Niharika S. D'Souza
Automatic Prompt Optimization for Knowledge Graph Construction: Insights from an Empirical Study
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:A KG represents a network of entities and illustrates relationships between them. KGs are used for various applications, including semantic search and discovery, reasoning, decision-making, natural language processing, machine learning, and recommendation systems. Triple (subject-relation-object) extraction from text is the fundamental building block of KG construction and has been widely studied, for example, in early benchmarks such as ACE 2002 to more recent ones, such as WebNLG 2020, REBEL and SynthIE. While the use of LLMs is explored for KG construction, handcrafting reasonable task-specific prompts for LLMs is a labour-intensive exercise and can be brittle due to subtle changes in the LLM models employed. Recent work in NLP tasks (e.g. autonomy generation) uses automatic prompt optimization/engineering to address this challenge by generating optimal or near-optimal task-specific prompts given input-output examples. This empirical study explores the application of automatic prompt optimization for the triple extraction task using experimental benchmarking. We evaluate different settings by changing (a) the prompting strategy, (b) the LLM being used for prompt optimization and task execution, (c) the number of canonical relations in the schema (schema complexity), (d) the length and diversity of input text, (e) the metric used to drive the prompt optimization, and (f) the dataset being used for training and testing. We evaluate three different automatic prompt optimizers, namely, DSPy, APE, and TextGrad and use two different triple extraction datasets, SynthIE and REBEL. Through rigorous empirical evaluation, our main contribution highlights that automatic prompt optimization techniques can generate reasonable prompts similar to humans for triple extraction. In turn, these optimized prompts achieve improved results, particularly with increasing schema complexity and text size.
Modern Hopfield Networks meet Encoded Neural Representations -- Addressing Practical Considerations
Sep 24, 2024
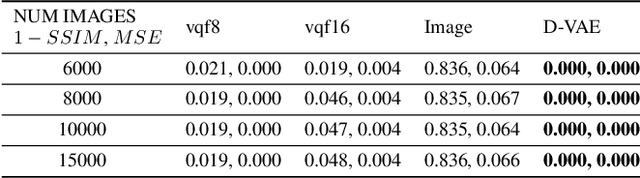
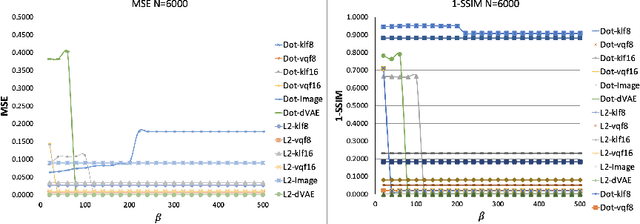
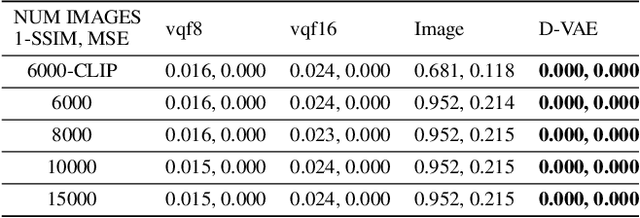
Abstract:Content-addressable memories such as Modern Hopfield Networks (MHN) have been studied as mathematical models of auto-association and storage/retrieval in the human declarative memory, yet their practical use for large-scale content storage faces challenges. Chief among them is the occurrence of meta-stable states, particularly when handling large amounts of high dimensional content. This paper introduces Hopfield Encoding Networks (HEN), a framework that integrates encoded neural representations into MHNs to improve pattern separability and reduce meta-stable states. We show that HEN can also be used for retrieval in the context of hetero association of images with natural language queries, thus removing the limitation of requiring access to partial content in the same domain. Experimental results demonstrate substantial reduction in meta-stable states and increased storage capacity while still enabling perfect recall of a significantly larger number of inputs advancing the practical utility of associative memory networks for real-world tasks.
Geo-UNet: A Geometrically Constrained Neural Framework for Clinical-Grade Lumen Segmentation in Intravascular Ultrasound
Aug 09, 2024



Abstract:Precisely estimating lumen boundaries in intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) is needed for sizing interventional stents to treat deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Unfortunately, current segmentation networks like the UNet lack the precision needed for clinical adoption in IVUS workflows. This arises due to the difficulty of automatically learning accurate lumen contour from limited training data while accounting for the radial geometry of IVUS imaging. We propose the Geo-UNet framework to address these issues via a design informed by the geometry of the lumen contour segmentation task. We first convert the input data and segmentation targets from Cartesian to polar coordinates. Starting from a convUNet feature extractor, we propose a two-task setup, one for conventional pixel-wise labeling and the other for single boundary lumen-contour localization. We directly combine the two predictions by passing the predicted lumen contour through a new activation (named CDFeLU) to filter out spurious pixel-wise predictions. Our unified loss function carefully balances area-based, distance-based, and contour-based penalties to provide near clinical-grade generalization in unseen patient data. We also introduce a lightweight, inference-time technique to enhance segmentation smoothness. The efficacy of our framework on a venous IVUS dataset is shown against state-of-the-art models.
Multimodal Sleep Apnea Detection with Missing or Noisy Modalities
Feb 24, 2024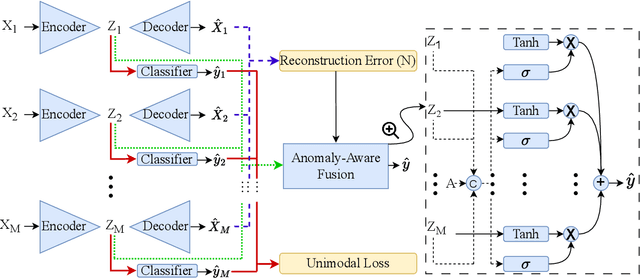
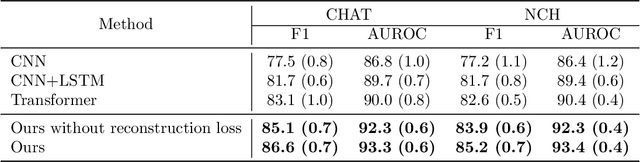
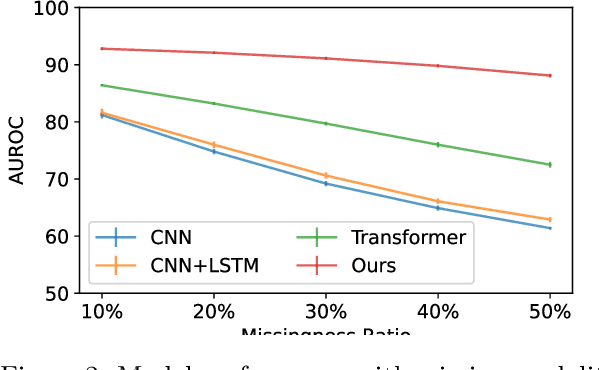
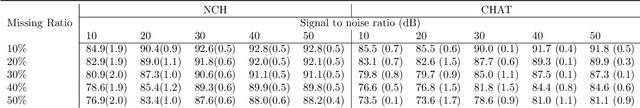
Abstract:Polysomnography (PSG) is a type of sleep study that records multimodal physiological signals and is widely used for purposes such as sleep staging and respiratory event detection. Conventional machine learning methods assume that each sleep study is associated with a fixed set of observed modalities and that all modalities are available for each sample. However, noisy and missing modalities are a common issue in real-world clinical settings. In this study, we propose a comprehensive pipeline aiming to compensate for the missing or noisy modalities when performing sleep apnea detection. Unlike other existing studies, our proposed model works with any combination of available modalities. Our experiments show that the proposed model outperforms other state-of-the-art approaches in sleep apnea detection using various subsets of available data and different levels of noise, and maintains its high performance (AUROC>0.9) even in the presence of high levels of noise or missingness. This is especially relevant in settings where the level of noise and missingness is high (such as pediatric or outside-of-clinic scenarios).
MaxCorrMGNN: A Multi-Graph Neural Network Framework for Generalized Multimodal Fusion of Medical Data for Outcome Prediction
Jul 13, 2023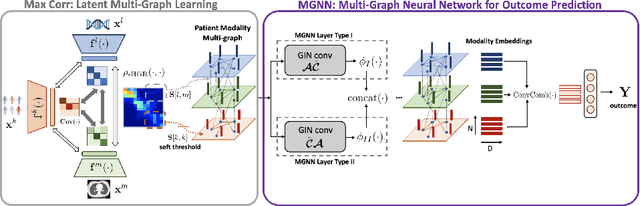
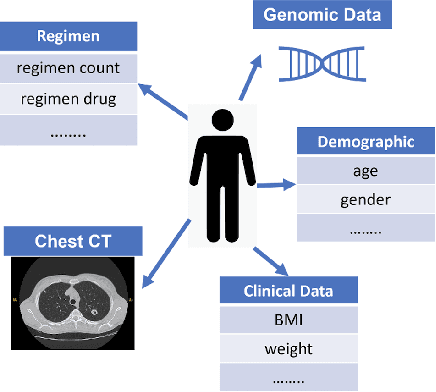
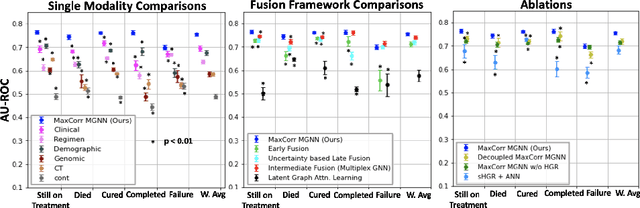
Abstract:With the emergence of multimodal electronic health records, the evidence for an outcome may be captured across multiple modalities ranging from clinical to imaging and genomic data. Predicting outcomes effectively requires fusion frameworks capable of modeling fine-grained and multi-faceted complex interactions between modality features within and across patients. We develop an innovative fusion approach called MaxCorr MGNN that models non-linear modality correlations within and across patients through Hirschfeld-Gebelein-Renyi maximal correlation (MaxCorr) embeddings, resulting in a multi-layered graph that preserves the identities of the modalities and patients. We then design, for the first time, a generalized multi-layered graph neural network (MGNN) for task-informed reasoning in multi-layered graphs, that learns the parameters defining patient-modality graph connectivity and message passing in an end-to-end fashion. We evaluate our model an outcome prediction task on a Tuberculosis (TB) dataset consistently outperforming several state-of-the-art neural, graph-based and traditional fusion techniques.
mSPD-NN: A Geometrically Aware Neural Framework for Biomarker Discovery from Functional Connectomics Manifolds
Mar 27, 2023



Abstract:Connectomics has emerged as a powerful tool in neuroimaging and has spurred recent advancements in statistical and machine learning methods for connectivity data. Despite connectomes inhabiting a matrix manifold, most analytical frameworks ignore the underlying data geometry. This is largely because simple operations, such as mean estimation, do not have easily computable closed-form solutions. We propose a geometrically aware neural framework for connectomes, i.e., the mSPD-NN, designed to estimate the geodesic mean of a collections of symmetric positive definite (SPD) matrices. The mSPD-NN is comprised of bilinear fully connected layers with tied weights and utilizes a novel loss function to optimize the matrix-normal equation arising from Fr\'echet mean estimation. Via experiments on synthetic data, we demonstrate the efficacy of our mSPD-NN against common alternatives for SPD mean estimation, providing competitive performance in terms of scalability and robustness to noise. We illustrate the real-world flexibility of the mSPD-NN in multiple experiments on rs-fMRI data and demonstrate that it uncovers stable biomarkers associated with subtle network differences among patients with ADHD-ASD comorbidities and healthy controls.
Fusing Modalities by Multiplexed Graph Neural Networks for Outcome Prediction in Tuberculosis
Oct 25, 2022Abstract:In a complex disease such as tuberculosis, the evidence for the disease and its evolution may be present in multiple modalities such as clinical, genomic, or imaging data. Effective patient-tailored outcome prediction and therapeutic guidance will require fusing evidence from these modalities. Such multimodal fusion is difficult since the evidence for the disease may not be uniform across all modalities, not all modality features may be relevant, or not all modalities may be present for all patients. All these nuances make simple methods of early, late, or intermediate fusion of features inadequate for outcome prediction. In this paper, we present a novel fusion framework using multiplexed graphs and derive a new graph neural network for learning from such graphs. Specifically, the framework allows modalities to be represented through their targeted encodings, and models their relationship explicitly via multiplexed graphs derived from salient features in a combined latent space. We present results that show that our proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods of fusing modalities for multi-outcome prediction on a large Tuberculosis (TB) dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge