Nancy Amato
Latent Adversarial Regularization for Offline Preference Optimization
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Learning from human feedback typically relies on preference optimization that constrains policy updates through token-level regularization. However, preference optimization for language models is particularly challenging because token-space similarity does not imply semantic or behavioral similarity. To address this challenge, we leverage latent-space regularization for language model preference optimization. We introduce GANPO, which achieves latent-space regularization by penalizing divergence between the internal representations of a policy model and a reference model. Given that latent representations are not associated with explicit probability densities, we adopt an adversarial approach inspired by GANs to minimize latent-space divergence. We integrate GANPO as a regularizer into existing offline preference optimization objectives. Experiments across multiple model architectures and tasks show consistent improvements from latent-space regularization. Further, by comparing GANPO-induced inferential biases with those from token-level regularization, we find that GANPO provides more robust structural feedback under distributional shift and noise while maintaining comparable downstream performance with minor computational overhead.
Faster Motion Planning via Restarts
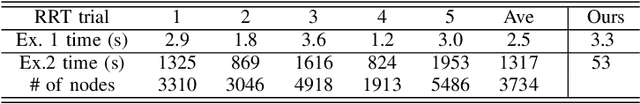
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Randomized methods such as PRM and RRT are widely used in motion planning. However, in some cases, their running-time suffers from inherent instability, leading to ``catastrophic'' performance even for relatively simple instances. We apply stochastic restart techniques, some of them new, for speeding up Las Vegas algorithms, that provide dramatic speedups in practice (a factor of $3$ [or larger] in many cases). Our experiments demonstrate that the new algorithms have faster runtimes, shorter paths, and greater gains from multi-threading (when compared with straightforward parallel implementation). We prove the optimality of the new variants. Our implementation is open source, available on github, and is easy to deploy and use.
Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Robot Learning and Planning
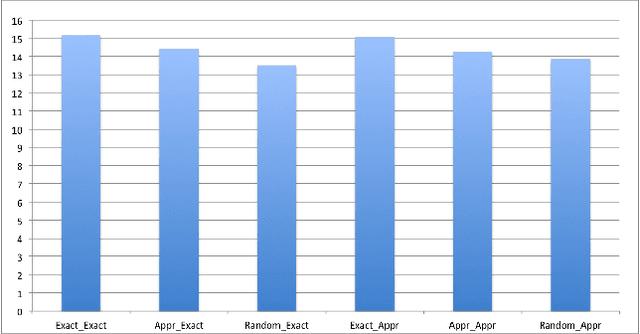
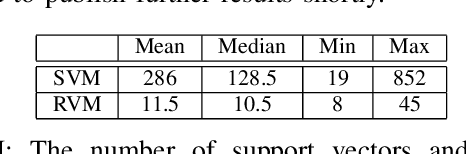
Oct 08, 2016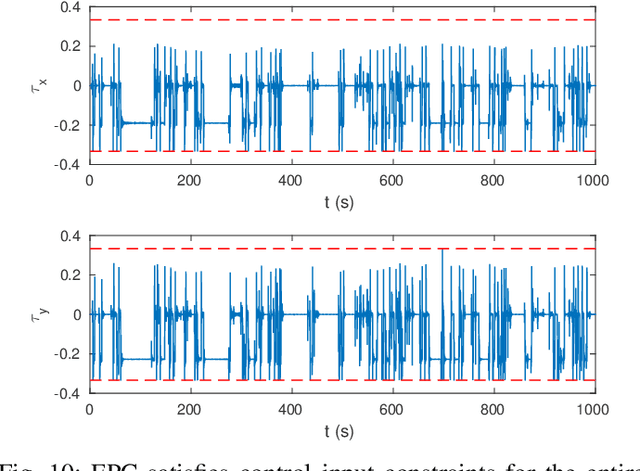
Abstract:Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Robot Learning and Planning (RLP 2016)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge