Naye Ji
DiM-Gestor: Co-Speech Gesture Generation with Adaptive Layer Normalization Mamba-2
Nov 23, 2024
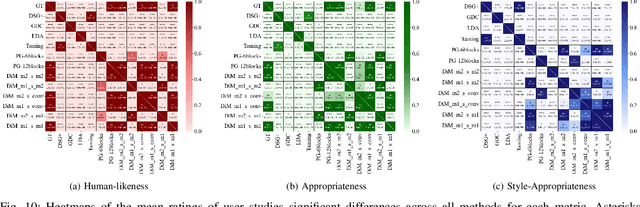
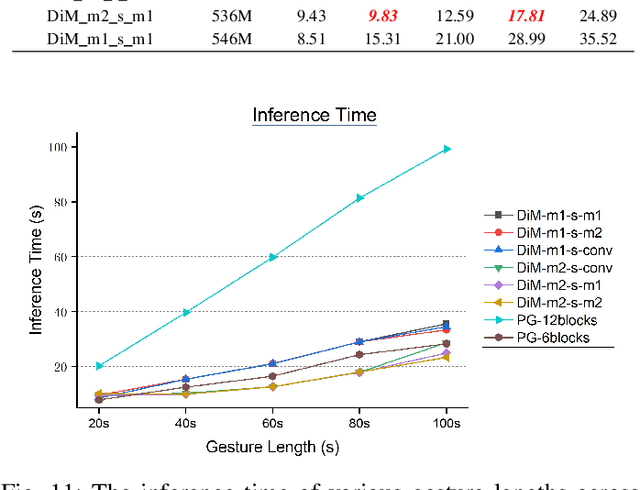
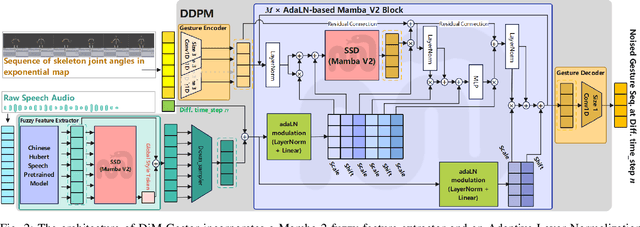
Abstract:Speech-driven gesture generation using transformer-based generative models represents a rapidly advancing area within virtual human creation. However, existing models face significant challenges due to their quadratic time and space complexities, limiting scalability and efficiency. To address these limitations, we introduce DiM-Gestor, an innovative end-to-end generative model leveraging the Mamba-2 architecture. DiM-Gestor features a dual-component framework: (1) a fuzzy feature extractor and (2) a speech-to-gesture mapping module, both built on the Mamba-2. The fuzzy feature extractor, integrated with a Chinese Pre-trained Model and Mamba-2, autonomously extracts implicit, continuous speech features. These features are synthesized into a unified latent representation and then processed by the speech-to-gesture mapping module. This module employs an Adaptive Layer Normalization (AdaLN)-enhanced Mamba-2 mechanism to uniformly apply transformations across all sequence tokens. This enables precise modeling of the nuanced interplay between speech features and gesture dynamics. We utilize a diffusion model to train and infer diverse gesture outputs. Extensive subjective and objective evaluations conducted on the newly released Chinese Co-Speech Gestures dataset corroborate the efficacy of our proposed model. Compared with Transformer-based architecture, the assessments reveal that our approach delivers competitive results and significantly reduces memory usage, approximately 2.4 times, and enhances inference speeds by 2 to 4 times. Additionally, we released the CCG dataset, a Chinese Co-Speech Gestures dataset, comprising 15.97 hours (six styles across five scenarios) of 3D full-body skeleton gesture motion performed by professional Chinese TV broadcasters.
DiM-Gesture: Co-Speech Gesture Generation with Adaptive Layer Normalization Mamba-2 framework
Aug 01, 2024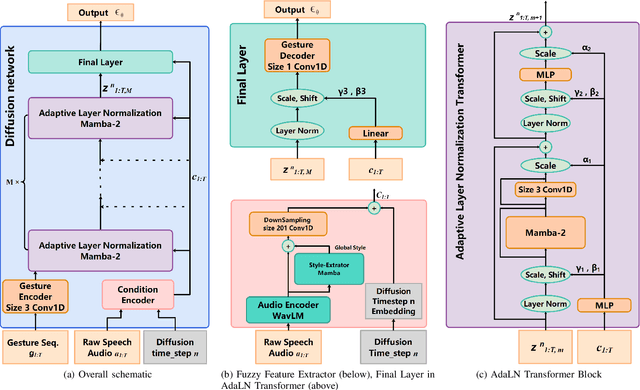
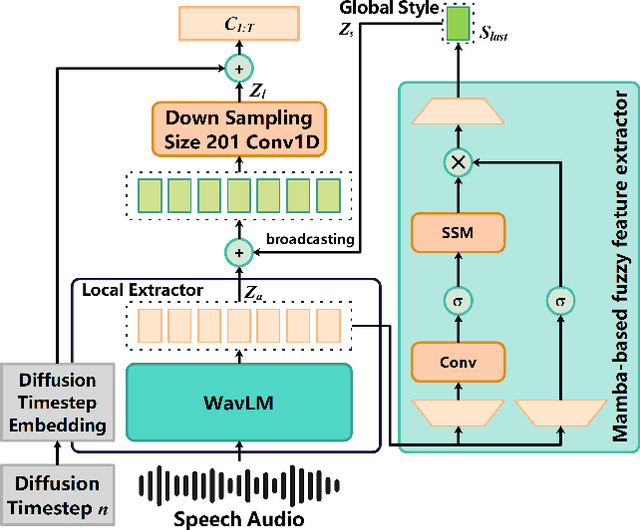
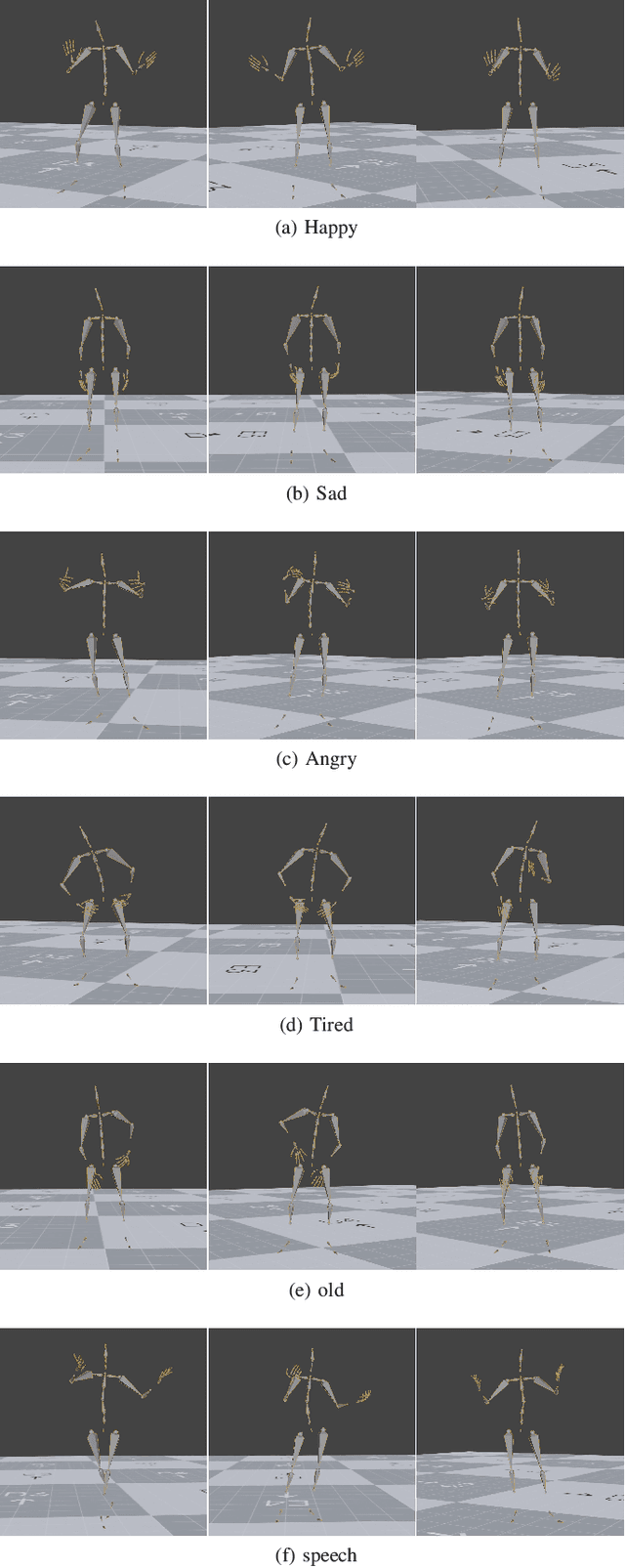
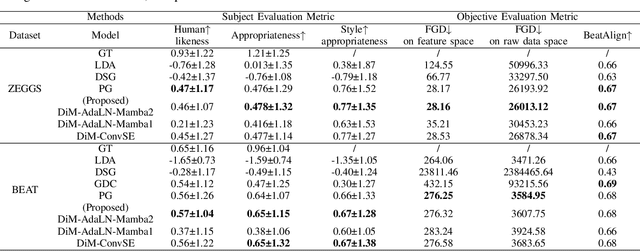
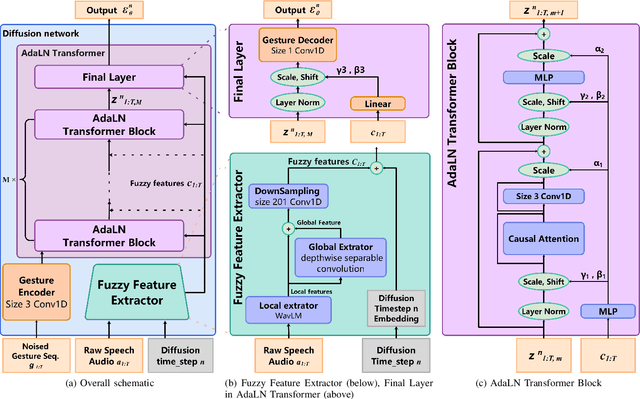
Abstract:Speech-driven gesture generation is an emerging domain within virtual human creation, where current methods predominantly utilize Transformer-based architectures that necessitate extensive memory and are characterized by slow inference speeds. In response to these limitations, we propose \textit{DiM-Gestures}, a novel end-to-end generative model crafted to create highly personalized 3D full-body gestures solely from raw speech audio, employing Mamba-based architectures. This model integrates a Mamba-based fuzzy feature extractor with a non-autoregressive Adaptive Layer Normalization (AdaLN) Mamba-2 diffusion architecture. The extractor, leveraging a Mamba framework and a WavLM pre-trained model, autonomously derives implicit, continuous fuzzy features, which are then unified into a singular latent feature. This feature is processed by the AdaLN Mamba-2, which implements a uniform conditional mechanism across all tokens to robustly model the interplay between the fuzzy features and the resultant gesture sequence. This innovative approach guarantees high fidelity in gesture-speech synchronization while maintaining the naturalness of the gestures. Employing a diffusion model for training and inference, our framework has undergone extensive subjective and objective evaluations on the ZEGGS and BEAT datasets. These assessments substantiate our model's enhanced performance relative to contemporary state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating competitive outcomes with the DiTs architecture (Persona-Gestors) while optimizing memory usage and accelerating inference speed.
Speech-driven Personalized Gesture Synthetics: Harnessing Automatic Fuzzy Feature Inference
Mar 16, 2024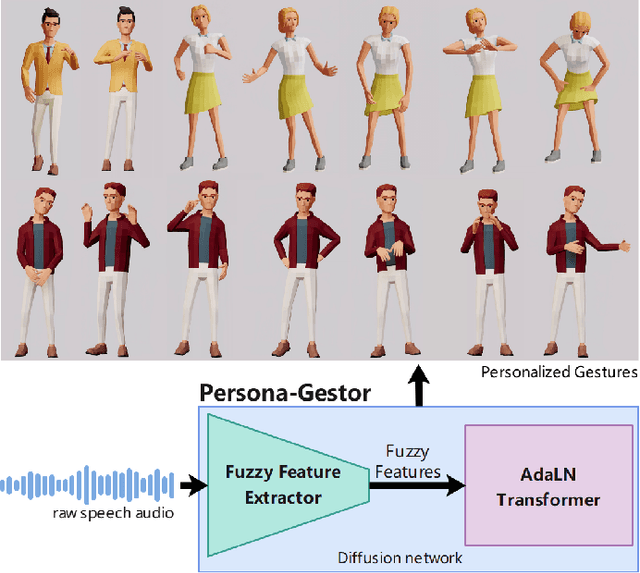
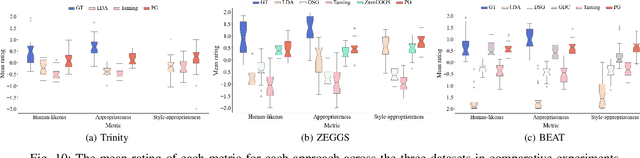
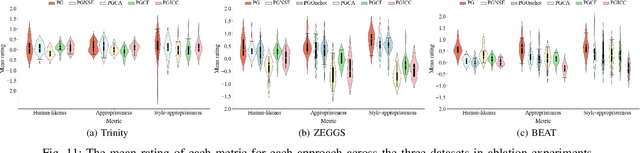
Abstract:Speech-driven gesture generation is an emerging field within virtual human creation. However, a significant challenge lies in accurately determining and processing the multitude of input features (such as acoustic, semantic, emotional, personality, and even subtle unknown features). Traditional approaches, reliant on various explicit feature inputs and complex multimodal processing, constrain the expressiveness of resulting gestures and limit their applicability. To address these challenges, we present Persona-Gestor, a novel end-to-end generative model designed to generate highly personalized 3D full-body gestures solely relying on raw speech audio. The model combines a fuzzy feature extractor and a non-autoregressive Adaptive Layer Normalization (AdaLN) transformer diffusion architecture. The fuzzy feature extractor harnesses a fuzzy inference strategy that automatically infers implicit, continuous fuzzy features. These fuzzy features, represented as a unified latent feature, are fed into the AdaLN transformer. The AdaLN transformer introduces a conditional mechanism that applies a uniform function across all tokens, thereby effectively modeling the correlation between the fuzzy features and the gesture sequence. This module ensures a high level of gesture-speech synchronization while preserving naturalness. Finally, we employ the diffusion model to train and infer various gestures. Extensive subjective and objective evaluations on the Trinity, ZEGGS, and BEAT datasets confirm our model's superior performance to the current state-of-the-art approaches. Persona-Gestor improves the system's usability and generalization capabilities, setting a new benchmark in speech-driven gesture synthesis and broadening the horizon for virtual human technology. Supplementary videos and code can be accessed at https://zf223669.github.io/Diffmotion-v2-website/
Audio is all in one: speech-driven gesture synthetics using WavLM pre-trained model
Aug 14, 2023Abstract:The generation of co-speech gestures for digital humans is an emerging area in the field of virtual human creation. Prior research has made progress by using acoustic and semantic information as input and adopting classify method to identify the person's ID and emotion for driving co-speech gesture generation. However, this endeavour still faces significant challenges. These challenges go beyond the intricate interplay between co-speech gestures, speech acoustic, and semantics; they also encompass the complexities associated with personality, emotion, and other obscure but important factors. This paper introduces "diffmotion-v2," a speech-conditional diffusion-based and non-autoregressive transformer-based generative model with WavLM pre-trained model. It can produce individual and stylized full-body co-speech gestures only using raw speech audio, eliminating the need for complex multimodal processing and manually annotated. Firstly, considering that speech audio not only contains acoustic and semantic features but also conveys personality traits, emotions, and more subtle information related to accompanying gestures, we pioneer the adaptation of WavLM, a large-scale pre-trained model, to extract low-level and high-level audio information. Secondly, we introduce an adaptive layer norm architecture in the transformer-based layer to learn the relationship between speech information and accompanying gestures. Extensive subjective evaluation experiments are conducted on the Trinity, ZEGGS, and BEAT datasets to confirm the WavLM and the model's ability to synthesize natural co-speech gestures with various styles.
Few-shots Portrait Generation with Style Enhancement and Identity Preservation
Mar 01, 2023



Abstract:Nowadays, the wide application of virtual digital human promotes the comprehensive prosperity and development of digital culture supported by digital economy. The personalized portrait automatically generated by AI technology needs both the natural artistic style and human sentiment. In this paper, we propose a novel StyleIdentityGAN model, which can ensure the identity and artistry of the generated portrait at the same time. Specifically, the style-enhanced module focuses on artistic style features decoupling and transferring to improve the artistry of generated virtual face images. Meanwhile, the identity-enhanced module preserves the significant features extracted from the input photo. Furthermore, the proposed method requires a small number of reference style data. Experiments demonstrate the superiority of StyleIdentityGAN over state-of-art methods in artistry and identity effects, with comparisons done qualitatively, quantitatively and through a perceptual user study. Code has been released on Github3.
DiffMotion: Speech-Driven Gesture Synthesis Using Denoising Diffusion Model
Feb 02, 2023Abstract:Speech-driven gesture synthesis is a field of growing interest in virtual human creation. However, a critical challenge is the inherent intricate one-to-many mapping between speech and gestures. Previous studies have explored and achieved significant progress with generative models. Notwithstanding, most synthetic gestures are still vastly less natural. This paper presents DiffMotion, a novel speech-driven gesture synthesis architecture based on diffusion models. The model comprises an autoregressive temporal encoder and a denoising diffusion probability Module. The encoder extracts the temporal context of the speech input and historical gestures. The diffusion module learns a parameterized Markov chain to gradually convert a simple distribution into a complex distribution and generates the gestures according to the accompanied speech. Compared with baselines, objective and subjective evaluations confirm that our approach can produce natural and diverse gesticulation and demonstrate the benefits of diffusion-based models on speech-driven gesture synthesis.
Mixed Reality Depth Contour Occlusion Using Binocular Similarity Matching and Three-dimensional Contour Optimisation
Mar 04, 2022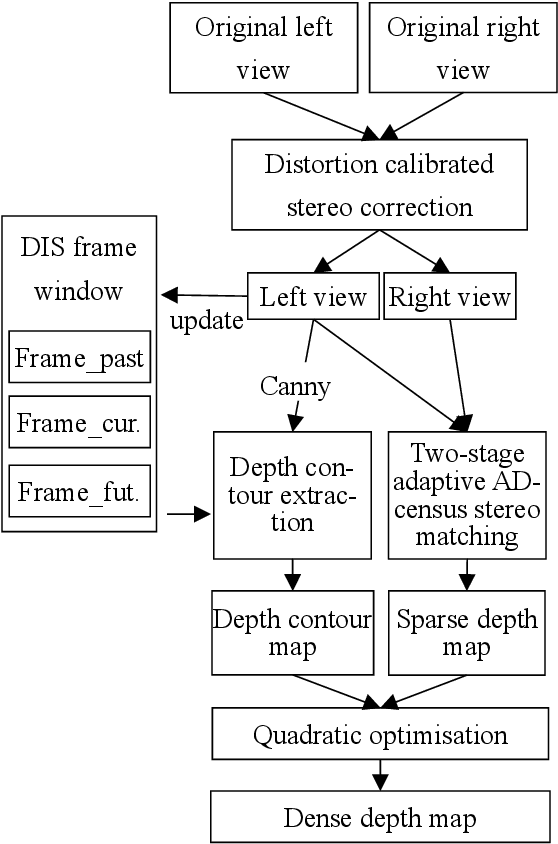
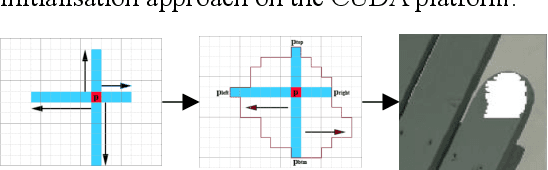
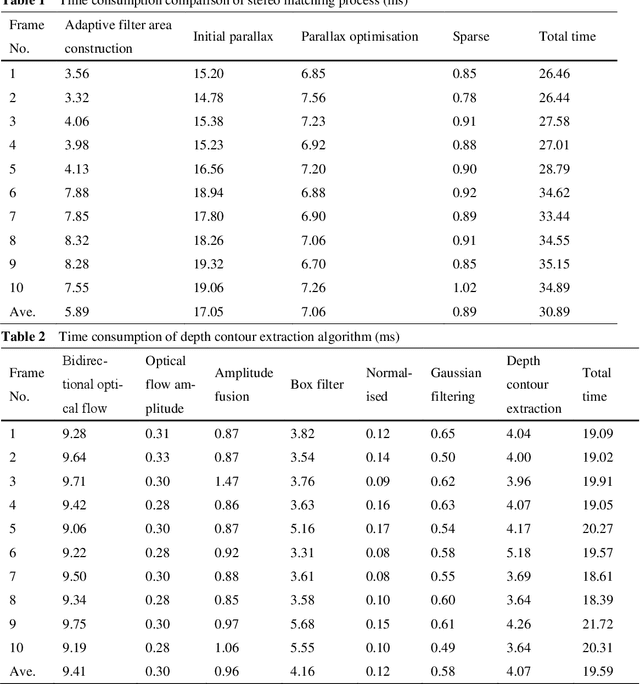
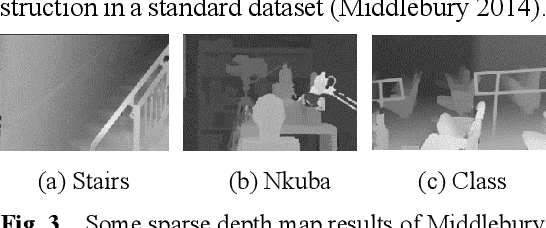
Abstract:Mixed reality applications often require virtual objects that are partly occluded by real objects. However, previous research and commercial products have limitations in terms of performance and efficiency. To address these challenges, we propose a novel depth contour occlusion (DCO) algorithm. The proposed method is based on the sensitivity of contour occlusion and a binocular stereoscopic vision device. In this method, a depth contour map is combined with a sparse depth map obtained from a two-stage adaptive filter area stereo matching algorithm and the depth contour information of the objects extracted by a digital image stabilisation optical flow method. We also propose a quadratic optimisation model with three constraints to generate an accurate dense map of the depth contour for high-quality real-virtual occlusion. The whole process is accelerated by GPU. To evaluate the effectiveness of the algorithm, we demonstrate a time con-sumption statistical analysis for each stage of the DCO algorithm execution. To verify the relia-bility of the real-virtual occlusion effect, we conduct an experimental analysis on single-sided, enclosed, and complex occlusions; subsequently, we compare it with the occlusion method without quadratic optimisation. With our GPU implementation for real-time DCO, the evaluation indicates that applying the presented DCO algorithm can enhance the real-time performance and the visual quality of real-virtual occlusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge