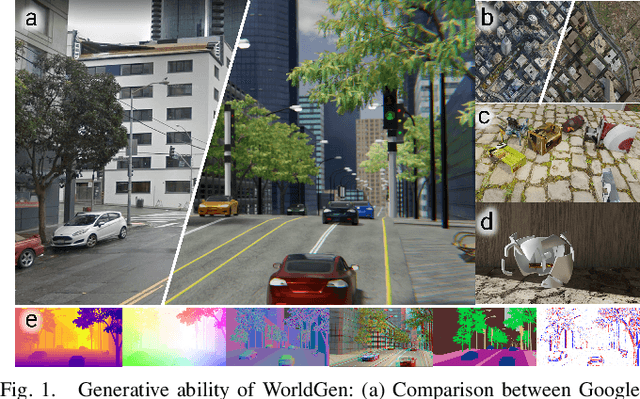
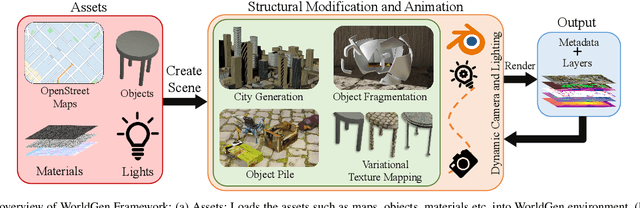
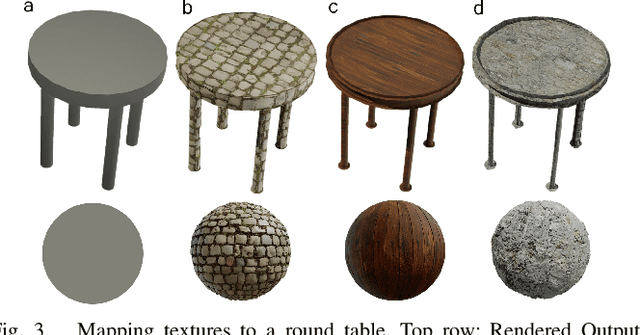

Abstract:In the era of deep learning, data is the critical determining factor in the performance of neural network models. Generating large datasets suffers from various difficulties such as scalability, cost efficiency and photorealism. To avoid expensive and strenuous dataset collection and annotations, researchers have inclined towards computer-generated datasets. Although, a lack of photorealism and a limited amount of computer-aided data, has bounded the accuracy of network predictions. To this end, we present WorldGen -- an open source framework to autonomously generate countless structured and unstructured 3D photorealistic scenes such as city view, object collection, and object fragmentation along with its rich ground truth annotation data. WorldGen being a generative model gives the user full access and control to features such as texture, object structure, motion, camera and lens properties for better generalizability by diminishing the data bias in the network. We demonstrate the effectiveness of WorldGen by presenting an evaluation on deep optical flow. We hope such a tool can open doors for future research in a myriad of domains related to robotics and computer vision by reducing manual labor and the cost of acquiring rich and high-quality data.
OysterNet: Enhanced Oyster Detection Using Simulation
Sep 16, 2022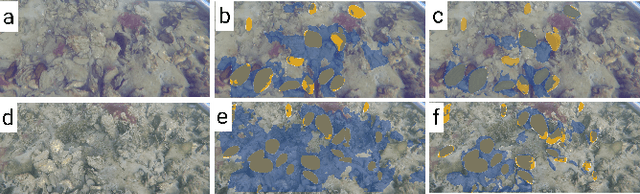
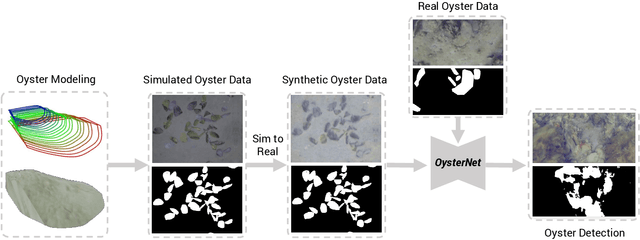

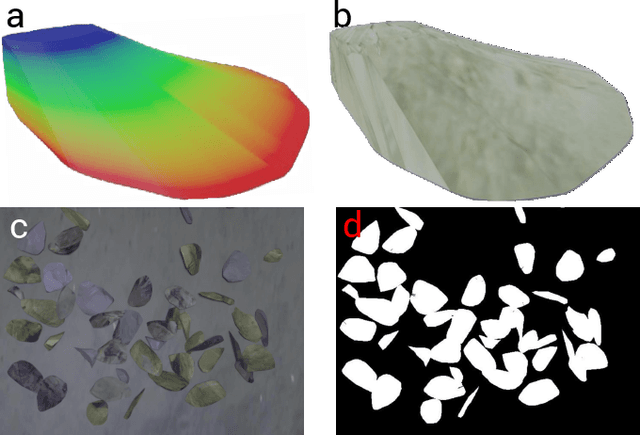
Abstract:Oysters play a pivotal role in the bay living ecosystem and are considered the living filters for the ocean. In recent years, oyster reefs have undergone major devastation caused by commercial over-harvesting, requiring preservation to maintain ecological balance. The foundation of this preservation is to estimate the oyster density which requires accurate oyster detection. However, systems for accurate oyster detection require large datasets obtaining which is an expensive and labor-intensive task in underwater environments. To this end, we present a novel method to mathematically model oysters and render images of oysters in simulation to boost the detection performance with minimal real data. Utilizing our synthetic data along with real data for oyster detection, we obtain up to 35.1% boost in performance as compared to using only real data with our OysterNet network. We also improve the state-of-the-art by 12.7%. This shows that using underlying geometrical properties of objects can help to enhance recognition task accuracy on limited datasets successfully and we hope more researchers adopt such a strategy for hard-to-obtain datasets.
DiffPoseNet: Direct Differentiable Camera Pose Estimation
Mar 21, 2022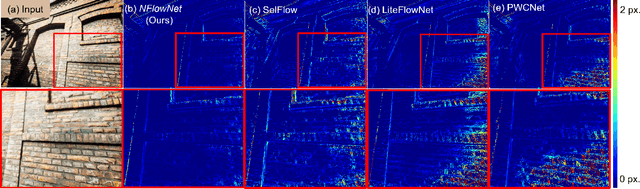

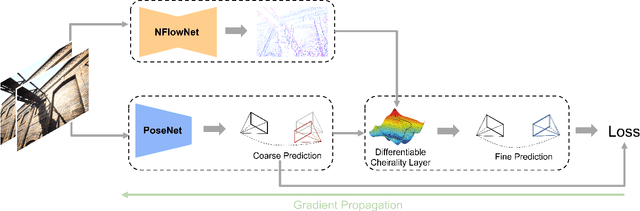

Abstract:Current deep neural network approaches for camera pose estimation rely on scene structure for 3D motion estimation, but this decreases the robustness and thereby makes cross-dataset generalization difficult. In contrast, classical approaches to structure from motion estimate 3D motion utilizing optical flow and then compute depth. Their accuracy, however, depends strongly on the quality of the optical flow. To avoid this issue, direct methods have been proposed, which separate 3D motion from depth estimation but compute 3D motion using only image gradients in the form of normal flow. In this paper, we introduce a network NFlowNet, for normal flow estimation which is used to enforce robust and direct constraints. In particular, normal flow is used to estimate relative camera pose based on the cheirality (depth positivity) constraint. We achieve this by formulating the optimization problem as a differentiable cheirality layer, which allows for end-to-end learning of camera pose. We perform extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluation of the proposed DiffPoseNet's sensitivity to noise and its generalization across datasets. We compare our approach to existing state-of-the-art methods on KITTI, TartanAir, and TUM-RGBD datasets.
Fast Active Monocular Distance Estimation from Time-to-Contact
Mar 14, 2022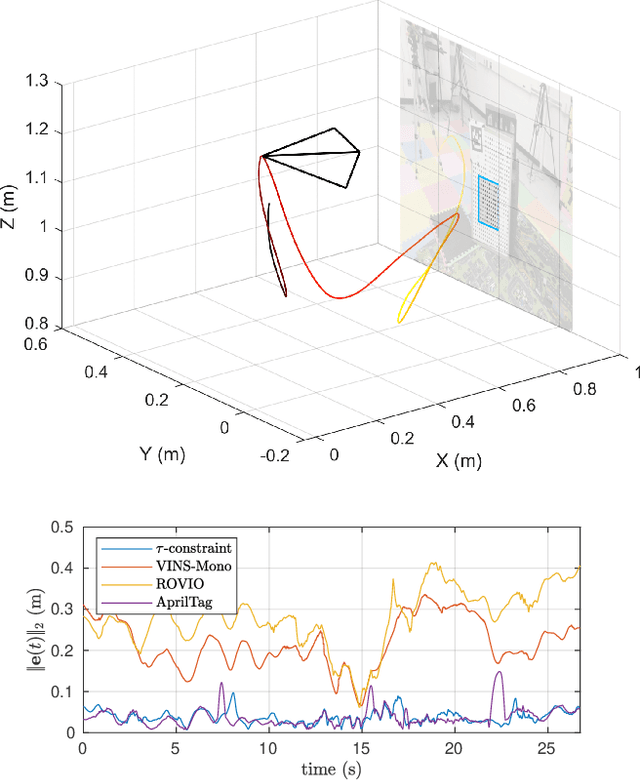
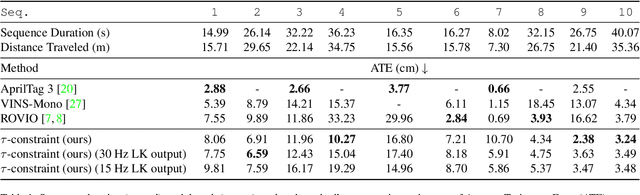
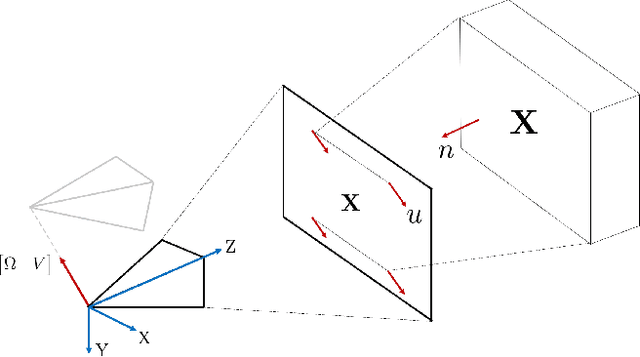
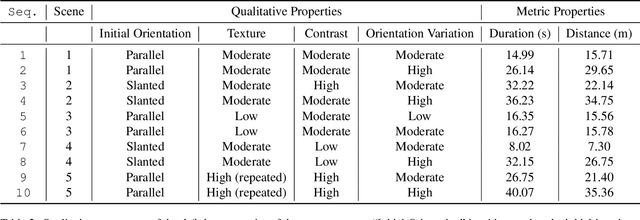
Abstract:Distance estimation is fundamental for a variety of robotic applications including navigation, manipulation and planning. Inspired by the mammal's visual system, which gazes at specific objects (active fixation), and estimates when the object will reach it (time-to-contact), we develop a novel constraint between time-to-contact, acceleration, and distance that we call the $\tau$-constraint. It allows an active monocular camera to estimate depth using time-to-contact and inertial measurements (linear accelerations and angular velocities) within a window of time. Our work differs from other approaches by focusing on patches instead of feature points. This is, because the change in the patch area determines the time-to-contact directly. The result enables efficient estimation of distance while using only a small portion of the image, leading to a large speedup. We successfully validate the proposed $\tau$-constraint in the application of estimating camera position with a monocular grayscale camera and an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU). Specifically, we test our method on different real-world planar objects over trajectories 8-40 seconds in duration and 7-35 meters long. Our method achieves 8.5 cm Average Trajectory Error (ATE) while the popular Visual-Inertial Odometry methods VINS-Mono and ROVIO achieve 12.2 and 16.9 cm ATE respectively. Additionally, our implementation runs 27$\times$ faster than VINS-Mono's and 6.8$\times$ faster than ROVIO's. We believe these results indicate the $\tau$-constraints potential to be the basis of robust, sophisticated algorithms for a multitude of applications involving an active camera and an IMU.
GradTac: Spatio-Temporal Gradient Based Tactile Sensing
Mar 14, 2022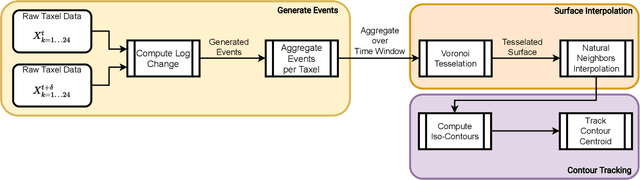
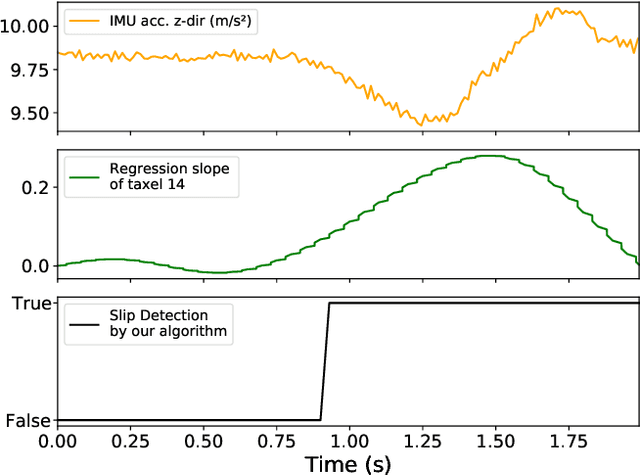
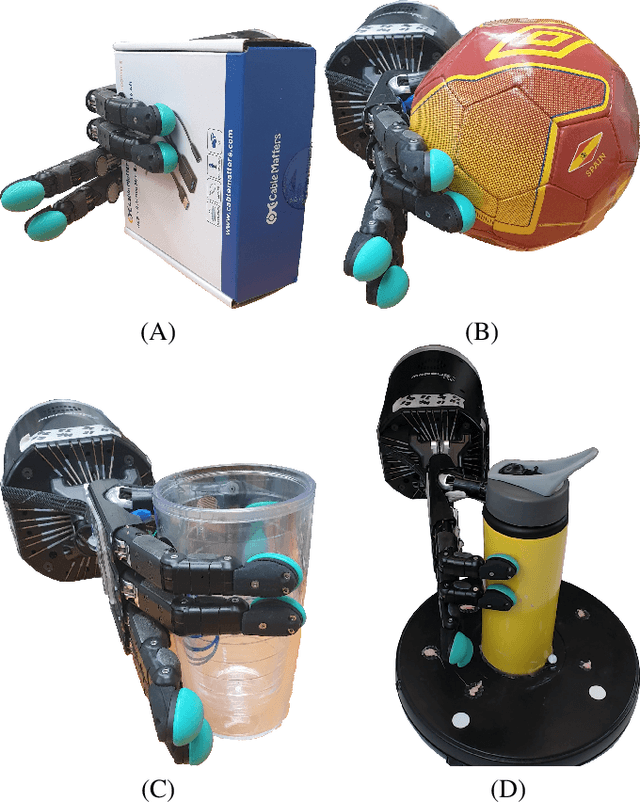
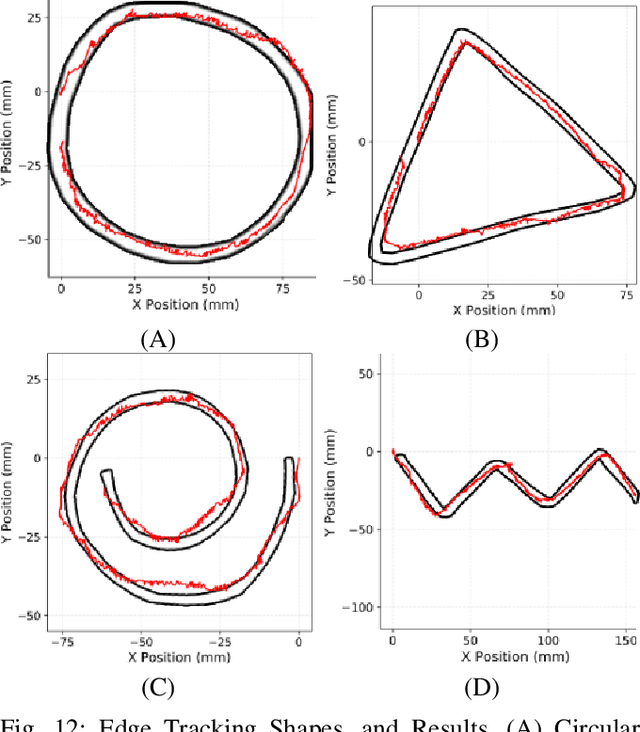
Abstract:Tactile sensing for robotics is achieved through a variety of mechanisms, including magnetic, optical-tactile, and conductive fluid. Currently, the fluid-based sensors have struck the right balance of anthropomorphic sizes and shapes and accuracy of tactile response measurement. However, this design is plagued by a low Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) due to the fluid based sensing mechanism "damping" the measurement values that are hard to model. To this end, we present a spatio-temporal gradient representation on the data obtained from fluid-based tactile sensors, which is inspired from neuromorphic principles of event based sensing. We present a novel algorithm (GradTac) that converts discrete data points from spatial tactile sensors into spatio-temporal surfaces and tracks tactile contours across these surfaces. Processing the tactile data using the proposed spatio-temporal domain is robust, makes it less susceptible to the inherent noise from the fluid based sensors, and allows accurate tracking of regions of touch as compared to using the raw data. We successfully evaluate and demonstrate the efficacy of GradTac on many real-world experiments performed using the Shadow Dexterous Hand, equipped with the BioTac SP sensors. Specifically, we use it for tracking tactile input across the sensor's surface, measuring relative forces, detecting linear and rotational slip, and for edge tracking. We also release an accompanying task-agnostic dataset for the BioTac SP, which we hope will provide a resource to compare and quantify various novel approaches, and motivate further research.
NudgeSeg: Zero-Shot Object Segmentation by Repeated Physical Interaction
Sep 22, 2021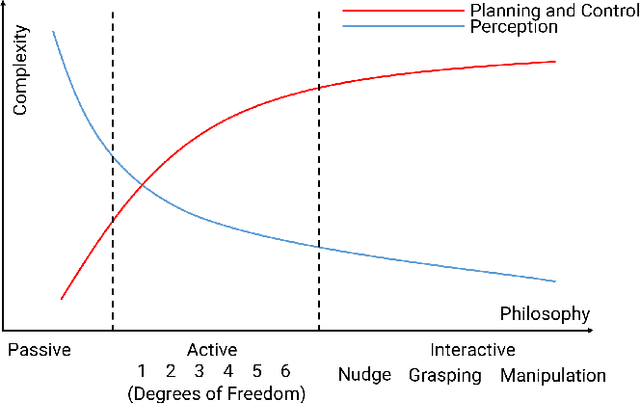
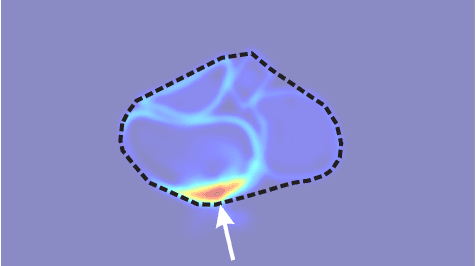
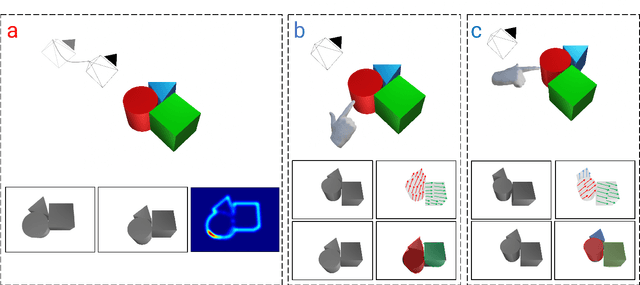

Abstract:Recent advances in object segmentation have demonstrated that deep neural networks excel at object segmentation for specific classes in color and depth images. However, their performance is dictated by the number of classes and objects used for training, thereby hindering generalization to never seen objects or zero-shot samples. To exacerbate the problem further, object segmentation using image frames rely on recognition and pattern matching cues. Instead, we utilize the 'active' nature of a robot and their ability to 'interact' with the environment to induce additional geometric constraints for segmenting zero-shot samples. In this paper, we present the first framework to segment unknown objects in a cluttered scene by repeatedly 'nudging' at the objects and moving them to obtain additional motion cues at every step using only a monochrome monocular camera. We call our framework NudgeSeg. These motion cues are used to refine the segmentation masks. We successfully test our approach to segment novel objects in various cluttered scenes and provide an extensive study with image and motion segmentation methods. We show an impressive average detection rate of over 86% on zero-shot objects.
* 8 Pages, 7 Figures, 3 Tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge