Naohiro Tawara
Mitigating Non-Target Speaker Bias in Guided Speaker Embedding
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Obtaining high-quality speaker embeddings in multi-speaker conditions is crucial for many applications. A recently proposed guided speaker embedding framework, which utilizes speech activities of target and non-target speakers as clues, drastically improved embeddings under severe overlap with small degradation in low-overlap cases. However, since extreme overlaps are rare in natural conversations, this degradation cannot be overlooked. This paper first reveals that the degradation is caused by the global-statistics-based modules, widely used in speaker embedding extractors, being overly sensitive to intervals containing only non-target speakers. As a countermeasure, we propose an extension of such modules that exploit the target speaker activity clues, to compute statistics from intervals where the target is active. The proposed method improves speaker verification performance in both low and high overlap ratios, and diarization performance on multiple datasets.
Dissecting the Segmentation Model of End-to-End Diarization with Vector Clustering
Jun 13, 2025



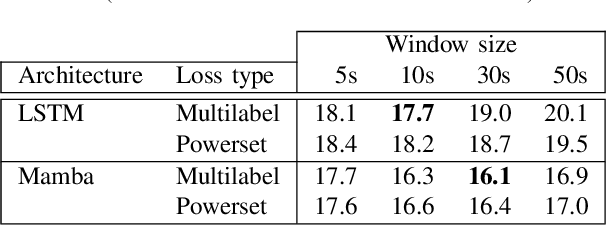
Abstract:End-to-End Neural Diarization with Vector Clustering is a powerful and practical approach to perform Speaker Diarization. Multiple enhancements have been proposed for the segmentation model of these pipelines, but their synergy had not been thoroughly evaluated. In this work, we provide an in-depth analysis on the impact of major architecture choices on the performance of the pipeline. We investigate different encoders (SincNet, pretrained and finetuned WavLM), different decoders (LSTM, Mamba, and Conformer), different losses (multilabel and multiclass powerset), and different chunk sizes. Through in-depth experiments covering nine datasets, we found that the finetuned WavLM-based encoder always results in the best systems by a wide margin. The LSTM decoder is outclassed by Mamba- and Conformer-based decoders, and while we found Mamba more robust to other architecture choices, it is slightly inferior to our best architecture, which uses a Conformer encoder. We found that multilabel and multiclass powerset losses do not have the same distribution of errors. We confirmed that the multiclass loss helps almost all models attain superior performance, except when finetuning WavLM, in which case, multilabel is the superior choice. We also evaluated the impact of the chunk size on all aforementioned architecture choices and found that newer architectures tend to better handle long chunk sizes, which can greatly improve pipeline performance. Our best system achieved state-of-the-art results on five widely used speaker diarization datasets.
Pretraining Multi-Speaker Identification for Neural Speaker Diarization
May 30, 2025Abstract:End-to-end speaker diarization enables accurate overlap-aware diarization by jointly estimating multiple speakers' speech activities in parallel. This approach is data-hungry, requiring a large amount of labeled conversational data, which cannot be fully obtained from real datasets alone. To address this issue, large-scale simulated data is often used for pretraining, but it requires enormous storage and I/O capacity, and simulating data that closely resembles real conversations remains challenging. In this paper, we propose pretraining a model to identify multiple speakers from an input fully overlapped mixture as an alternative to pretraining a diarization model. This method eliminates the need to prepare a large-scale simulated dataset while leveraging large-scale speaker recognition datasets for training. Through comprehensive experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed method enables a highly accurate yet lightweight local diarization model without simulated conversational data.
Guided Speaker Embedding
Oct 16, 2024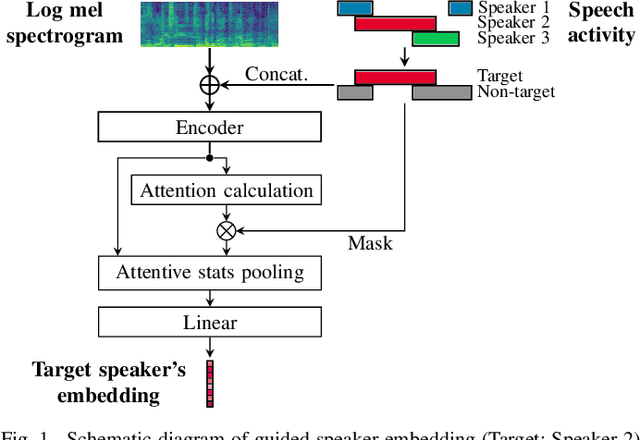

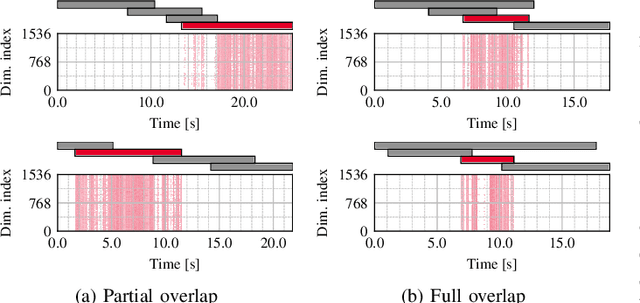

Abstract:This paper proposes a guided speaker embedding extraction system, which extracts speaker embeddings of the target speaker using speech activities of target and interference speakers as clues. Several methods for long-form overlapped multi-speaker audio processing are typically two-staged: i) segment-level processing and ii) inter-segment speaker matching. Speaker embeddings are often used for the latter purpose. Typical speaker embedding extraction approaches only use single-speaker intervals to avoid corrupting the embeddings with speech from interference speakers. However, this often makes speaker embeddings impossible to extract because sufficiently long non-overlapping intervals are not always available. In this paper, we propose using speaker activities as clues to extract the embedding of the speaker-of-interest directly from overlapping speech. Specifically, we concatenate the activity of target and non-target speakers to acoustic features before being fed to the model. We also condition the attention weights used for pooling so that the attention weights of the intervals in which the target speaker is inactive are zero. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated in speaker verification and speaker diarization.
Mamba-based Segmentation Model for Speaker Diarization
Oct 10, 2024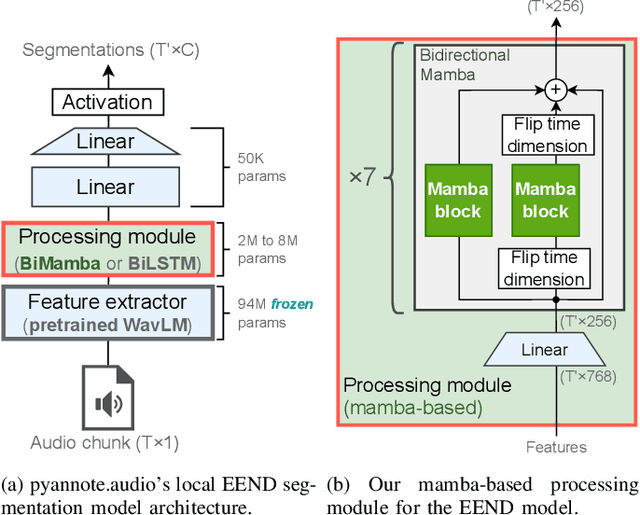
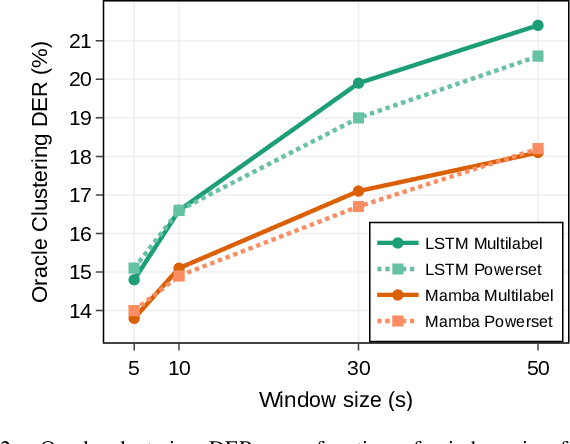
Abstract:Mamba is a newly proposed architecture which behaves like a recurrent neural network (RNN) with attention-like capabilities. These properties are promising for speaker diarization, as attention-based models have unsuitable memory requirements for long-form audio, and traditional RNN capabilities are too limited. In this paper, we propose to assess the potential of Mamba for diarization by comparing the state-of-the-art neural segmentation of the pyannote pipeline with our proposed Mamba-based variant. Mamba's stronger processing capabilities allow usage of longer local windows, which significantly improve diarization quality by making the speaker embedding extraction more reliable. We find Mamba to be a superior alternative to both traditional RNN and the tested attention-based model. Our proposed Mamba-based system achieves state-of-the-art performance on three widely used diarization datasets.
NTT Multi-Speaker ASR System for the DASR Task of CHiME-8 Challenge
Sep 09, 2024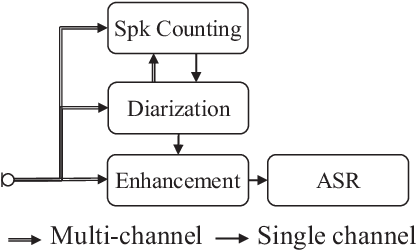
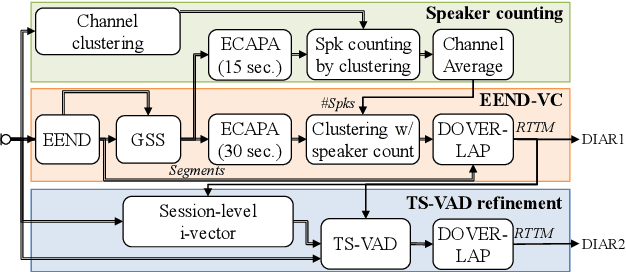

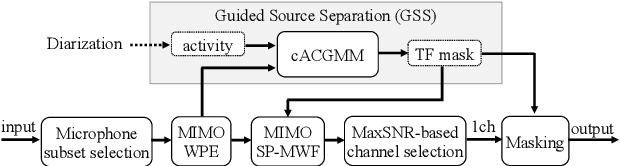
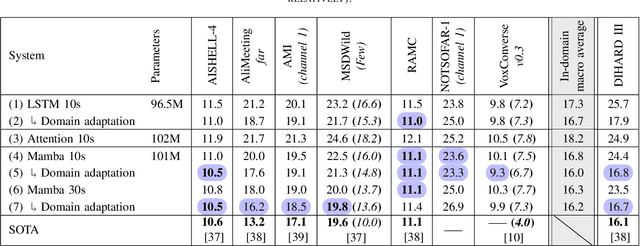
Abstract:We present a distant automatic speech recognition (DASR) system developed for the CHiME-8 DASR track. It consists of a diarization first pipeline. For diarization, we use end-to-end diarization with vector clustering (EEND-VC) followed by target speaker voice activity detection (TS-VAD) refinement. To deal with various numbers of speakers, we developed a new multi-channel speaker counting approach. We then apply guided source separation (GSS) with several improvements to the baseline system. Finally, we perform ASR using a combination of systems built from strong pre-trained models. Our proposed system achieves a macro tcpWER of 21.3 % on the dev set, which is a 57 % relative improvement over the baseline.
Recursive Attentive Pooling for Extracting Speaker Embeddings from Multi-Speaker Recordings
Aug 30, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes a method for extracting speaker embedding for each speaker from a variable-length recording containing multiple speakers. Speaker embeddings are crucial not only for speaker recognition but also for various multi-speaker speech applications such as speaker diarization and target-speaker speech processing. Despite the challenges of obtaining a single speaker's speech without pre-registration in multi-speaker scenarios, most studies on speaker embedding extraction focus on extracting embeddings only from single-speaker recordings. Some methods have been proposed for extracting speaker embeddings directly from multi-speaker recordings, but they typically require preparing a model for each possible number of speakers or involve complicated training procedures. The proposed method computes the embeddings of multiple speakers by focusing on different parts of the frame-wise embeddings extracted from the input multi-speaker audio. This is achieved by recursively computing attention weights for pooling the frame-wise embeddings. Additionally, we propose using the calculated attention weights to estimate the number of speakers in the recording, which allows the same model to be applied to various numbers of speakers. Experimental evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in speaker verification and diarization tasks.
Interaural time difference loss for binaural target sound extraction
Aug 01, 2024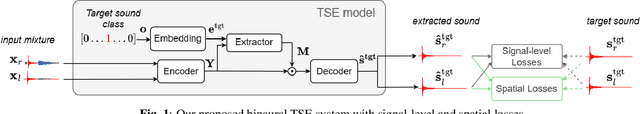
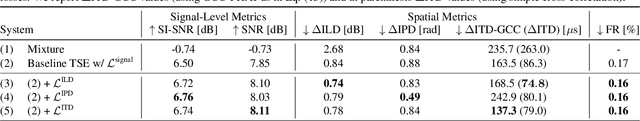
Abstract:Binaural target sound extraction (TSE) aims to extract a desired sound from a binaural mixture of arbitrary sounds while preserving the spatial cues of the desired sound. Indeed, for many applications, the target sound signal and its spatial cues carry important information about the sound source. Binaural TSE can be realized with a neural network trained to output only the desired sound given a binaural mixture and an embedding characterizing the desired sound class as inputs. Conventional TSE systems are trained using signal-level losses, which measure the difference between the extracted and reference signals for the left and right channels. In this paper, we propose adding explicit spatial losses to better preserve the spatial cues of the target sound. In particular, we explore losses aiming at preserving the interaural level (ILD), phase (IPD), and time differences (ITD). We show experimentally that adding such spatial losses, particularly our newly proposed ITD loss, helps preserve better spatial cues while maintaining the signal-level metrics.
Applying LLMs for Rescoring N-best ASR Hypotheses of Casual Conversations: Effects of Domain Adaptation and Context Carry-over
Jun 27, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been successfully applied for rescoring automatic speech recognition (ASR) hypotheses. However, their ability to rescore ASR hypotheses of casual conversations has not been sufficiently explored. In this study, we reveal it by performing N-best ASR hypotheses rescoring using Llama2 on the CHiME-7 distant ASR (DASR) task. Llama2 is one of the most representative LLMs, and the CHiME-7 DASR task provides datasets of casual conversations between multiple participants. We investigate the effects of domain adaptation of the LLM and context carry-over when performing N-best rescoring. Experimental results show that, even without domain adaptation, Llama2 outperforms a standard-size domain-adapted Transformer-LM, especially when using a long context. Domain adaptation shortens the context length needed with Llama2 to achieve its best performance, i.e., it reduces the computational cost of Llama2.
BLSTM-Based Confidence Estimation for End-to-End Speech Recognition
Dec 22, 2023Abstract:Confidence estimation, in which we estimate the reliability of each recognized token (e.g., word, sub-word, and character) in automatic speech recognition (ASR) hypotheses and detect incorrectly recognized tokens, is an important function for developing ASR applications. In this study, we perform confidence estimation for end-to-end (E2E) ASR hypotheses. Recent E2E ASR systems show high performance (e.g., around 5% token error rates) for various ASR tasks. In such situations, confidence estimation becomes difficult since we need to detect infrequent incorrect tokens from mostly correct token sequences. To tackle this imbalanced dataset problem, we employ a bidirectional long short-term memory (BLSTM)-based model as a strong binary-class (correct/incorrect) sequence labeler that is trained with a class balancing objective. We experimentally confirmed that, by utilizing several types of ASR decoding scores as its auxiliary features, the model steadily shows high confidence estimation performance under highly imbalanced settings. We also confirmed that the BLSTM-based model outperforms Transformer-based confidence estimation models, which greatly underestimate incorrect tokens.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge