Nikolaos Barmpalios
MGDoc: Pre-training with Multi-granular Hierarchy for Document Image Understanding
Nov 27, 2022Abstract:Document images are a ubiquitous source of data where the text is organized in a complex hierarchical structure ranging from fine granularity (e.g., words), medium granularity (e.g., regions such as paragraphs or figures), to coarse granularity (e.g., the whole page). The spatial hierarchical relationships between content at different levels of granularity are crucial for document image understanding tasks. Existing methods learn features from either word-level or region-level but fail to consider both simultaneously. Word-level models are restricted by the fact that they originate from pure-text language models, which only encode the word-level context. In contrast, region-level models attempt to encode regions corresponding to paragraphs or text blocks into a single embedding, but they perform worse with additional word-level features. To deal with these issues, we propose MGDoc, a new multi-modal multi-granular pre-training framework that encodes page-level, region-level, and word-level information at the same time. MGDoc uses a unified text-visual encoder to obtain multi-modal features across different granularities, which makes it possible to project the multi-granular features into the same hyperspace. To model the region-word correlation, we design a cross-granular attention mechanism and specific pre-training tasks for our model to reinforce the model of learning the hierarchy between regions and words. Experiments demonstrate that our proposed model can learn better features that perform well across granularities and lead to improvements in downstream tasks.
User-Entity Differential Privacy in Learning Natural Language Models
Nov 09, 2022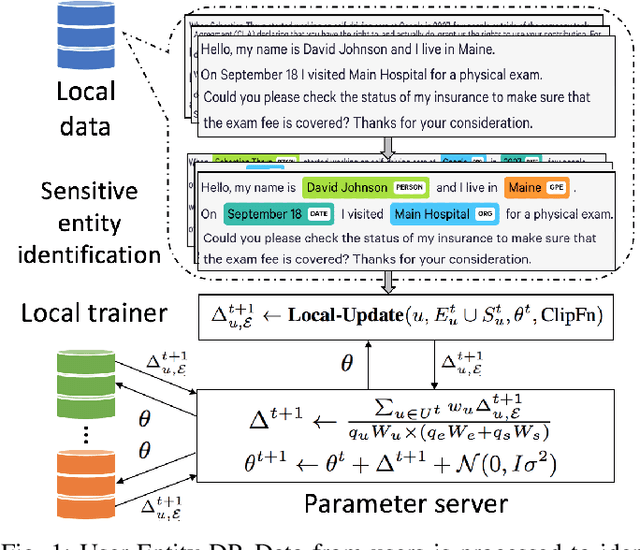
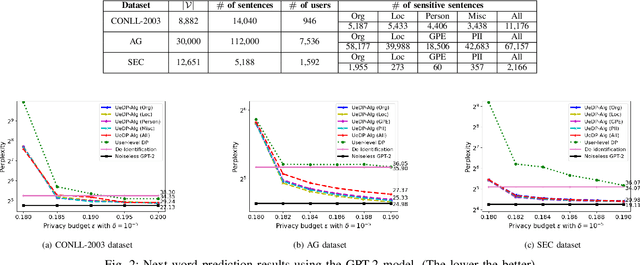
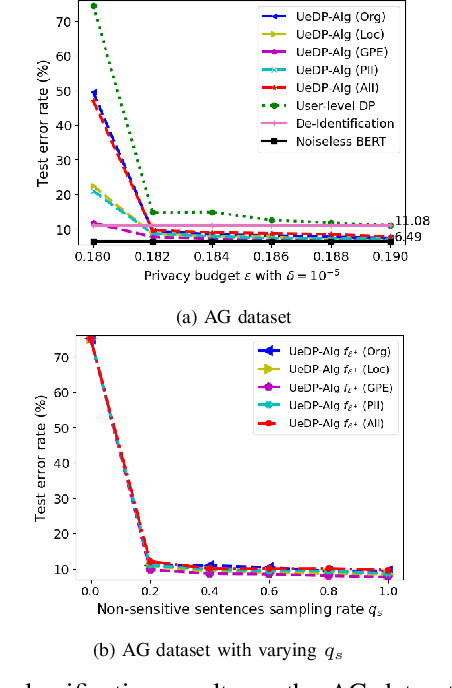
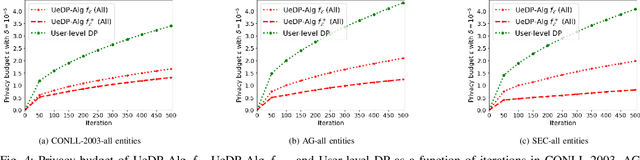
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel concept of user-entity differential privacy (UeDP) to provide formal privacy protection simultaneously to both sensitive entities in textual data and data owners in learning natural language models (NLMs). To preserve UeDP, we developed a novel algorithm, called UeDP-Alg, optimizing the trade-off between privacy loss and model utility with a tight sensitivity bound derived from seamlessly combining user and sensitive entity sampling processes. An extensive theoretical analysis and evaluation show that our UeDP-Alg outperforms baseline approaches in model utility under the same privacy budget consumption on several NLM tasks, using benchmark datasets.
Unified Pretraining Framework for Document Understanding
Apr 28, 2022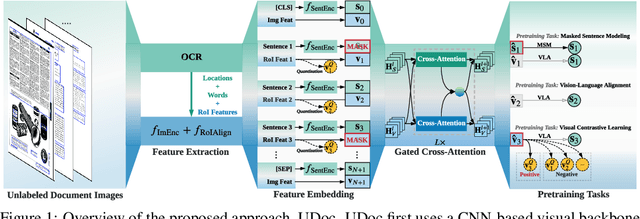
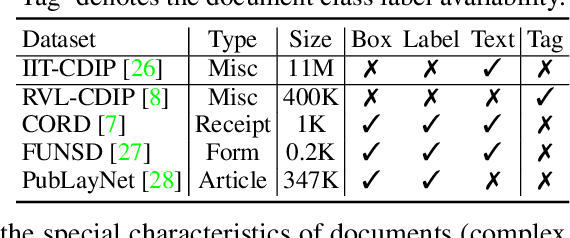
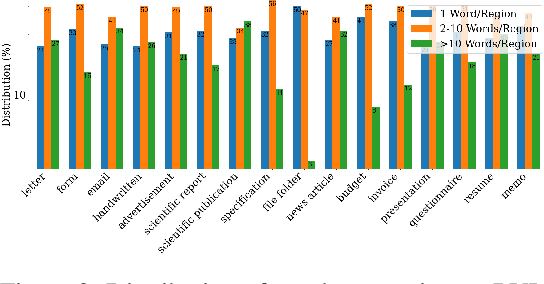
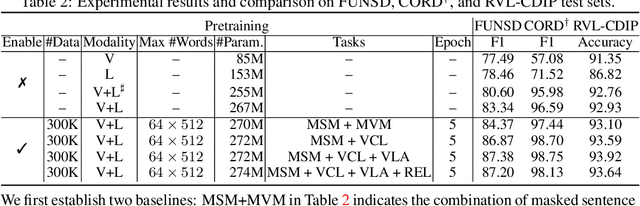
Abstract:Document intelligence automates the extraction of information from documents and supports many business applications. Recent self-supervised learning methods on large-scale unlabeled document datasets have opened up promising directions towards reducing annotation efforts by training models with self-supervised objectives. However, most of the existing document pretraining methods are still language-dominated. We present UDoc, a new unified pretraining framework for document understanding. UDoc is designed to support most document understanding tasks, extending the Transformer to take multimodal embeddings as input. Each input element is composed of words and visual features from a semantic region of the input document image. An important feature of UDoc is that it learns a generic representation by making use of three self-supervised losses, encouraging the representation to model sentences, learn similarities, and align modalities. Extensive empirical analysis demonstrates that the pretraining procedure learns better joint representations and leads to improvements in downstream tasks.
RPCL: A Framework for Improving Cross-Domain Detection with Auxiliary Tasks
Apr 18, 2021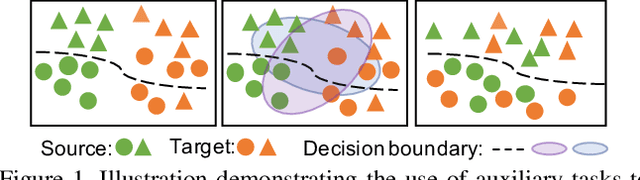
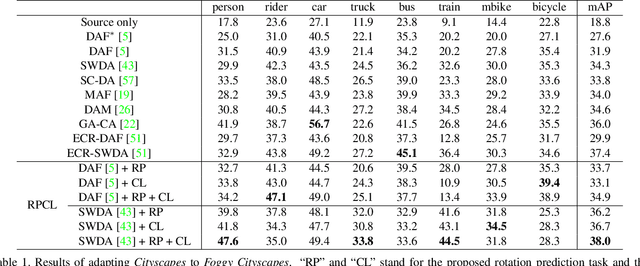
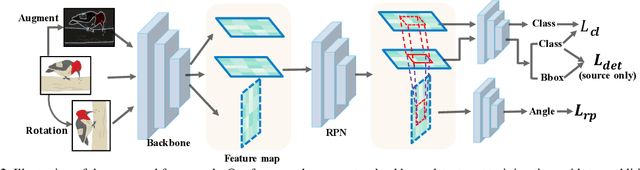
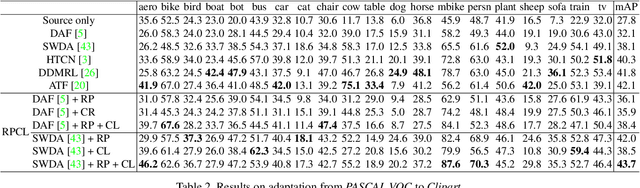
Abstract:Cross-Domain Detection (XDD) aims to train an object detector using labeled image from a source domain but have good performance in the target domain with only unlabeled images. Existing approaches achieve this either by aligning the feature maps or the region proposals from the two domains, or by transferring the style of source images to that of target image. Contrasted with prior work, this paper provides a complementary solution to align domains by learning the same auxiliary tasks in both domains simultaneously. These auxiliary tasks push image from both domains towards shared spaces, which bridges the domain gap. Specifically, this paper proposes Rotation Prediction and Consistency Learning (PRCL), a framework complementing existing XDD methods for domain alignment by leveraging the two auxiliary tasks. The first one encourages the model to extract region proposals from foreground regions by rotating an image and predicting the rotation angle from the extracted region proposals. The second task encourages the model to be robust to changes in the image space by optimizing the model to make consistent class predictions for region proposals regardless of image perturbations. Experiments show the detection performance can be consistently and significantly enhanced by applying the two proposed tasks to existing XDD methods.
Cross-Domain Document Object Detection: Benchmark Suite and Method
Mar 30, 2020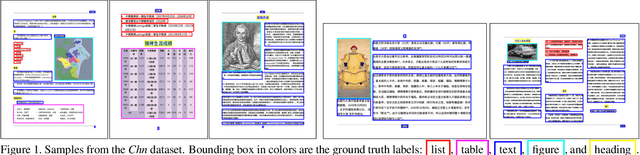
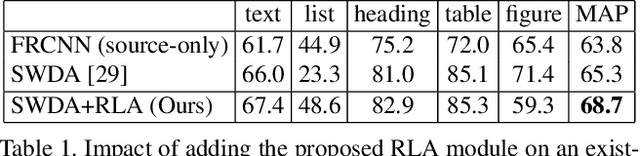
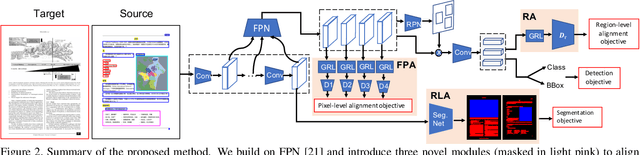
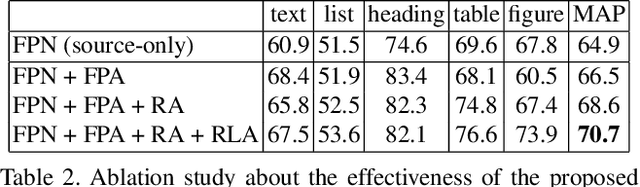
Abstract:Decomposing images of document pages into high-level semantic regions (e.g., figures, tables, paragraphs), document object detection (DOD) is fundamental for downstream tasks like intelligent document editing and understanding. DOD remains a challenging problem as document objects vary significantly in layout, size, aspect ratio, texture, etc. An additional challenge arises in practice because large labeled training datasets are only available for domains that differ from the target domain. We investigate cross-domain DOD, where the goal is to learn a detector for the target domain using labeled data from the source domain and only unlabeled data from the target domain. Documents from the two domains may vary significantly in layout, language, and genre. We establish a benchmark suite consisting of different types of PDF document datasets that can be utilized for cross-domain DOD model training and evaluation. For each dataset, we provide the page images, bounding box annotations, PDF files, and the rendering layers extracted from the PDF files. Moreover, we propose a novel cross-domain DOD model which builds upon the standard detection model and addresses domain shifts by incorporating three novel alignment modules: Feature Pyramid Alignment (FPA) module, Region Alignment (RA) module and Rendering Layer alignment (RLA) module. Extensive experiments on the benchmark suite substantiate the efficacy of the three proposed modules and the proposed method significantly outperforms the baseline methods. The project page is at \url{https://github.com/kailigo/cddod}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge