Minghang Zheng
Hierarchical Event Memory for Accurate and Low-latency Online Video Temporal Grounding
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we tackle the task of online video temporal grounding (OnVTG), which requires the model to locate events related to a given text query within a video stream. Unlike regular video temporal grounding, OnVTG requires the model to make predictions without observing future frames. As online videos are streaming inputs and can go on indefinitely, it is impractical and inefficient to store all historical inputs. The existing OnVTG models employ memory to store recent historical video frame features and predict scores indicating whether the current frame corresponds to the start or end time of the target event. However, these methods lack effective event modeling and cannot retain long-term historical information, leading to low performance. To tackle these challenges, we propose a hierarchical event memory for OnVTG. We propose an event-based OnVTG framework that makes predictions based on event proposals that model event-level information with various durations. To preserve historically valuable event information, we introduce a hierarchical event memory that retains historical events, allowing the model to access both recent and long-term information. To enable the real-time prediction, we further propose a future prediction branch that predicts whether the target event will occur shortly and further regresses the start time of the event. We achieve state-of-the-art performance on the TACoS, ActivityNet Captions, and MAD datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/minghangz/OnVTG.
Training-free Video Temporal Grounding using Large-scale Pre-trained Models
Aug 29, 2024Abstract:Video temporal grounding aims to identify video segments within untrimmed videos that are most relevant to a given natural language query. Existing video temporal localization models rely on specific datasets for training and have high data collection costs, but they exhibit poor generalization capability under the across-dataset and out-of-distribution (OOD) settings. In this paper, we propose a Training-Free Video Temporal Grounding (TFVTG) approach that leverages the ability of pre-trained large models. A naive baseline is to enumerate proposals in the video and use the pre-trained visual language models (VLMs) to select the best proposal according to the vision-language alignment. However, most existing VLMs are trained on image-text pairs or trimmed video clip-text pairs, making it struggle to (1) grasp the relationship and distinguish the temporal boundaries of multiple events within the same video; (2) comprehend and be sensitive to the dynamic transition of events (the transition from one event to another) in the video. To address these issues, we propose leveraging large language models (LLMs) to analyze multiple sub-events contained in the query text and analyze the temporal order and relationships between these events. Secondly, we split a sub-event into dynamic transition and static status parts and propose the dynamic and static scoring functions using VLMs to better evaluate the relevance between the event and the description. Finally, for each sub-event description, we use VLMs to locate the top-k proposals and leverage the order and relationships between sub-events provided by LLMs to filter and integrate these proposals. Our method achieves the best performance on zero-shot video temporal grounding on Charades-STA and ActivityNet Captions datasets without any training and demonstrates better generalization capabilities in cross-dataset and OOD settings.
ResVG: Enhancing Relation and Semantic Understanding in Multiple Instances for Visual Grounding
Aug 29, 2024Abstract:Visual grounding aims to localize the object referred to in an image based on a natural language query. Although progress has been made recently, accurately localizing target objects within multiple-instance distractions (multiple objects of the same category as the target) remains a significant challenge. Existing methods demonstrate a significant performance drop when there are multiple distractions in an image, indicating an insufficient understanding of the fine-grained semantics and spatial relationships between objects. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, the Relation and Semantic-sensitive Visual Grounding (ResVG) model, to address this issue. Firstly, we enhance the model's understanding of fine-grained semantics by injecting semantic prior information derived from text queries into the model. This is achieved by leveraging text-to-image generation models to produce images representing the semantic attributes of target objects described in queries. Secondly, we tackle the lack of training samples with multiple distractions by introducing a relation-sensitive data augmentation method. This method generates additional training data by synthesizing images containing multiple objects of the same category and pseudo queries based on their spatial relationships. The proposed ReSVG model significantly improves the model's ability to comprehend both object semantics and spatial relations, leading to enhanced performance in visual grounding tasks, particularly in scenarios with multiple-instance distractions. We conduct extensive experiments to validate the effectiveness of our methods on five datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/minghangz/ResVG.
Diff-BGM: A Diffusion Model for Video Background Music Generation
May 20, 2024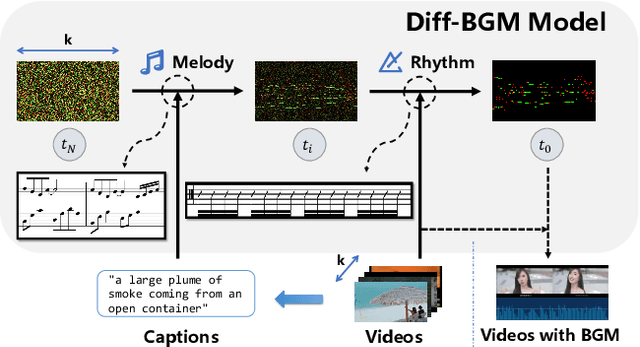

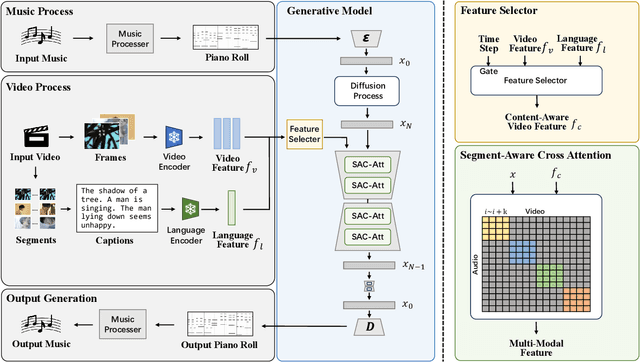

Abstract:When editing a video, a piece of attractive background music is indispensable. However, video background music generation tasks face several challenges, for example, the lack of suitable training datasets, and the difficulties in flexibly controlling the music generation process and sequentially aligning the video and music. In this work, we first propose a high-quality music-video dataset BGM909 with detailed annotation and shot detection to provide multi-modal information about the video and music. We then present evaluation metrics to assess music quality, including music diversity and alignment between music and video with retrieval precision metrics. Finally, we propose the Diff-BGM framework to automatically generate the background music for a given video, which uses different signals to control different aspects of the music during the generation process, i.e., uses dynamic video features to control music rhythm and semantic features to control the melody and atmosphere. We propose to align the video and music sequentially by introducing a segment-aware cross-attention layer. Experiments verify the effectiveness of our proposed method. The code and models are available at https://github.com/sizhelee/Diff-BGM.
Team PKU-WICT-MIPL PIC Makeup Temporal Video Grounding Challenge 2022 Technical Report
Jul 06, 2022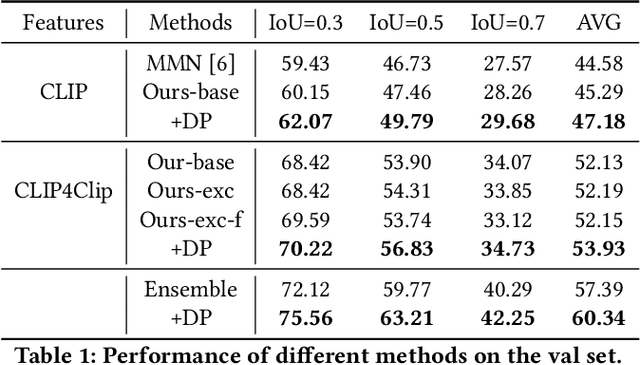
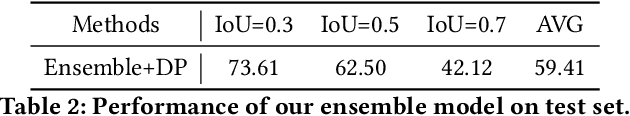
Abstract:In this technical report, we briefly introduce the solutions of our team `PKU-WICT-MIPL' for the PIC Makeup Temporal Video Grounding (MTVG) Challenge in ACM-MM 2022. Given an untrimmed makeup video and a step query, the MTVG aims to localize a temporal moment of the target makeup step in the video. To tackle this task, we propose a phrase relationship mining framework to exploit the temporal localization relationship relevant to the fine-grained phrase and the whole sentence. Besides, we propose to constrain the localization results of different step sentence queries to not overlap with each other through a dynamic programming algorithm. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Our final submission ranked 2nd on the leaderboard, with only a 0.55\% gap from the first.
Fast Convergence of DETR with Spatially Modulated Co-Attention
Aug 05, 2021



Abstract:The recently proposed Detection Transformer (DETR) model successfully applies Transformer to objects detection and achieves comparable performance with two-stage object detection frameworks, such as Faster-RCNN. However, DETR suffers from its slow convergence. Training DETR from scratch needs 500 epochs to achieve a high accuracy. To accelerate its convergence, we propose a simple yet effective scheme for improving the DETR framework, namely Spatially Modulated Co-Attention (SMCA) mechanism. The core idea of SMCA is to conduct location-aware co-attention in DETR by constraining co-attention responses to be high near initially estimated bounding box locations. Our proposed SMCA increases DETR's convergence speed by replacing the original co-attention mechanism in the decoder while keeping other operations in DETR unchanged. Furthermore, by integrating multi-head and scale-selection attention designs into SMCA, our fully-fledged SMCA can achieve better performance compared to DETR with a dilated convolution-based backbone (45.6 mAP at 108 epochs vs. 43.3 mAP at 500 epochs). We perform extensive ablation studies on COCO dataset to validate SMCA. Code is released at https://github.com/gaopengcuhk/SMCA-DETR .
End-to-End Object Detection with Adaptive Clustering Transformer
Nov 18, 2020



Abstract:End-to-end Object Detection with Transformer (DETR)proposes to perform object detection with Transformer and achieve comparable performance with two-stage object detection like Faster-RCNN. However, DETR needs huge computational resources for training and inference due to the high-resolution spatial input. In this paper, a novel variant of transformer named Adaptive Clustering Transformer(ACT) has been proposed to reduce the computation cost for high-resolution input. ACT cluster the query features adaptively using Locality Sensitive Hashing (LSH) and ap-proximate the query-key interaction using the prototype-key interaction. ACT can reduce the quadratic O(N2) complexity inside self-attention into O(NK) where K is the number of prototypes in each layer. ACT can be a drop-in module replacing the original self-attention module without any training. ACT achieves a good balance between accuracy and computation cost (FLOPs). The code is available as supplementary for the ease of experiment replication and verification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge