Satish Kumar
RareSpot: Spotting Small and Rare Wildlife in Aerial Imagery with Multi-Scale Consistency and Context-Aware Augmentation
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Automated detection of small and rare wildlife in aerial imagery is crucial for effective conservation, yet remains a significant technical challenge. Prairie dogs exemplify this issue: their ecological importance as keystone species contrasts sharply with their elusive presence--marked by small size, sparse distribution, and subtle visual features--which undermines existing detection approaches. To address these challenges, we propose RareSpot, a robust detection framework integrating multi-scale consistency learning and context-aware augmentation. Our multi-scale consistency approach leverages structured alignment across feature pyramids, enhancing fine-grained object representation and mitigating scale-related feature loss. Complementarily, context-aware augmentation strategically synthesizes challenging training instances by embedding difficult-to-detect samples into realistic environmental contexts, significantly boosting model precision and recall. Evaluated on an expert-annotated prairie dog drone imagery benchmark, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, improving detection accuracy by over 35% compared to baseline methods. Importantly, it generalizes effectively across additional wildlife datasets, demonstrating broad applicability. The RareSpot benchmark and approach not only support critical ecological monitoring but also establish a new foundation for detecting small, rare species in complex aerial scenes.
MethaneMapper: Spectral Absorption aware Hyperspectral Transformer for Methane Detection
Apr 05, 2023Abstract:Methane (CH$_4$) is the chief contributor to global climate change. Recent Airborne Visible-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer-Next Generation (AVIRIS-NG) has been very useful in quantitative mapping of methane emissions. Existing methods for analyzing this data are sensitive to local terrain conditions, often require manual inspection from domain experts, prone to significant error and hence are not scalable. To address these challenges, we propose a novel end-to-end spectral absorption wavelength aware transformer network, MethaneMapper, to detect and quantify the emissions. MethaneMapper introduces two novel modules that help to locate the most relevant methane plume regions in the spectral domain and uses them to localize these accurately. Thorough evaluation shows that MethaneMapper achieves 0.63 mAP in detection and reduces the model size (by 5x) compared to the current state of the art. In addition, we also introduce a large-scale dataset of methane plume segmentation mask for over 1200 AVIRIS-NG flight lines from 2015-2022. It contains over 4000 methane plume sites. Our dataset will provide researchers the opportunity to develop and advance new methods for tackling this challenging green-house gas detection problem with significant broader social impact. Dataset and source code are public
In-situ Water quality monitoring in Oil and Gas operations
Jan 20, 2023Abstract:From agriculture to mining, to energy, surface water quality monitoring is an essential task. As oil and gas operators work to reduce the consumption of freshwater, it is increasingly important to actively manage fresh and non-fresh water resources over the long term. For large-scale monitoring, manual sampling at many sites has become too time-consuming and unsustainable, given the sheer number of dispersed ponds, small lakes, playas, and wetlands over a large area. Therefore, satellite-based environmental monitoring presents great potential. Many existing satellite-based monitoring studies utilize index-based methods to monitor large water bodies such as rivers and oceans. However, these existing methods fail when monitoring small ponds-the reflectance signal received from small water bodies is too weak to detect. To address this challenge, we propose a new Water Quality Enhanced Index (WQEI) Model, which is designed to enable users to determine contamination levels in water bodies with weak reflectance patterns. Our results show that 1) WQEI is a good indicator of water turbidity validated with 1200 water samples measured in the laboratory, and 2) by applying our method to commonly available satellite data (e.g. LandSat8), one can achieve high accuracy water quality monitoring efficiently in large regions. This provides a tool for operators to optimize the quality of water stored within surface storage ponds and increasing the readiness and availability of non-fresh water.
DDS: Decoupled Dynamic Scene-Graph Generation Network
Jan 18, 2023Abstract:Scene-graph generation involves creating a structural representation of the relationships between objects in a scene by predicting subject-object-relation triplets from input data. However, existing methods show poor performance in detecting triplets outside of a predefined set, primarily due to their reliance on dependent feature learning. To address this issue we propose DDS -- a decoupled dynamic scene-graph generation network -- that consists of two independent branches that can disentangle extracted features. The key innovation of the current paper is the decoupling of the features representing the relationships from those of the objects, which enables the detection of novel object-relationship combinations. The DDS model is evaluated on three datasets and outperforms previous methods by a significant margin, especially in detecting previously unseen triplets.
LOCL: Learning Object-Attribute Composition using Localization
Oct 07, 2022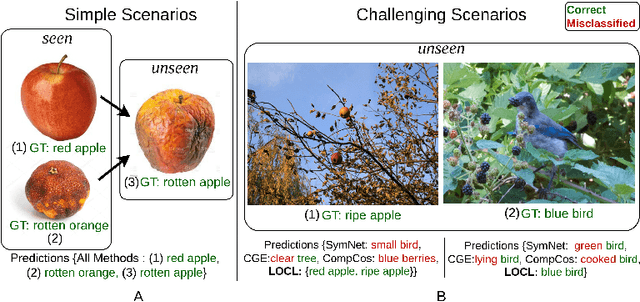
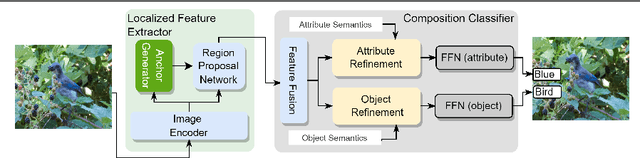
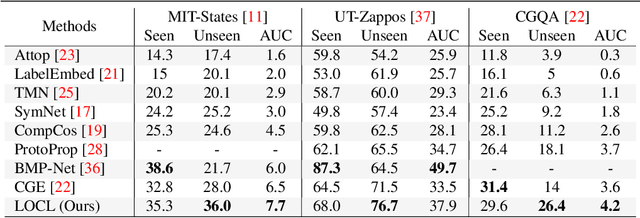
Abstract:This paper describes LOCL (Learning Object Attribute Composition using Localization) that generalizes composition zero shot learning to objects in cluttered and more realistic settings. The problem of unseen Object Attribute (OA) associations has been well studied in the field, however, the performance of existing methods is limited in challenging scenes. In this context, our key contribution is a modular approach to localizing objects and attributes of interest in a weakly supervised context that generalizes robustly to unseen configurations. Localization coupled with a composition classifier significantly outperforms state of the art (SOTA) methods, with an improvement of about 12% on currently available challenging datasets. Further, the modularity enables the use of localized feature extractor to be used with existing OA compositional learning methods to improve their overall performance.
GTNet:Guided Transformer Network for Detecting Human-Object Interactions
Aug 03, 2021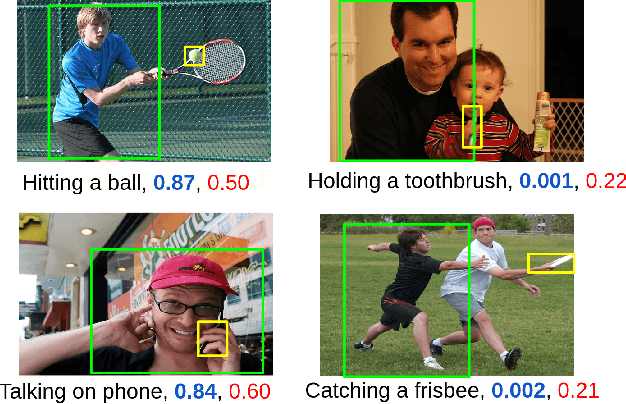
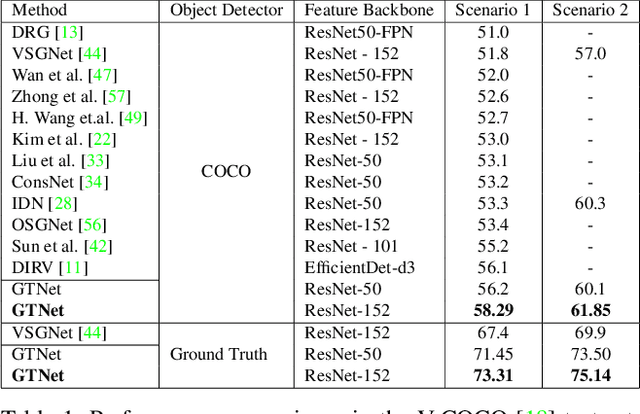
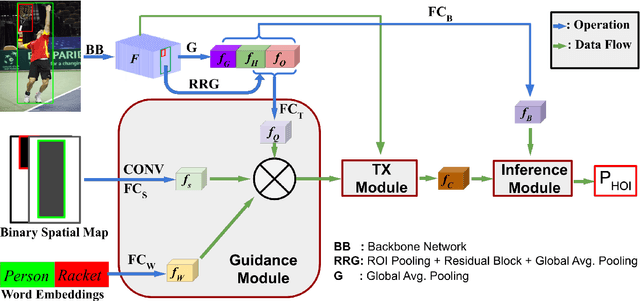
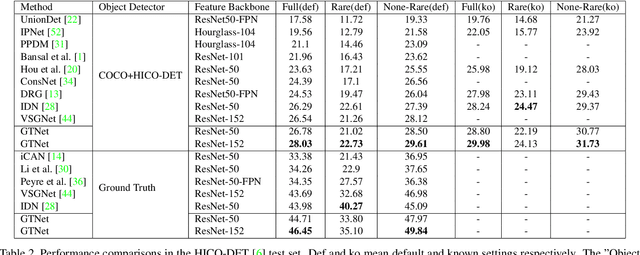
Abstract:The human-object interaction (HOI) detection task refers to localizing humans, localizing objects, and predicting the interactions between each human-object pair. HOI is considered one of the fundamental steps in truly understanding complex visual scenes. For detecting HOI, it is important to utilize relative spatial configurations and object semantics to find salient spatial regions of images that highlight the interactions between human object pairs. This issue is addressed by the proposed self-attention based guided transformer network, GTNet. GTNet encodes this spatial contextual information in human and object visual features via self-attention while achieving a 4%-6% improvement over previous state of the art results on both the V-COCO and HICO-DET datasets. Code will be made available online.
StressNet: Detecting Stress in Thermal Videos
Nov 23, 2020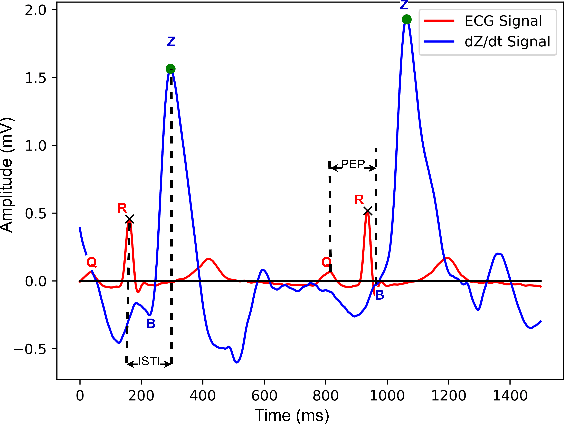
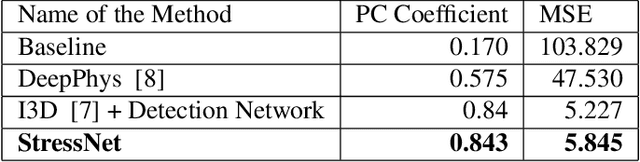
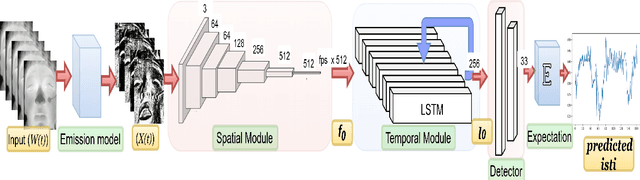
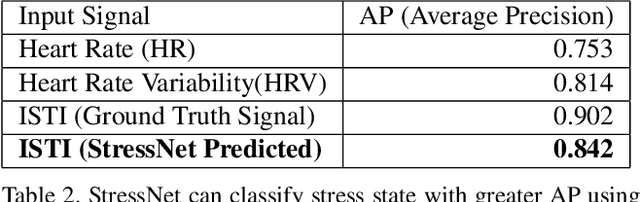
Abstract:Precise measurement of physiological signals is critical for the effective monitoring of human vital signs. Recent developments in computer vision have demonstrated that signals such as pulse rate and respiration rate can be extracted from digital video of humans, increasing the possibility of contact-less monitoring. This paper presents a novel approach to obtaining physiological signals and classifying stress states from thermal video. The proposed network--"StressNet"--features a hybrid emission representation model that models the direct emission and absorption of heat by the skin and underlying blood vessels. This results in an information-rich feature representation of the face, which is used by spatio-temporal network for reconstructing the ISTI ( Initial Systolic Time Interval: a measure of change in cardiac sympathetic activity that is considered to be a quantitative index of stress in humans ). The reconstructed ISTI signal is fed into a stress-detection model to detect and classify the individual's stress state ( i.e. stress or no stress ). A detailed evaluation demonstrates that StressNet achieves estimated the ISTI signal with 95% accuracy and detect stress with average precision of 0.842. The source code is available on Github.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge