Modern Hopfield Networks meet Encoded Neural Representations -- Addressing Practical Considerations
Paper and Code
Sep 24, 2024
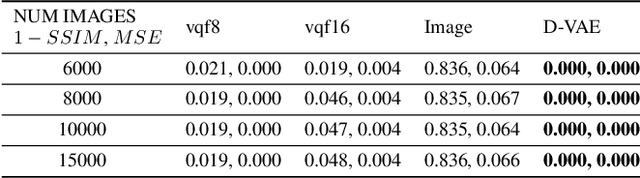
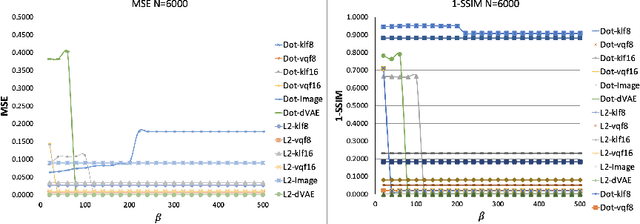
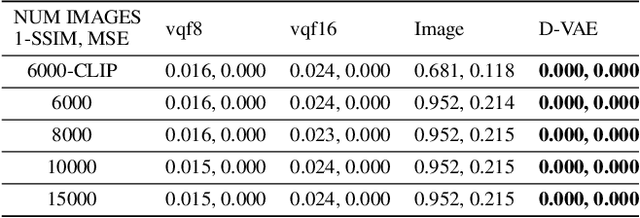
Content-addressable memories such as Modern Hopfield Networks (MHN) have been studied as mathematical models of auto-association and storage/retrieval in the human declarative memory, yet their practical use for large-scale content storage faces challenges. Chief among them is the occurrence of meta-stable states, particularly when handling large amounts of high dimensional content. This paper introduces Hopfield Encoding Networks (HEN), a framework that integrates encoded neural representations into MHNs to improve pattern separability and reduce meta-stable states. We show that HEN can also be used for retrieval in the context of hetero association of images with natural language queries, thus removing the limitation of requiring access to partial content in the same domain. Experimental results demonstrate substantial reduction in meta-stable states and increased storage capacity while still enabling perfect recall of a significantly larger number of inputs advancing the practical utility of associative memory networks for real-world tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge