Mingwei Zhang
An Exhaustive DPLL Approach to Model Counting over Integer Linear Constraints with Simplification Techniques
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Linear constraints are one of the most fundamental constraints in fields such as computer science, operations research and optimization. Many applications reduce to the task of model counting over integer linear constraints (MCILC). In this paper, we design an exact approach to MCILC based on an exhaustive DPLL architecture. To improve the efficiency, we integrate several effective simplification techniques from mixed integer programming into the architecture. We compare our approach to state-of-the-art MCILC counters and propositional model counters on 2840 random and 4131 application benchmarks. Experimental results show that our approach significantly outperforms all exact methods in random benchmarks solving 1718 instances while the state-of-the-art approach only computes 1470 instances. In addition, our approach is the only approach to solve all 4131 application instances.
Variants of Tagged Sentential Decision Diagrams
Nov 16, 2023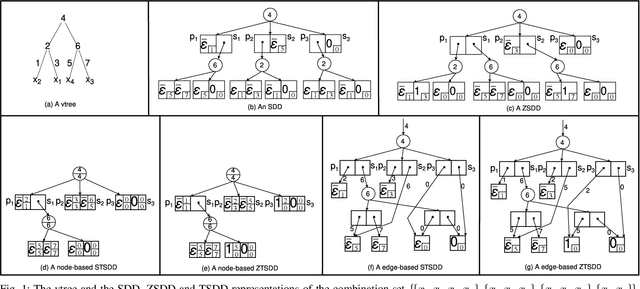

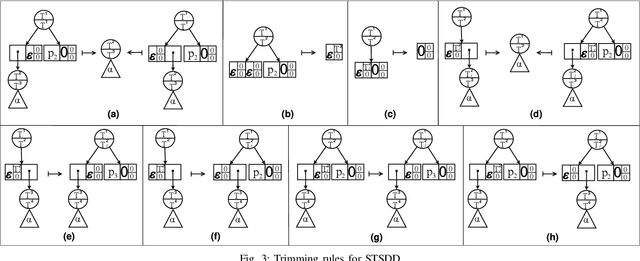
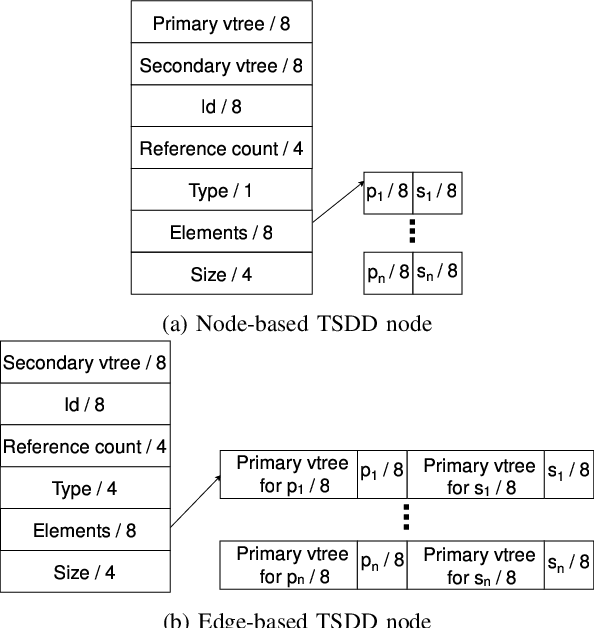
Abstract:A recently proposed canonical form of Boolean functions, namely tagged sentential decision diagrams (TSDDs), exploits both the standard and zero-suppressed trimming rules. The standard ones minimize the size of sentential decision diagrams (SDDs) while the zero-suppressed trimming rules have the same objective as the standard ones but for zero-suppressed sentential decision diagrams (ZSDDs). The original TSDDs, which we call zero-suppressed TSDDs (ZTSDDs), firstly fully utilize the zero-suppressed trimming rules, and then the standard ones. In this paper, we present a variant of TSDDs which we call standard TSDDs (STSDDs) by reversing the order of trimming rules. We then prove the canonicity of STSDDs and present the algorithms for binary operations on TSDDs. In addition, we offer two kinds of implementations of STSDDs and ZTSDDs and acquire three variations of the original TSDDs. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that the four versions of TSDDs have the size advantage over SDDs and ZSDDs.
CSSR: A Context-Aware Sequential Software Service Recommendation Model
Dec 20, 2021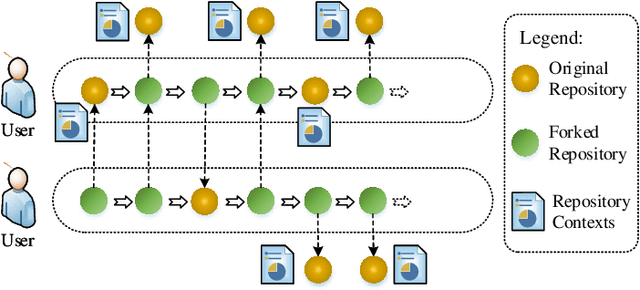
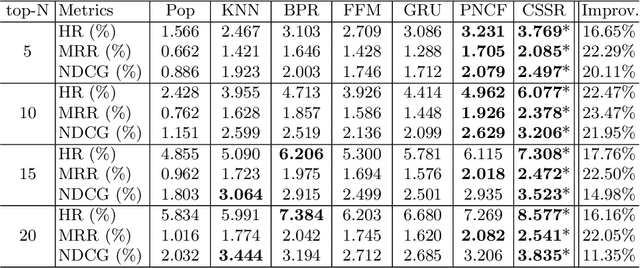
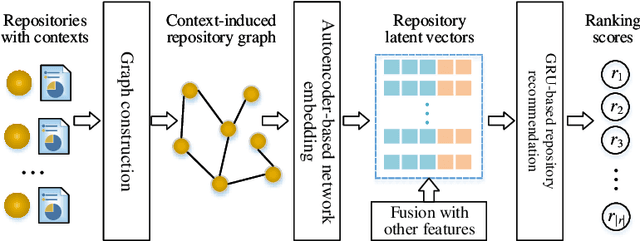
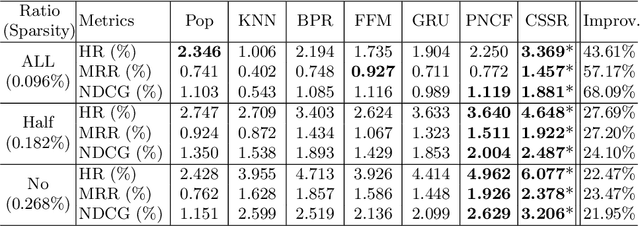
Abstract:We propose a novel software service recommendation model to help users find their suitable repositories in GitHub. Our model first designs a novel context-induced repository graph embedding method to leverage rich contextual information of repositories to alleviate the difficulties caused by the data sparsity issue. It then leverages sequence information of user-repository interactions for the first time in the software service recommendation field. Specifically, a deep-learning based sequential recommendation technique is adopted to capture the dynamics of user preferences. Comprehensive experiments have been conducted on a large dataset collected from GitHub against a list of existing methods. The results illustrate the superiority of our method in various aspects.
* 16 pages, 5 figures, 2 tables, The long version of the paper with the same title in ICSoC 2021
Generalized Operating Procedure for Deep Learning: an Unconstrained Optimal Design Perspective
Dec 31, 2020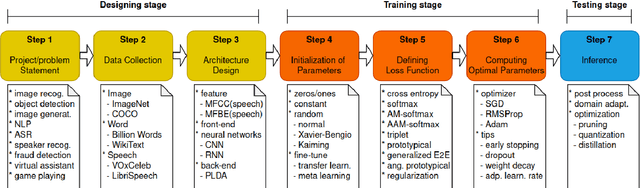
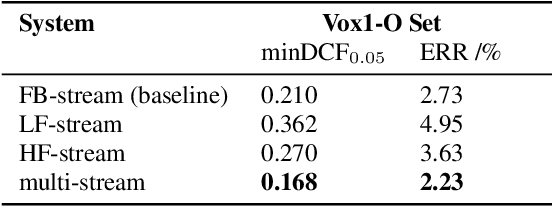
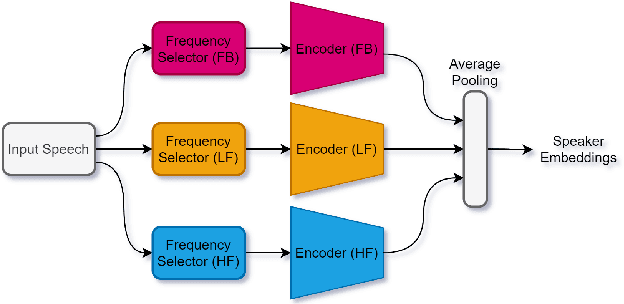
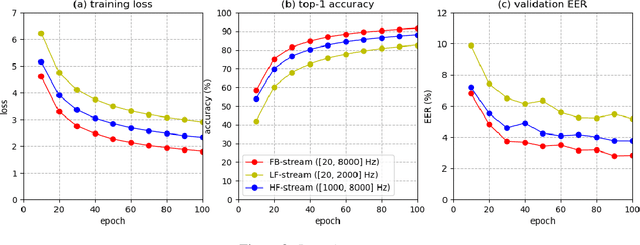
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) has brought about remarkable breakthrough in processing images, video and speech due to its efficacy in extracting highly abstract representation and learning very complex functions. However, there is seldom operating procedure reported on how to make it for real use cases. In this paper, we intend to address this problem by presenting a generalized operating procedure for DL from the perspective of unconstrained optimal design, which is motivated by a simple intension to remove the barrier of using DL, especially for those scientists or engineers who are new but eager to use it. Our proposed procedure contains seven steps, which are project/problem statement, data collection, architecture design, initialization of parameters, defining loss function, computing optimal parameters, and inference, respectively. Following this procedure, we build a multi-stream end-to-end speaker verification system, in which the input speech utterance is processed by multiple parallel streams within different frequency range, so that the acoustic modeling can be more robust resulting from the diversity of features. Trained with VoxCeleb dataset, our experimental results verify the effectiveness of our proposed operating procedure, and also show that our multi-stream framework outperforms single-stream baseline with 20 % relative reduction in minimum decision cost function (minDCF).
A Knowledge Graph based Approach for Mobile Application Recommendation
Sep 18, 2020



Abstract:With the rapid prevalence of mobile devices and the dramatic proliferation of mobile applications (apps), app recommendation becomes an emergent task that would benefit both app users and stockholders. How to effectively organize and make full use of rich side information of users and apps is a key challenge to address the sparsity issue for traditional approaches. To meet this challenge, we proposed a novel end-to-end Knowledge Graph Convolutional Embedding Propagation Model (KGEP) for app recommendation. Specifically, we first designed a knowledge graph construction method to model the user and app side information, then adopted KG embedding techniques to capture the factual triplet-focused semantics of the side information related to the first-order structure of the KG, and finally proposed a relation-weighted convolutional embedding propagation model to capture the recommendation-focused semantics related to high-order structure of the KG. Extensive experiments conducted on a real-world dataset validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach compared to the state-of-the-art recommendation approaches.
Semi-supervised classification for dynamic Android malware detection
Apr 19, 2017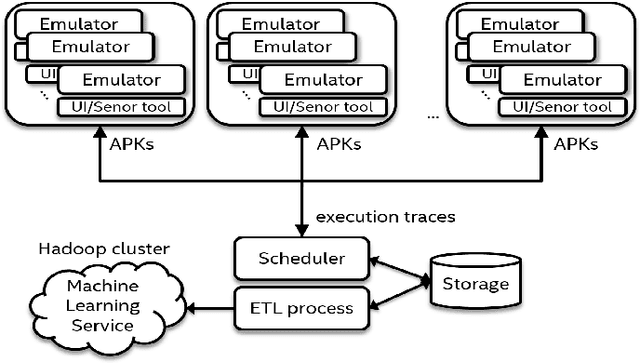
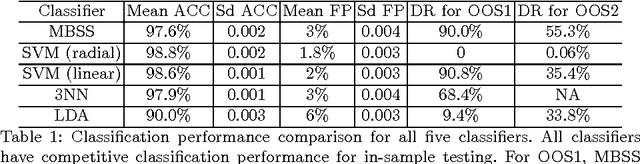
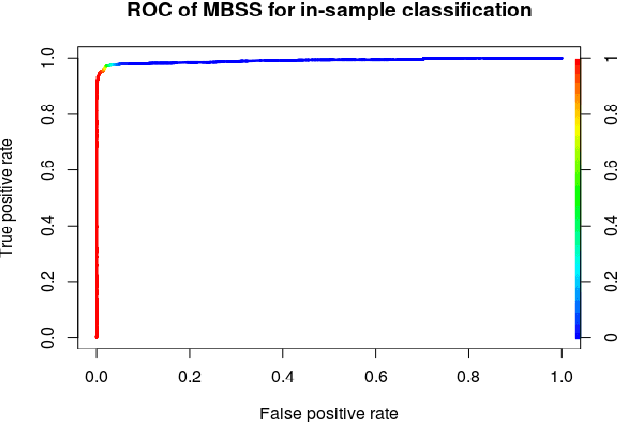
Abstract:A growing number of threats to Android phones creates challenges for malware detection. Manually labeling the samples into benign or different malicious families requires tremendous human efforts, while it is comparably easy and cheap to obtain a large amount of unlabeled APKs from various sources. Moreover, the fast-paced evolution of Android malware continuously generates derivative malware families. These families often contain new signatures, which can escape detection when using static analysis. These practical challenges can also cause traditional supervised machine learning algorithms to degrade in performance. In this paper, we propose a framework that uses model-based semi-supervised (MBSS) classification scheme on the dynamic Android API call logs. The semi-supervised approach efficiently uses the labeled and unlabeled APKs to estimate a finite mixture model of Gaussian distributions via conditional expectation-maximization and efficiently detects malwares during out-of-sample testing. We compare MBSS with the popular malware detection classifiers such as support vector machine (SVM), $k$-nearest neighbor (kNN) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA). Under the ideal classification setting, MBSS has competitive performance with 98\% accuracy and very low false positive rate for in-sample classification. For out-of-sample testing, the out-of-sample test data exhibit similar behavior of retrieving phone information and sending to the network, compared with in-sample training set. When this similarity is strong, MBSS and SVM with linear kernel maintain 90\% detection rate while $k$NN and LDA suffer great performance degradation. When this similarity is slightly weaker, all classifiers degrade in performance, but MBSS still performs significantly better than other classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge