Mengyue Zhou
Evaluating Large Language Models for Radiology Natural Language Processing
Jul 27, 2023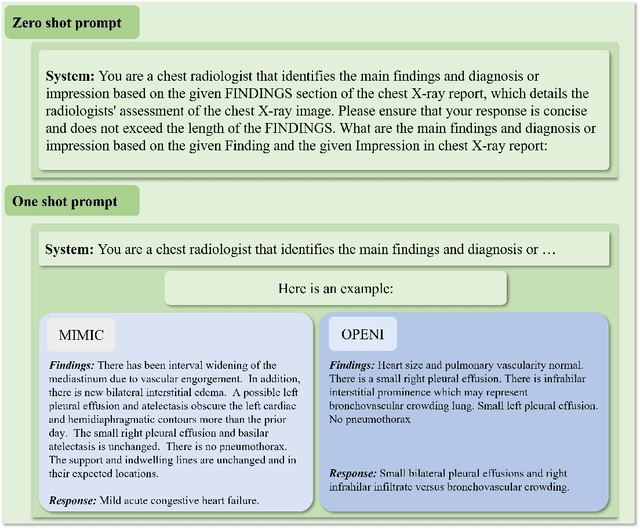
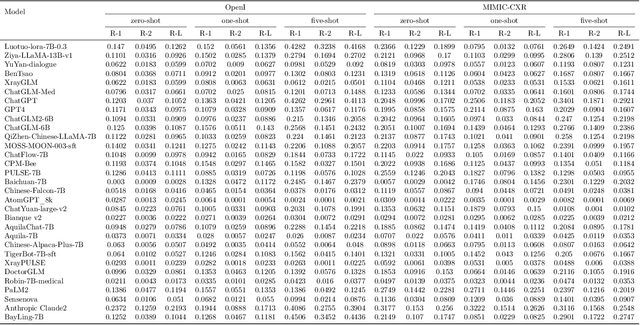
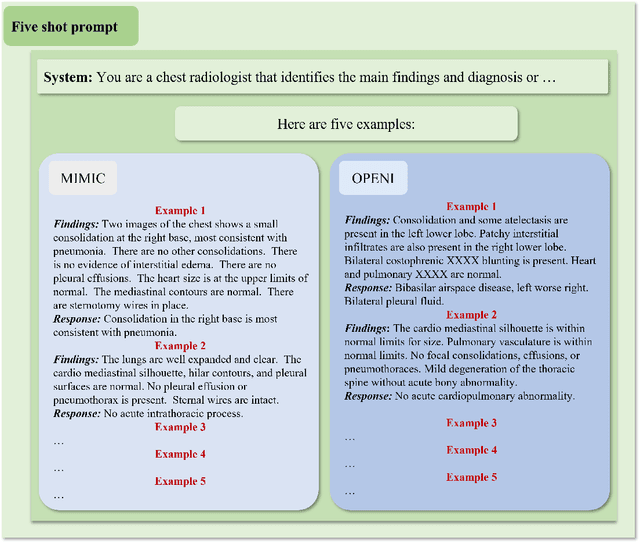
Abstract:The rise of large language models (LLMs) has marked a pivotal shift in the field of natural language processing (NLP). LLMs have revolutionized a multitude of domains, and they have made a significant impact in the medical field. Large language models are now more abundant than ever, and many of these models exhibit bilingual capabilities, proficient in both English and Chinese. However, a comprehensive evaluation of these models remains to be conducted. This lack of assessment is especially apparent within the context of radiology NLP. This study seeks to bridge this gap by critically evaluating thirty two LLMs in interpreting radiology reports, a crucial component of radiology NLP. Specifically, the ability to derive impressions from radiologic findings is assessed. The outcomes of this evaluation provide key insights into the performance, strengths, and weaknesses of these LLMs, informing their practical applications within the medical domain.
Coupling Artificial Neurons in BERT and Biological Neurons in the Human Brain
Mar 27, 2023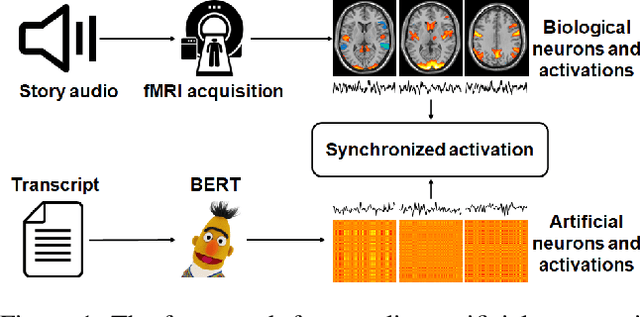
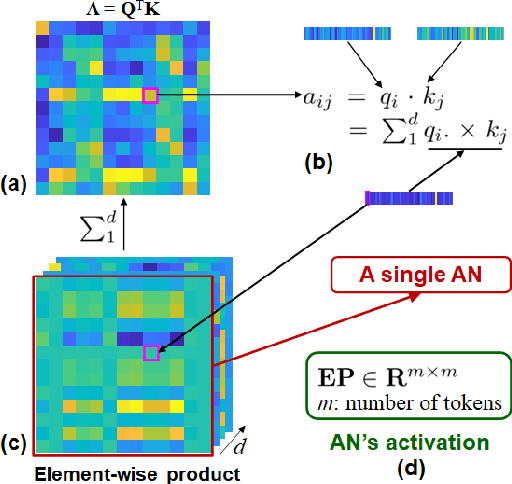
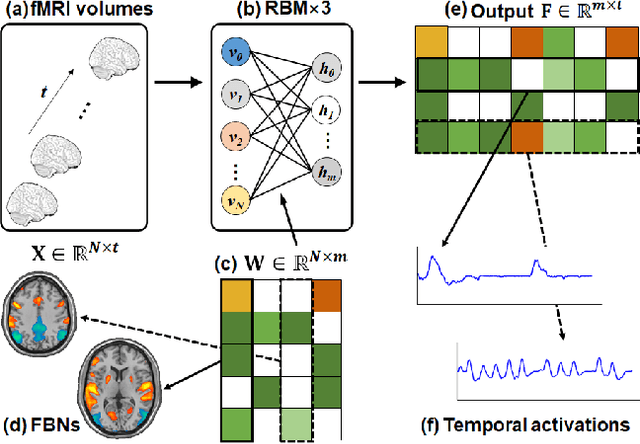
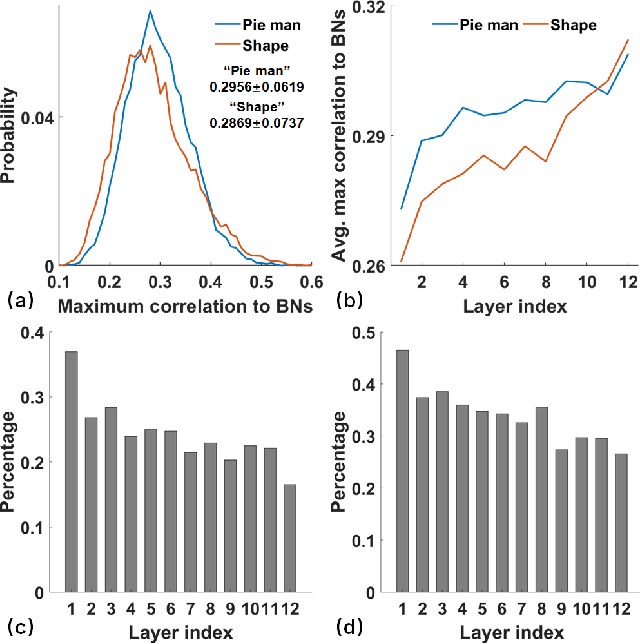
Abstract:Linking computational natural language processing (NLP) models and neural responses to language in the human brain on the one hand facilitates the effort towards disentangling the neural representations underpinning language perception, on the other hand provides neurolinguistics evidence to evaluate and improve NLP models. Mappings of an NLP model's representations of and the brain activities evoked by linguistic input are typically deployed to reveal this symbiosis. However, two critical problems limit its advancement: 1) The model's representations (artificial neurons, ANs) rely on layer-level embeddings and thus lack fine-granularity; 2) The brain activities (biological neurons, BNs) are limited to neural recordings of isolated cortical unit (i.e., voxel/region) and thus lack integrations and interactions among brain functions. To address those problems, in this study, we 1) define ANs with fine-granularity in transformer-based NLP models (BERT in this study) and measure their temporal activations to input text sequences; 2) define BNs as functional brain networks (FBNs) extracted from functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data to capture functional interactions in the brain; 3) couple ANs and BNs by maximizing the synchronization of their temporal activations. Our experimental results demonstrate 1) The activations of ANs and BNs are significantly synchronized; 2) the ANs carry meaningful linguistic/semantic information and anchor to their BN signatures; 3) the anchored BNs are interpretable in a neurolinguistic context. Overall, our study introduces a novel, general, and effective framework to link transformer-based NLP models and neural activities in response to language and may provide novel insights for future studies such as brain-inspired evaluation and development of NLP models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge