Niansong Zhang
From Pragmas to Partners: A Symbiotic Evolution of Agentic High-Level Synthesis
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:The rise of large language models has sparked interest in AI-driven hardware design, raising the question: does high-level synthesis (HLS) still matter in the agentic era? We argue that HLS remains essential. While we expect mature agentic hardware systems to leverage both HLS and RTL, this paper focuses on HLS and its role in enabling agentic optimization. HLS offers faster iteration cycles, portability, and design permutability that make it a natural layer for agentic optimization. This position paper makes three contributions. First, we explain why HLS serves as a practical abstraction layer and a golden reference for agentic hardware design. Second, we identify key limitations of current HLS tools, namely inadequate performance feedback, rigid interfaces, and limited debuggability that agents are uniquely positioned to address. Third, we propose a taxonomy for the symbiotic evolution of agentic HLS, clarifying how responsibility shifts from human designers to AI agents as systems advance from copilots to autonomous design partners.
Allo: A Programming Model for Composable Accelerator Design
Apr 07, 2024



Abstract:Special-purpose hardware accelerators are increasingly pivotal for sustaining performance improvements in emerging applications, especially as the benefits of technology scaling continue to diminish. However, designers currently lack effective tools and methodologies to construct complex, high-performance accelerator architectures in a productive manner. Existing high-level synthesis (HLS) tools often require intrusive source-level changes to attain satisfactory quality of results. Despite the introduction of several new accelerator design languages (ADLs) aiming to enhance or replace HLS, their advantages are more evident in relatively simple applications with a single kernel. Existing ADLs prove less effective for realistic hierarchical designs with multiple kernels, even if the design hierarchy is flattened. In this paper, we introduce Allo, a composable programming model for efficient spatial accelerator design. Allo decouples hardware customizations, including compute, memory, communication, and data type from algorithm specification, and encapsulates them as a set of customization primitives. Allo preserves the hierarchical structure of an input program by combining customizations from different functions in a bottom-up, type-safe manner. This approach facilitates holistic optimizations that span across function boundaries. We conduct comprehensive experiments on commonly-used HLS benchmarks and several realistic deep learning models. Our evaluation shows that Allo can outperform state-of-the-art HLS tools and ADLs on all test cases in the PolyBench. For the GPT2 model, the inference latency of the Allo generated accelerator is 1.7x faster than the NVIDIA A100 GPU with 5.4x higher energy efficiency, demonstrating the capability of Allo to handle large-scale designs.
Understanding the Potential of FPGA-Based Spatial Acceleration for Large Language Model Inference
Dec 23, 2023



Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) boasting billions of parameters have generated a significant demand for efficient deployment in inference workloads. The majority of existing approaches rely on temporal architectures that reuse hardware units for different network layers and operators. However, these methods often encounter challenges in achieving low latency due to considerable memory access overhead. This paper investigates the feasibility and potential of model-specific spatial acceleration for LLM inference on FPGAs. Our approach involves the specialization of distinct hardware units for specific operators or layers, facilitating direct communication between them through a dataflow architecture while minimizing off-chip memory accesses. We introduce a comprehensive analytical model for estimating the performance of a spatial LLM accelerator, taking into account the on-chip compute and memory resources available on an FPGA. Through our analysis, we can determine the scenarios in which FPGA-based spatial acceleration can outperform its GPU-based counterpart. To enable more productive implementations of an LLM model on FPGAs, we further provide a library of high-level synthesis (HLS) kernels that are composable and reusable. This library will be made available as open-source. To validate the effectiveness of both our analytical model and HLS library, we have implemented BERT and GPT2 on an AMD Alveo U280 FPGA device. Experimental results demonstrate our approach can achieve up to 16.1x speedup when compared to previous FPGA-based accelerators for the BERT model. For GPT generative inference, we attain a 2.2x speedup compared to DFX, an FPGA overlay, in the prefill stage, while achieving a 1.9x speedup and a 5.7x improvement in energy efficiency compared to the NVIDIA A100 GPU in the decode stage.
CodedVTR: Codebook-based Sparse Voxel Transformer with Geometric Guidance
Mar 27, 2022



Abstract:Transformers have gained much attention by outperforming convolutional neural networks in many 2D vision tasks. However, they are known to have generalization problems and rely on massive-scale pre-training and sophisticated training techniques. When applying to 3D tasks, the irregular data structure and limited data scale add to the difficulty of transformer's application. We propose CodedVTR (Codebook-based Voxel TRansformer), which improves data efficiency and generalization ability for 3D sparse voxel transformers. On the one hand, we propose the codebook-based attention that projects an attention space into its subspace represented by the combination of "prototypes" in a learnable codebook. It regularizes attention learning and improves generalization. On the other hand, we propose geometry-aware self-attention that utilizes geometric information (geometric pattern, density) to guide attention learning. CodedVTR could be embedded into existing sparse convolution-based methods, and bring consistent performance improvements for indoor and outdoor 3D semantic segmentation tasks
aw_nas: A Modularized and Extensible NAS framework
Nov 25, 2020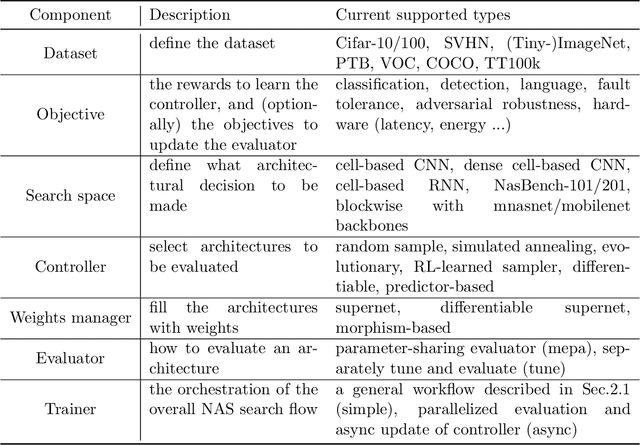
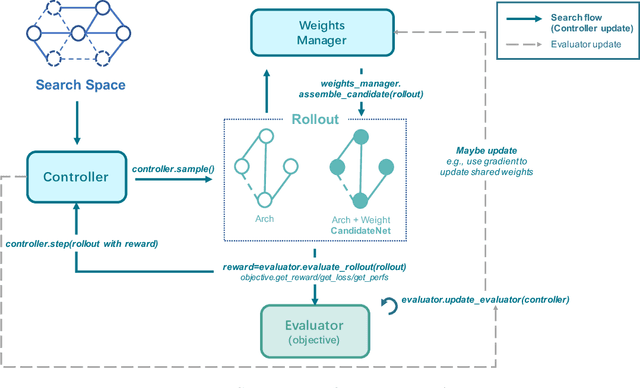
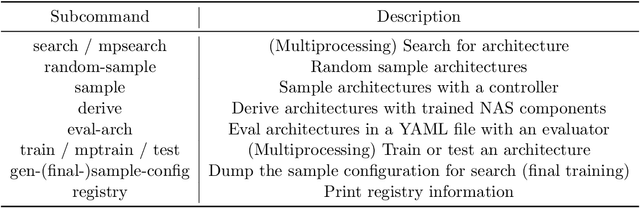
Abstract:Neural Architecture Search (NAS) has received extensive attention due to its capability to discover neural network architectures in an automated manner. aw_nas is an open-source Python framework implementing various NAS algorithms in a modularized manner. Currently, aw_nas can be used to reproduce the results of mainstream NAS algorithms of various types. Also, due to the modularized design, one can simply experiment with different NAS algorithms for various applications with awnas (e.g., classification, detection, text modeling, fault tolerance, adversarial robustness, hardware efficiency, and etc.). Codes and documentation are available at https://github.com/walkerning/aw_nas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge