Nitesh Kumar
The Persistent Robot Charging Problem for Long-Duration Autonomy
Sep 01, 2024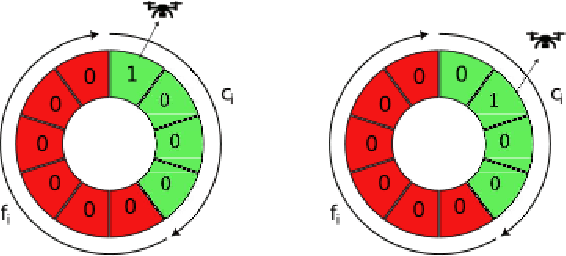
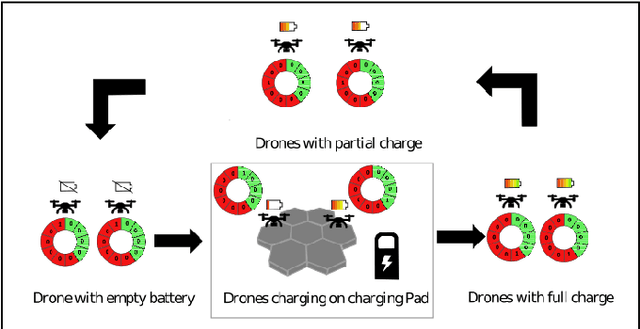
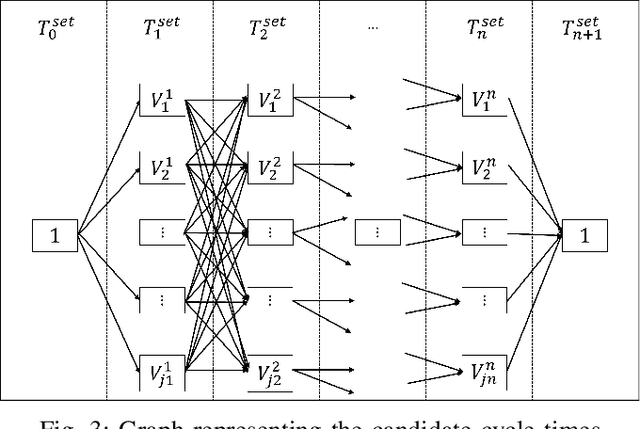
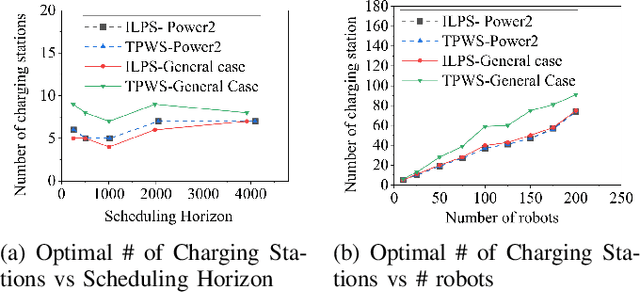
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel formulation aimed at determining the optimal schedule for recharging a fleet of $n$ heterogeneous robots, with the primary objective of minimizing resource utilization. This study provides a foundational framework applicable to Multi-Robot Mission Planning, particularly in scenarios demanding Long-Duration Autonomy (LDA) or other contexts that necessitate periodic recharging of multiple robots. A novel Integer Linear Programming (ILP) model is proposed to calculate the optimal initial conditions (partial charge) for individual robots, leading to the minimal utilization of charging stations. This formulation was further generalized to maximize the servicing time for robots given adequate charging stations. The efficacy of the proposed formulation is evaluated through a comparative analysis, measuring its performance against the thrift price scheduling algorithm documented in the existing literature. The findings not only validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach but also underscore its potential as a valuable tool in optimizing resource allocation for a range of robotic and engineering applications.
Ranking Entities along Conceptual Space Dimensions with LLMs: An Analysis of Fine-Tuning Strategies
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:Conceptual spaces represent entities in terms of their primitive semantic features. Such representations are highly valuable but they are notoriously difficult to learn, especially when it comes to modelling perceptual and subjective features. Distilling conceptual spaces from Large Language Models (LLMs) has recently emerged as a promising strategy. However, existing work has been limited to probing pre-trained LLMs using relatively simple zero-shot strategies. We focus in particular on the task of ranking entities according to a given conceptual space dimension. Unfortunately, we cannot directly fine-tune LLMs on this task, because ground truth rankings for conceptual space dimensions are rare. We therefore use more readily available features as training data and analyse whether the ranking capabilities of the resulting models transfer to perceptual and subjective features. We find that this is indeed the case, to some extent, but having perceptual and subjective features in the training data seems essential for achieving the best results. We furthermore find that pointwise ranking strategies are competitive against pairwise approaches, in defiance of common wisdom.
Solving Hard Analogy Questions with Relation Embedding Chains
Oct 18, 2023Abstract:Modelling how concepts are related is a central topic in Lexical Semantics. A common strategy is to rely on knowledge graphs (KGs) such as ConceptNet, and to model the relation between two concepts as a set of paths. However, KGs are limited to a fixed set of relation types, and they are incomplete and often noisy. Another strategy is to distill relation embeddings from a fine-tuned language model. However, this is less suitable for words that are only indirectly related and it does not readily allow us to incorporate structured domain knowledge. In this paper, we aim to combine the best of both worlds. We model relations as paths but associate their edges with relation embeddings. The paths are obtained by first identifying suitable intermediate words and then selecting those words for which informative relation embeddings can be obtained. We empirically show that our proposed representations are useful for solving hard analogy questions.
Modeling and parametric optimization of 3D tendon-sheath actuator system for upper limb soft exosuit
Jun 30, 2023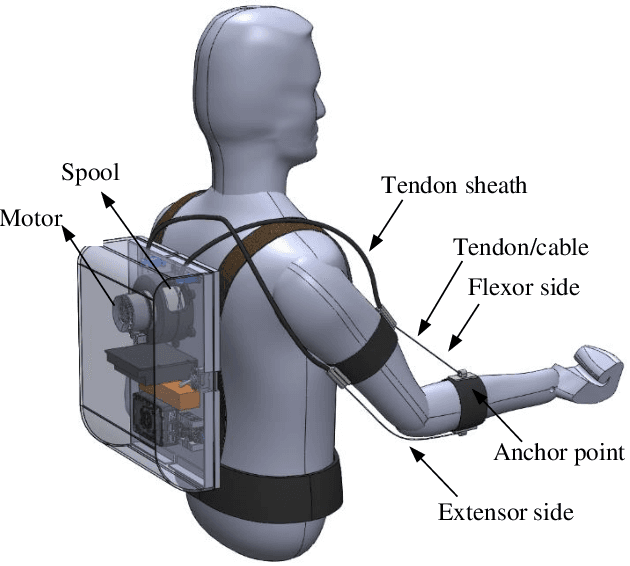
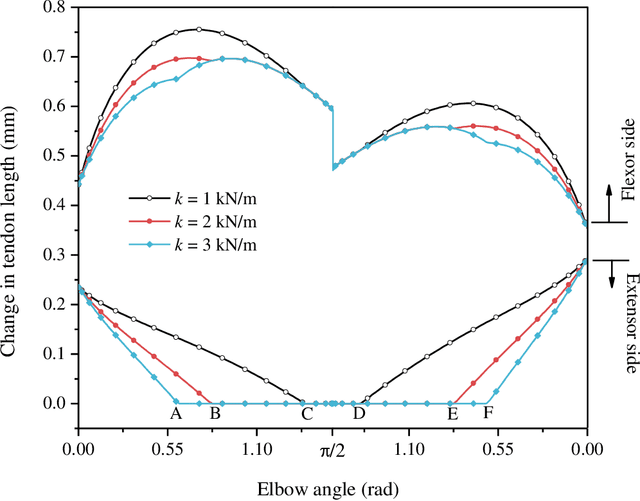
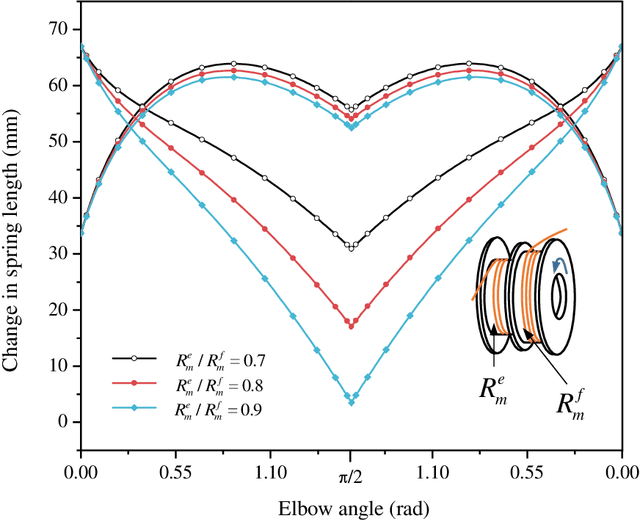
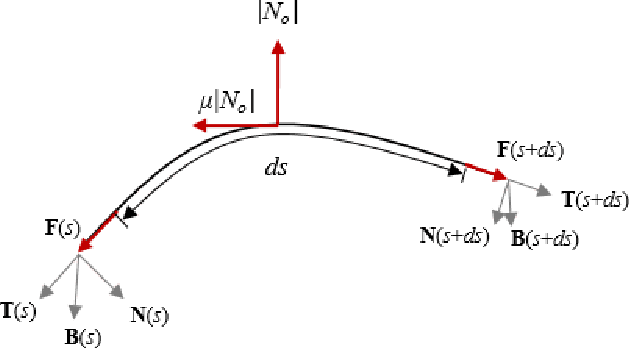
Abstract:This paper presents an analysis of parametric characterization of a motor driven tendon-sheath actuator system for use in upper limb augmentation for applications such as rehabilitation, therapy, and industrial automation. The double tendon sheath system, which uses two sets of cables (agonist and antagonist side) guided through a sheath, is considered to produce smooth and natural-looking movements of the arm. The exoskeleton is equipped with a single motor capable of controlling both the flexion and extension motions. One of the key challenges in the implementation of a double tendon sheath system is the possibility of slack in the tendon, which can impact the overall performance of the system. To address this issue, a robust mathematical model is developed and a comprehensive parametric study is carried out to determine the most effective strategies for overcoming the problem of slack and improving the transmission. The study suggests that incorporating a series spring into the system's tendon leads to a universally applicable design, eliminating the need for individual customization. The results also show that the slack in the tendon can be effectively controlled by changing the pretension, spring constant, and size and geometry of spool mounted on the axle of motor.
Adaptive Gravity Compensation Control of a Cable-Driven Upper-Arm Soft Exosuit
Apr 28, 2023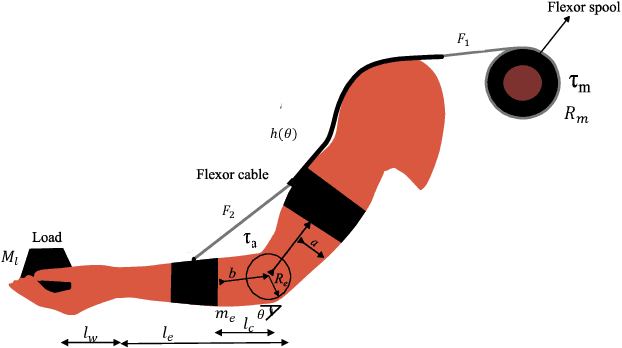
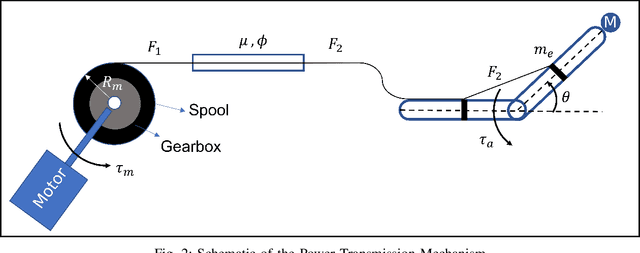
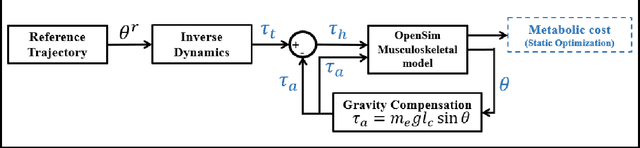
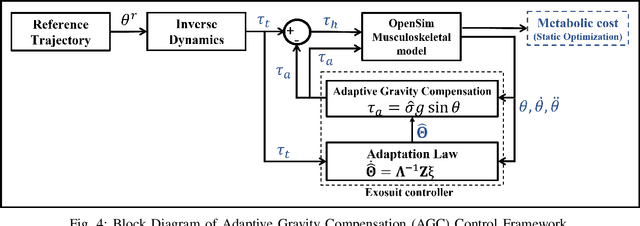
Abstract:This paper proposes an adaptive gravity compensation (AGC) control strategy for a cable-driven upper-limb exosuit intended to assist the wearer with lifting tasks. Unlike most model-based control techniques used for this human-robot interaction task, the proposed control design does not assume knowledge of the anthropometric parameters of the wearer's arm and the payload. Instead, the uncertainties in human arm parameters, such as mass, length, and payload, are estimated online using an indirect adaptive control law that compensates for the gravity moment about the elbow joint. Additionally, the AGC controller is agnostic to the desired joint trajectory followed by the human arm. For the purpose of controller design, the human arm is modeled using a 1-DOF manipulator model. Further, a cable-driven actuator model is proposed that maps the assistive elbow torque to the actuator torque. The performance of the proposed method is verified through a co-simulation, wherein the control input realized in MATLAB is applied to the human bio-mechanical model in OpenSim under varying payload conditions. Significant reductions in human effort in terms of human muscle torque and metabolic cost are observed with the proposed control strategy. Further, simulation results show that the performance of the AGC controller converges to that of the gravity compensation (GC) controller, demonstrating the efficacy of AGC-based online parameter learning.
Hybrid Probabilistic Logic Programming: Inference and Learning
Feb 10, 2023Abstract:This thesis focuses on advancing probabilistic logic programming (PLP), which combines probability theory for uncertainty and logic programming for relations. The thesis aims to extend PLP to support both discrete and continuous random variables, which is necessary for applications with numeric data. The first contribution is the introduction of context-specific likelihood weighting (CS-LW), a new sampling algorithm that exploits context-specific independencies for computational gains. Next, a new hybrid PLP, DC#, is introduced, which integrates the syntax of Distributional Clauses with Bayesian logic programs and represents three types of independencies: i) conditional independencies (CIs) modeled in Bayesian networks; ii) context-specific independencies (CSIs) represented by logical rules, and iii) independencies amongst attributes of related objects in relational models expressed by combining rules. The scalable inference algorithm FO-CS-LW is introduced for DC#. Finally, the thesis addresses the lack of approaches for learning hybrid PLP from relational data with missing values and (probabilistic) background knowledge with the introduction of DiceML, which learns the structure and parameters of hybrid PLP and tackles the relational autocompletion problem. The conclusion discusses future directions and open challenges for hybrid PLP.
First-Order Context-Specific Likelihood Weighting in Hybrid Probabilistic Logic Programs
Jan 26, 2022
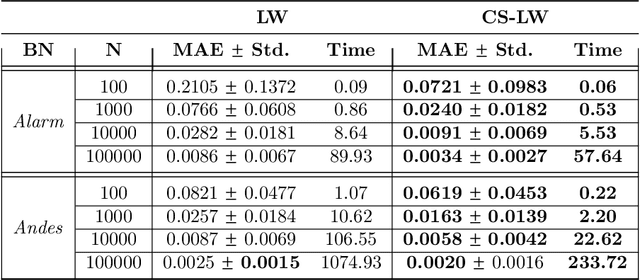

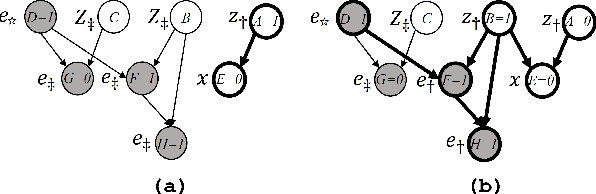
Abstract:Statistical relational AI and probabilistic logic programming have so far mostly focused on discrete probabilistic models. The reasons for this is that one needs to provide constructs to succinctly model the independencies in such models, and also provide efficient inference. Three types of independencies are important to represent and exploit for scalable inference in hybrid models: conditional independencies elegantly modeled in Bayesian networks, context-specific independencies naturally represented by logical rules, and independencies amongst attributes of related objects in relational models succinctly expressed by combining rules. This paper introduces a hybrid probabilistic logic programming language, DC#, which integrates distributional clauses' syntax and semantics principles of Bayesian logic programs. It represents the three types of independencies qualitatively. More importantly, we also introduce the scalable inference algorithm FO-CS-LW for DC#. FO-CS-LW is a first-order extension of the context-specific likelihood weighting algorithm (CS-LW), a novel sampling method that exploits conditional independencies and context-specific independencies in ground models. The FO-CS-LW algorithm upgrades CS-LW with unification and combining rules to the first-order case.
Context-Specific Likelihood Weighting
Feb 09, 2021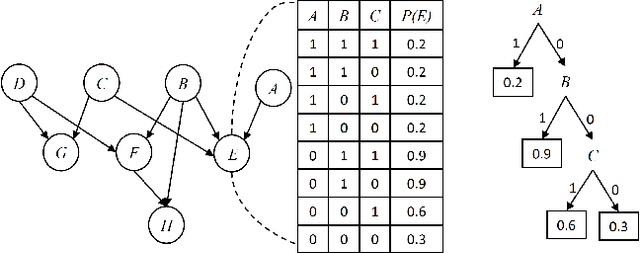



Abstract:Sampling is a popular method for approximate inference when exact inference is impractical. Generally, sampling algorithms do not exploit context-specific independence (CSI) properties of probability distributions. We introduce context-specific likelihood weighting (CS-LW), a new sampling methodology, which besides exploiting the classical conditional independence properties, also exploits CSI properties. Unlike the standard likelihood weighting, CS-LW is based on partial assignments of random variables and requires fewer samples for convergence due to the sampling variance reduction. Furthermore, the speed of generating samples increases. Our novel notion of contextual assignments theoretically justifies CS-LW. We empirically show that CS-LW is competitive with state-of-the-art algorithms for approximate inference in the presence of a significant amount of CSIs.
Symbolic Learning and Reasoning with Noisy Data for Probabilistic Anchoring
Feb 24, 2020
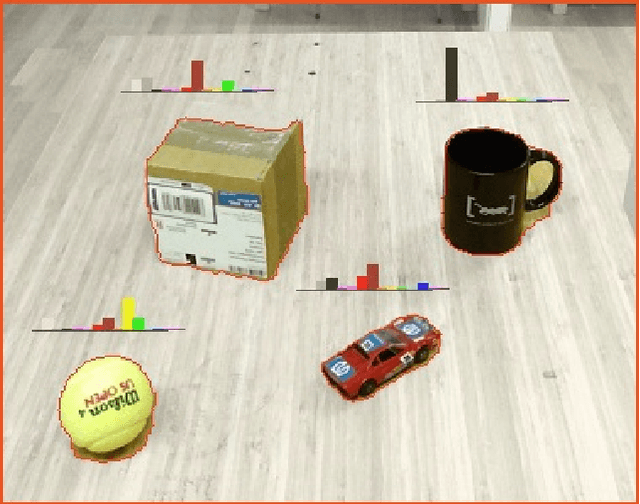
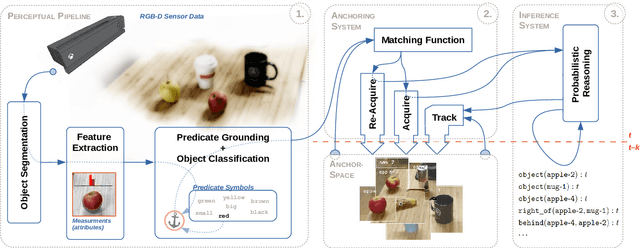


Abstract:Robotic agents should be able to learn from sub-symbolic sensor data, and at the same time, be able to reason about objects and communicate with humans on a symbolic level. This raises the question of how to overcome the gap between symbolic and sub-symbolic artificial intelligence. We propose a semantic world modeling approach based on bottom-up object anchoring using an object-centered representation of the world. Perceptual anchoring processes continuous perceptual sensor data and maintains a correspondence to a symbolic representation. We extend the definitions of anchoring to handle multi-modal probability distributions and we couple the resulting symbol anchoring system to a probabilistic logic reasoner for performing inference. Furthermore, we use statistical relational learning to enable the anchoring framework to learn symbolic knowledge in the form of a set of probabilistic logic rules of the world from noisy and sub-symbolic sensor input. The resulting framework, which combines perceptual anchoring and statistical relational learning, is able to maintain a semantic world model of all the objects that have been perceived over time, while still exploiting the expressiveness of logical rules to reason about the state of objects which are not directly observed through sensory input data. To validate our approach we demonstrate, on the one hand, the ability of our system to perform probabilistic reasoning over multi-modal probability distributions, and on the other hand, the learning of probabilistic logical rules from anchored objects produced by perceptual observations. The learned logical rules are, subsequently, used to assess our proposed probabilistic anchoring procedure. We demonstrate our system in a setting involving object interactions where object occlusions arise and where probabilistic inference is needed to correctly anchor objects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge