Adaptive Gravity Compensation Control of a Cable-Driven Upper-Arm Soft Exosuit
Paper and Code
Apr 28, 2023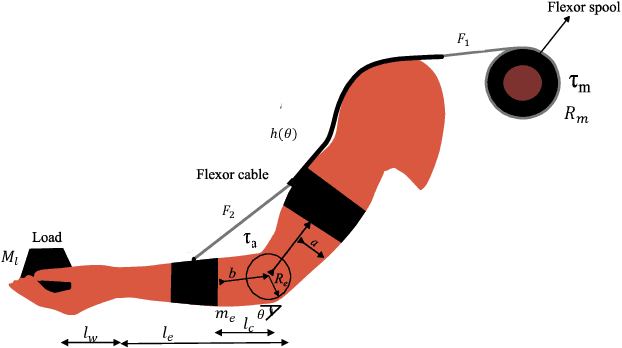
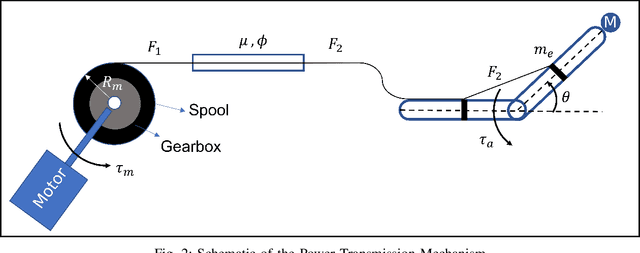
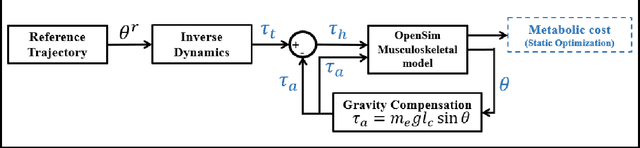
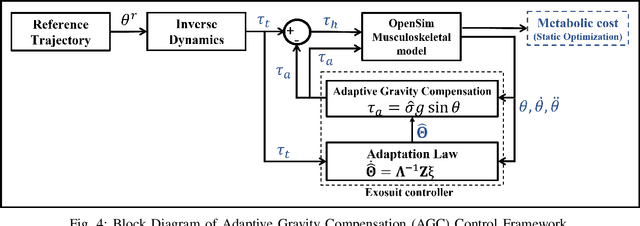
This paper proposes an adaptive gravity compensation (AGC) control strategy for a cable-driven upper-limb exosuit intended to assist the wearer with lifting tasks. Unlike most model-based control techniques used for this human-robot interaction task, the proposed control design does not assume knowledge of the anthropometric parameters of the wearer's arm and the payload. Instead, the uncertainties in human arm parameters, such as mass, length, and payload, are estimated online using an indirect adaptive control law that compensates for the gravity moment about the elbow joint. Additionally, the AGC controller is agnostic to the desired joint trajectory followed by the human arm. For the purpose of controller design, the human arm is modeled using a 1-DOF manipulator model. Further, a cable-driven actuator model is proposed that maps the assistive elbow torque to the actuator torque. The performance of the proposed method is verified through a co-simulation, wherein the control input realized in MATLAB is applied to the human bio-mechanical model in OpenSim under varying payload conditions. Significant reductions in human effort in terms of human muscle torque and metabolic cost are observed with the proposed control strategy. Further, simulation results show that the performance of the AGC controller converges to that of the gravity compensation (GC) controller, demonstrating the efficacy of AGC-based online parameter learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge