Michael I. Miller
Teresa
Prospective Learning: Back to the Future
Jan 19, 2022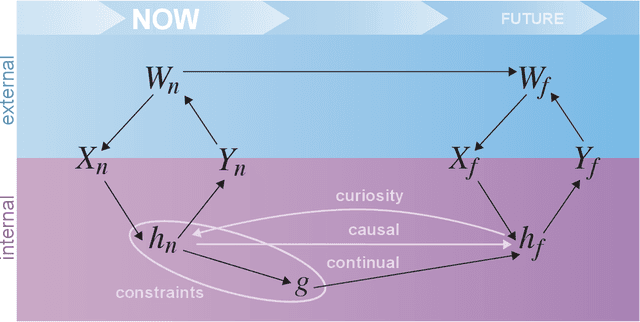
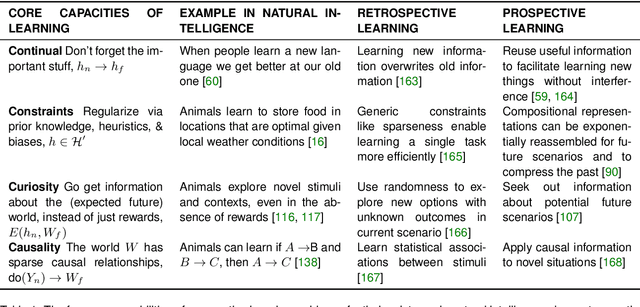
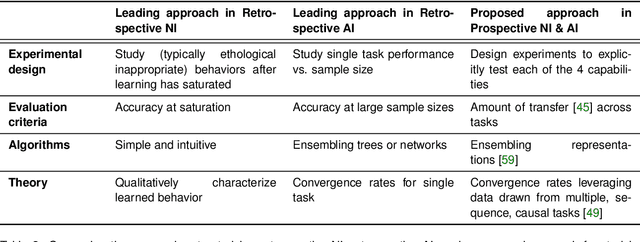
Abstract:Research on both natural intelligence (NI) and artificial intelligence (AI) generally assumes that the future resembles the past: intelligent agents or systems (what we call 'intelligence') observe and act on the world, then use this experience to act on future experiences of the same kind. We call this 'retrospective learning'. For example, an intelligence may see a set of pictures of objects, along with their names, and learn to name them. A retrospective learning intelligence would merely be able to name more pictures of the same objects. We argue that this is not what true intelligence is about. In many real world problems, both NIs and AIs will have to learn for an uncertain future. Both must update their internal models to be useful for future tasks, such as naming fundamentally new objects and using these objects effectively in a new context or to achieve previously unencountered goals. This ability to learn for the future we call 'prospective learning'. We articulate four relevant factors that jointly define prospective learning. Continual learning enables intelligences to remember those aspects of the past which it believes will be most useful in the future. Prospective constraints (including biases and priors) facilitate the intelligence finding general solutions that will be applicable to future problems. Curiosity motivates taking actions that inform future decision making, including in previously unmet situations. Causal estimation enables learning the structure of relations that guide choosing actions for specific outcomes, even when the specific action-outcome contingencies have never been observed before. We argue that a paradigm shift from retrospective to prospective learning will enable the communities that study intelligence to unite and overcome existing bottlenecks to more effectively explain, augment, and engineer intelligences.
Hidden Markov Modeling for Maximum Likelihood Neuron Reconstruction
Jun 04, 2021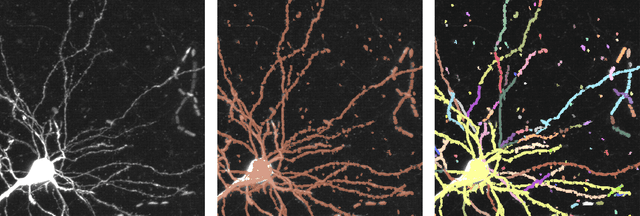


Abstract:Recent advances in brain clearing and imaging have made it possible to image entire mammalian brains at sub-micron resolution. These images offer the potential to assemble brain-wide atlases of projection neuron morphology, but manual neuron reconstruction remains a bottleneck. Here we present a method inspired by hidden Markov modeling and appearance modeling of fluorescent neuron images that can automatically trace neuronal processes. Our method leverages dynamic programming to scale to terabyte sized image data and can be applied to images with one or more neurons. We applied our algorithm to the output of image segmentation models where false negatives severed neuronal processes, and showed that it can follow axons in the presence of noise or nearby neurons. Our method has the potential to be integrated into a semi or fully automated reconstruction pipeline. Additionally, it creates a framework through which users can intervene with hard constraints to, for example, rule out certain reconstructions, or assign axons to particular cell bodies.
A Large Deformation Diffeomorphic Approach to Registration of CLARITY Images via Mutual Information
Aug 11, 2017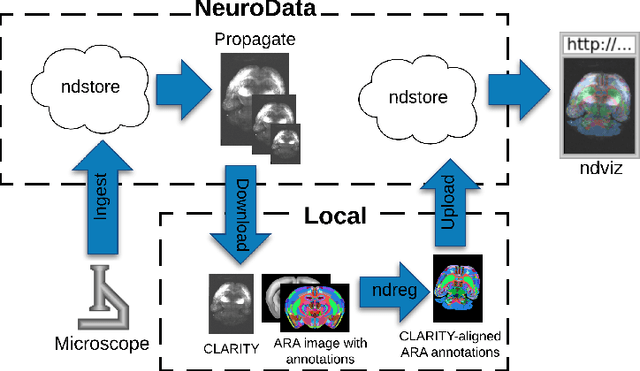
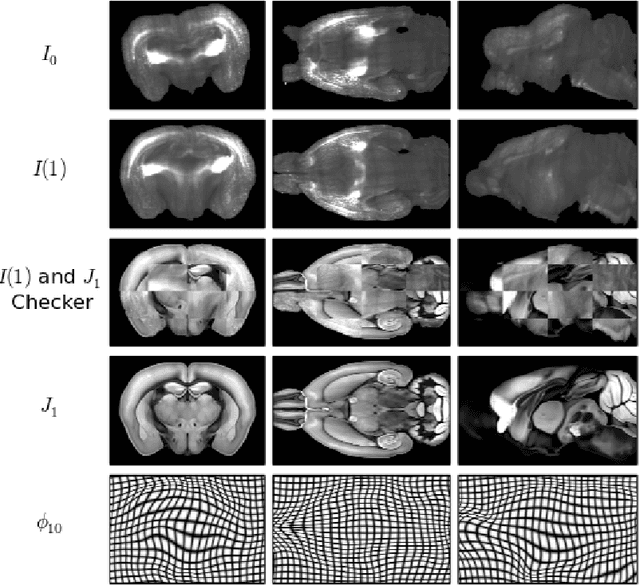
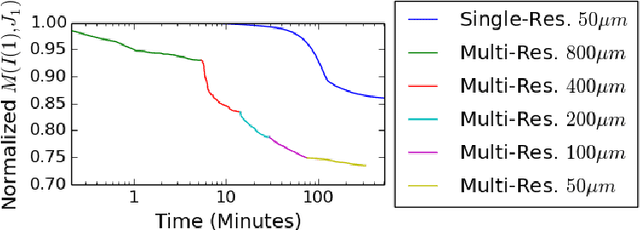
Abstract:CLARITY is a method for converting biological tissues into translucent and porous hydrogel-tissue hybrids. This facilitates interrogation with light sheet microscopy and penetration of molecular probes while avoiding physical slicing. In this work, we develop a pipeline for registering CLARIfied mouse brains to an annotated brain atlas. Due to the novelty of this microscopy technique it is impractical to use absolute intensity values to align these images to existing standard atlases. Thus we adopt a large deformation diffeomorphic approach for registering images via mutual information matching. Furthermore we show how a cascaded multi-resolution approach can improve registration quality while reducing algorithm run time. As acquired image volumes were over a terabyte in size, they were far too large for work on personal computers. Therefore the NeuroData computational infrastructure was deployed for multi-resolution storage and visualization of these images and aligned annotations on the web.
Deformably Registering and Annotating Whole CLARITY Brains to an Atlas via Masked LDDMM
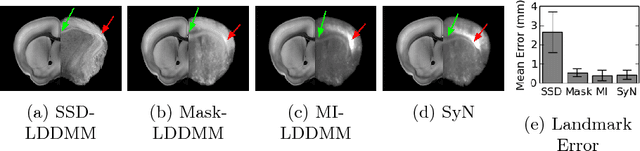
May 06, 2016Abstract:The CLARITY method renders brains optically transparent to enable high-resolution imaging in the structurally intact brain. Anatomically annotating CLARITY brains is necessary for discovering which regions contain signals of interest. Manually annotating whole-brain, terabyte CLARITY images is difficult, time-consuming, subjective, and error-prone. Automatically registering CLARITY images to a pre-annotated brain atlas offers a solution, but is difficult for several reasons. Removal of the brain from the skull and subsequent storage and processing cause variable non-rigid deformations, thus compounding inter-subject anatomical variability. Additionally, the signal in CLARITY images arises from various biochemical contrast agents which only sparsely label brain structures. This sparse labeling challenges the most commonly used registration algorithms that need to match image histogram statistics to the more densely labeled histological brain atlases. The standard method is a multiscale Mutual Information B-spline algorithm that dynamically generates an average template as an intermediate registration target. We determined that this method performs poorly when registering CLARITY brains to the Allen Institute's Mouse Reference Atlas (ARA), because the image histogram statistics are poorly matched. Therefore, we developed a method (Mask-LDDMM) for registering CLARITY images, that automatically find the brain boundary and learns the optimal deformation between the brain and atlas masks. Using Mask-LDDMM without an average template provided better results than the standard approach when registering CLARITY brains to the ARA. The LDDMM pipelines developed here provide a fast automated way to anatomically annotate CLARITY images. Our code is available as open source software at http://NeuroData.io.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge