Generalized Operating Procedure for Deep Learning: an Unconstrained Optimal Design Perspective
Paper and Code
Dec 31, 2020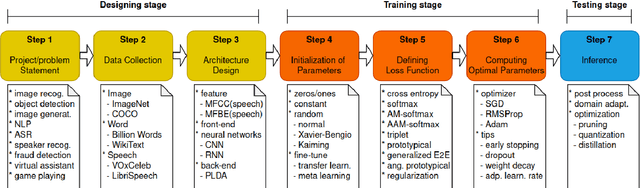
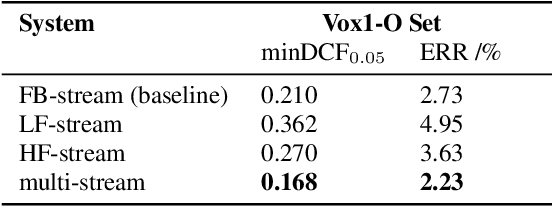
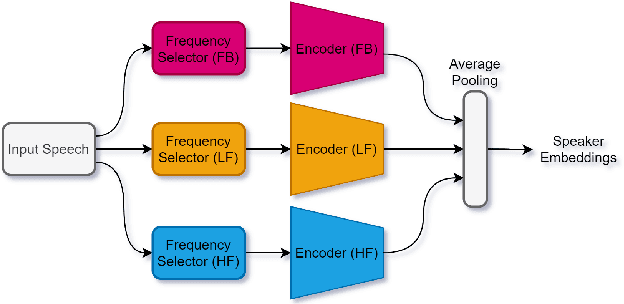
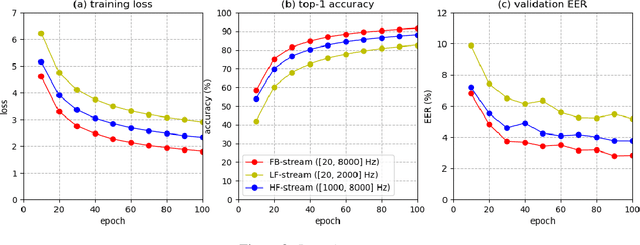
Deep learning (DL) has brought about remarkable breakthrough in processing images, video and speech due to its efficacy in extracting highly abstract representation and learning very complex functions. However, there is seldom operating procedure reported on how to make it for real use cases. In this paper, we intend to address this problem by presenting a generalized operating procedure for DL from the perspective of unconstrained optimal design, which is motivated by a simple intension to remove the barrier of using DL, especially for those scientists or engineers who are new but eager to use it. Our proposed procedure contains seven steps, which are project/problem statement, data collection, architecture design, initialization of parameters, defining loss function, computing optimal parameters, and inference, respectively. Following this procedure, we build a multi-stream end-to-end speaker verification system, in which the input speech utterance is processed by multiple parallel streams within different frequency range, so that the acoustic modeling can be more robust resulting from the diversity of features. Trained with VoxCeleb dataset, our experimental results verify the effectiveness of our proposed operating procedure, and also show that our multi-stream framework outperforms single-stream baseline with 20 % relative reduction in minimum decision cost function (minDCF).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge