Michael Goebel
3D Neuron Morphology Analysis
Dec 14, 2022
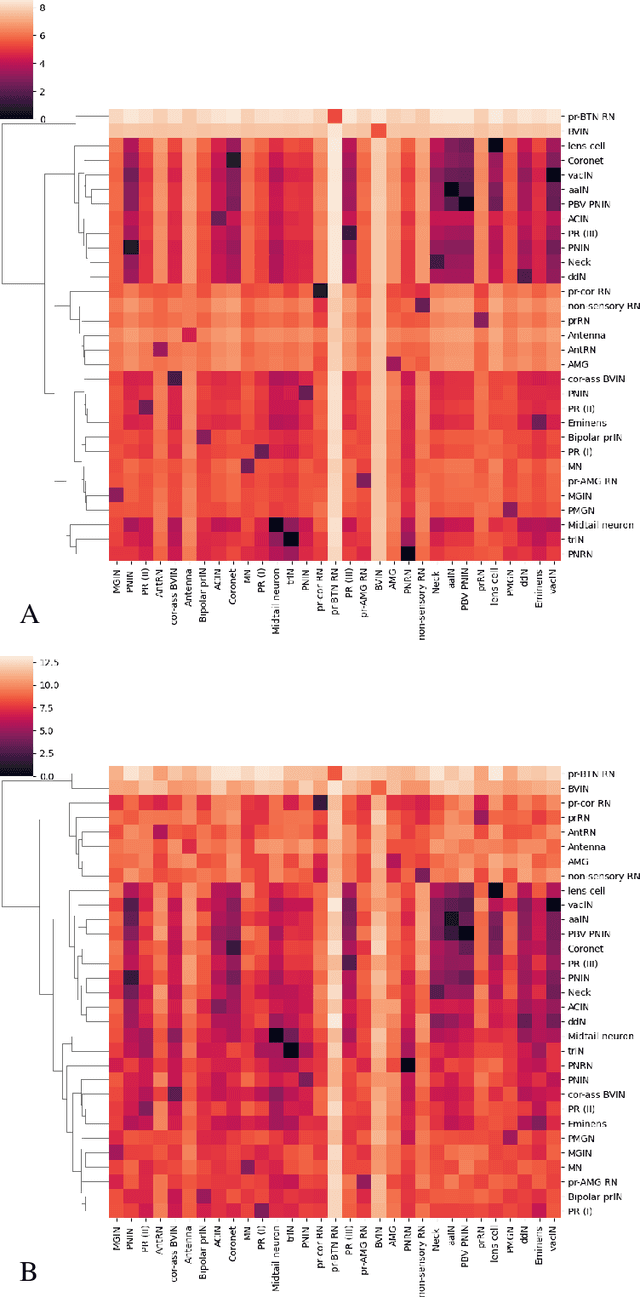


Abstract:We consider the problem of finding an accurate representation of neuron shapes, extracting sub-cellular features, and classifying neurons based on neuron shapes. In neuroscience research, the skeleton representation is often used as a compact and abstract representation of neuron shapes. However, existing methods are limited to getting and analyzing "curve" skeletons which can only be applied for tubular shapes. This paper presents a 3D neuron morphology analysis method for more general and complex neuron shapes. First, we introduce the concept of skeleton mesh to represent general neuron shapes and propose a novel method for computing mesh representations from 3D surface point clouds. A skeleton graph is then obtained from skeleton mesh and is used to extract sub-cellular features. Finally, an unsupervised learning method is used to embed the skeleton graph for neuron classification. Extensive experiment results are provided and demonstrate the robustness of our method to analyze neuron morphology.
Generalizable Deepfake Detection with Phase-Based Motion Analysis
Nov 17, 2022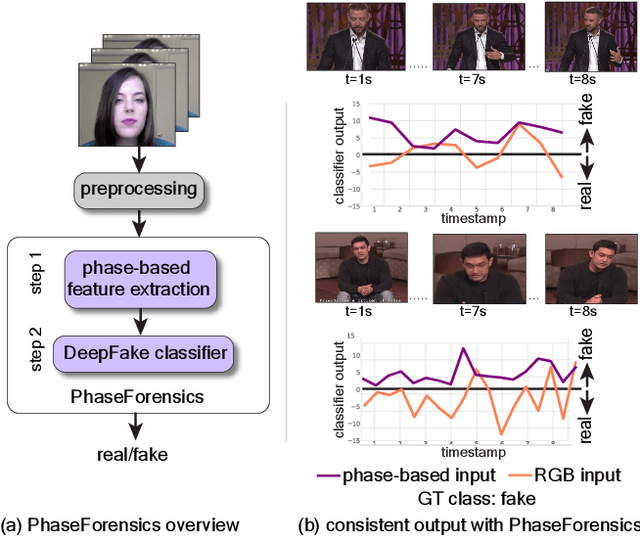
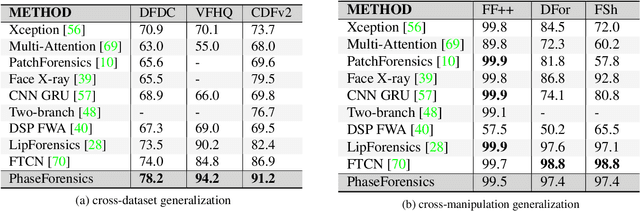

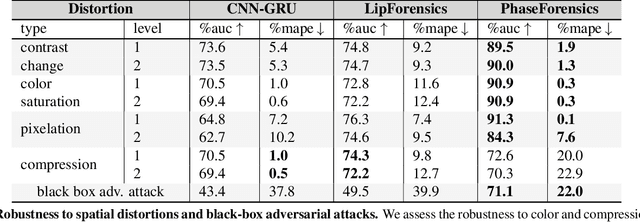
Abstract:We propose PhaseForensics, a DeepFake (DF) video detection method that leverages a phase-based motion representation of facial temporal dynamics. Existing methods relying on temporal inconsistencies for DF detection present many advantages over the typical frame-based methods. However, they still show limited cross-dataset generalization and robustness to common distortions. These shortcomings are partially due to error-prone motion estimation and landmark tracking, or the susceptibility of the pixel intensity-based features to spatial distortions and the cross-dataset domain shifts. Our key insight to overcome these issues is to leverage the temporal phase variations in the band-pass components of the Complex Steerable Pyramid on face sub-regions. This not only enables a robust estimate of the temporal dynamics in these regions, but is also less prone to cross-dataset variations. Furthermore, the band-pass filters used to compute the local per-frame phase form an effective defense against the perturbations commonly seen in gradient-based adversarial attacks. Overall, with PhaseForensics, we show improved distortion and adversarial robustness, and state-of-the-art cross-dataset generalization, with 91.2% video-level AUC on the challenging CelebDFv2 (a recent state-of-the-art compares at 86.9%).
Deep Learning Enabled Time-Lapse 3D Cell Analysis
Aug 17, 2022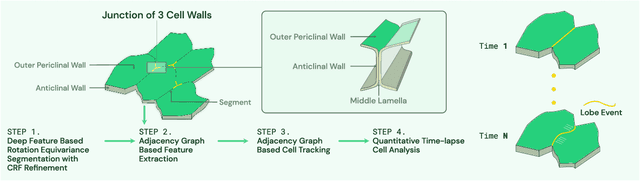
Abstract:This paper presents a method for time-lapse 3D cell analysis. Specifically, we consider the problem of accurately localizing and quantitatively analyzing sub-cellular features, and for tracking individual cells from time-lapse 3D confocal cell image stacks. The heterogeneity of cells and the volume of multi-dimensional images presents a major challenge for fully automated analysis of morphogenesis and development of cells. This paper is motivated by the pavement cell growth process, and building a quantitative morphogenesis model. We propose a deep feature based segmentation method to accurately detect and label each cell region. An adjacency graph based method is used to extract sub-cellular features of the segmented cells. Finally, the robust graph based tracking algorithm using multiple cell features is proposed for associating cells at different time instances. Extensive experiment results are provided and demonstrate the robustness of the proposed method. The code is available on Github and the method is available as a service through the BisQue portal.
Holistic Image Manipulation Detection using Pixel Co-occurrence Matrices
Apr 12, 2021



Abstract:Digital image forensics aims to detect images that have been digitally manipulated. Realistic image forgeries involve a combination of splicing, resampling, region removal, smoothing and other manipulation methods. While most detection methods in literature focus on detecting a particular type of manipulation, it is challenging to identify doctored images that involve a host of manipulations. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to holistically detect tampered images using a combination of pixel co-occurrence matrices and deep learning. We extract horizontal and vertical co-occurrence matrices on three color channels in the pixel domain and train a model using a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) framework. Our method is agnostic to the type of manipulation and classifies an image as tampered or untampered. We train and validate our model on a dataset of more than 86,000 images. Experimental results show that our approach is promising and achieves more than 0.99 area under the curve (AUC) evaluation metric on the training and validation subsets. Further, our approach also generalizes well and achieves around 0.81 AUC on an unseen test dataset comprising more than 19,740 images released as part of the Media Forensics Challenge (MFC) 2020. Our score was highest among all other teams that participated in the challenge, at the time of announcement of the challenge results.
Attribution of Gradient Based Adversarial Attacks for Reverse Engineering of Deceptions
Mar 19, 2021
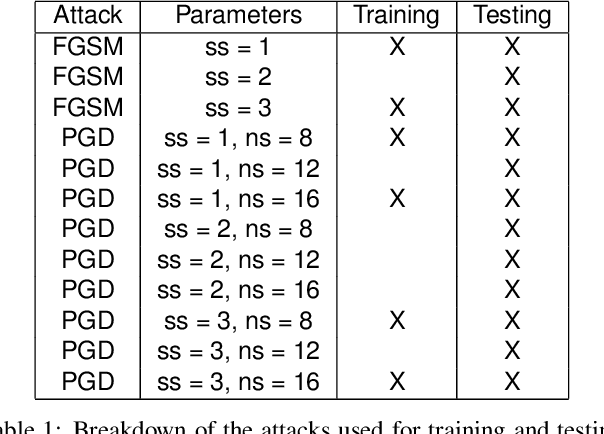
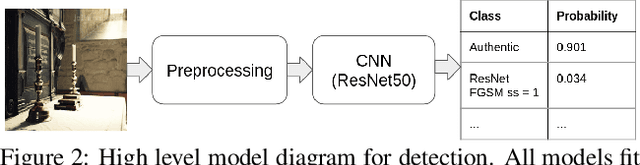
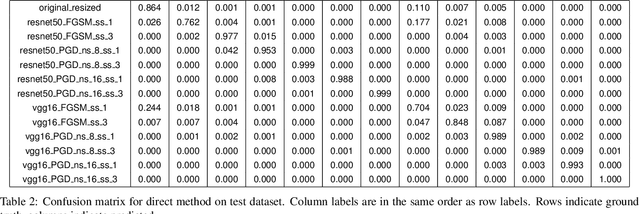
Abstract:Machine Learning (ML) algorithms are susceptible to adversarial attacks and deception both during training and deployment. Automatic reverse engineering of the toolchains behind these adversarial machine learning attacks will aid in recovering the tools and processes used in these attacks. In this paper, we present two techniques that support automated identification and attribution of adversarial ML attack toolchains using Co-occurrence Pixel statistics and Laplacian Residuals. Our experiments show that the proposed techniques can identify parameters used to generate adversarial samples. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first approach to attribute gradient based adversarial attacks and estimate their parameters. Source code and data is available at: https://github.com/michael-goebel/ei_red
StressNet: Detecting Stress in Thermal Videos
Nov 23, 2020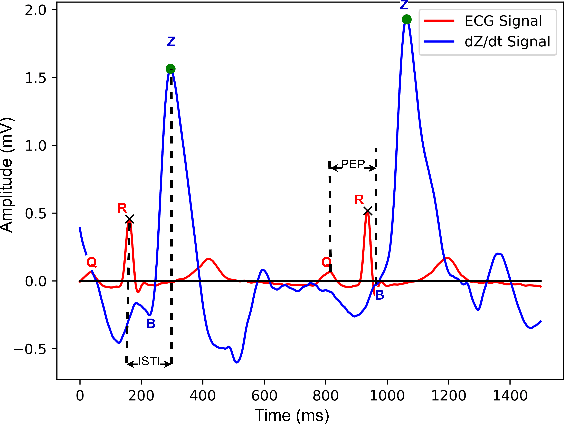
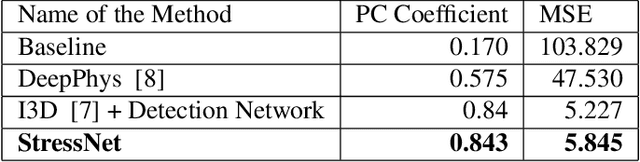
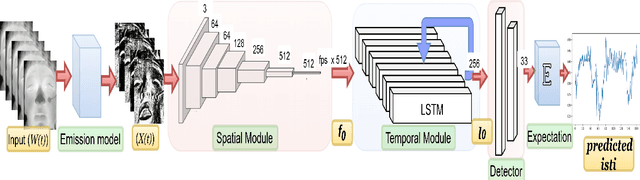
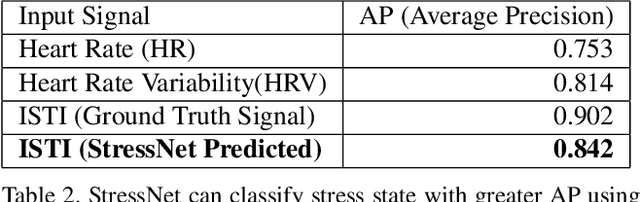
Abstract:Precise measurement of physiological signals is critical for the effective monitoring of human vital signs. Recent developments in computer vision have demonstrated that signals such as pulse rate and respiration rate can be extracted from digital video of humans, increasing the possibility of contact-less monitoring. This paper presents a novel approach to obtaining physiological signals and classifying stress states from thermal video. The proposed network--"StressNet"--features a hybrid emission representation model that models the direct emission and absorption of heat by the skin and underlying blood vessels. This results in an information-rich feature representation of the face, which is used by spatio-temporal network for reconstructing the ISTI ( Initial Systolic Time Interval: a measure of change in cardiac sympathetic activity that is considered to be a quantitative index of stress in humans ). The reconstructed ISTI signal is fed into a stress-detection model to detect and classify the individual's stress state ( i.e. stress or no stress ). A detailed evaluation demonstrates that StressNet achieves estimated the ISTI signal with 95% accuracy and detect stress with average precision of 0.842. The source code is available on Github.
Detection, Attribution and Localization of GAN Generated Images
Jul 20, 2020

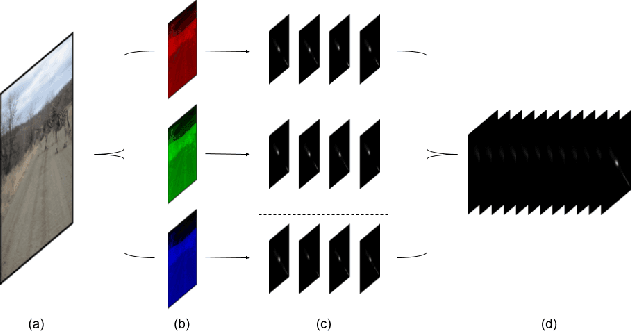

Abstract:Recent advances in Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have led to the creation of realistic-looking digital images that pose a major challenge to their detection by humans or computers. GANs are used in a wide range of tasks, from modifying small attributes of an image (StarGAN [14]), transferring attributes between image pairs (CycleGAN [91]), as well as generating entirely new images (ProGAN [36], StyleGAN [37], SPADE/GauGAN [64]). In this paper, we propose a novel approach to detect, attribute and localize GAN generated images that combines image features with deep learning methods. For every image, co-occurrence matrices are computed on neighborhood pixels of RGB channels in different directions (horizontal, vertical and diagonal). A deep learning network is then trained on these features to detect, attribute and localize these GAN generated/manipulated images. A large scale evaluation of our approach on 5 GAN datasets comprising over 2.76 million images (ProGAN, StarGAN, CycleGAN, StyleGAN and SPADE/GauGAN) shows promising results in detecting GAN generated images.
Predicting Fluid Intelligence of Children using T1-weighted MR Images and a StackNet
May 07, 2019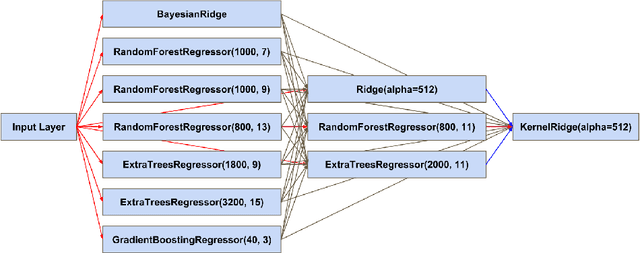

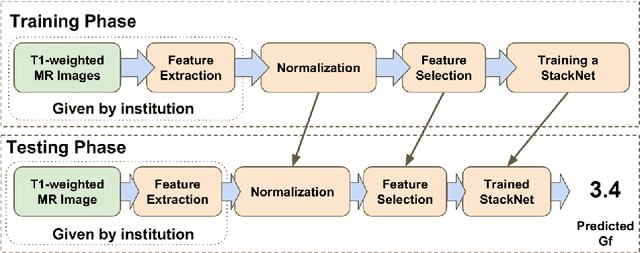

Abstract:In this work, we utilize T1-weighted MR images and StackNet to predict fluid intelligence in adolescents. Our framework includes feature extraction, feature normalization, feature denoising, feature selection, training a StackNet, and predicting fluid intelligence. The extracted feature is the distribution of different brain tissues in different brain parcellation regions. The proposed StackNet consists of three layers and 11 models. Each layer uses the predictions from all previous layers including the input layer. The proposed StackNet is tested on a public benchmark Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Neurocognitive Prediction Challenge 2019 and achieves a mean squared error of 82.42 on the combined training and validation set with 10-fold cross-validation. In addition, the proposed StackNet also achieves a mean squared error of 94.25 on the testing data. The source code is available on GitHub.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge