Mengying Zhu
TADS: Task-Aware Data Selection for Multi-Task Multimodal Pre-Training
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large-scale multimodal pre-trained models like CLIP rely heavily on high-quality training data, yet raw web-crawled datasets are often noisy, misaligned, and redundant, leading to inefficient training and suboptimal generalization. Existing data selection methods are either heuristic-based, suffering from bias and limited diversity, or data-driven but task-agnostic, failing to optimize for multi-task scenarios. To address these gaps, we introduce TADS (Task-Aware Data Selection), a novel framework for multi-task multimodal pre-training that integrates Intrinsic Quality, Task Relevance, and Distributional Diversity into a learnable value function. TADS employs a comprehensive quality assessment system with unimodal and cross-modal operators, quantifies task relevance via interpretable similarity vectors, and optimizes diversity through cluster-based weighting. A feedback-driven meta-learning mechanism adaptively refines the selection strategy based on proxy model performance across multiple downstream tasks. Experiments on CC12M demonstrate that TADS achieves superior zero-shot performance on benchmarks like ImageNet, CIFAR-100, MS-COCO, and Flickr30K, using only 36% of the data while outperforming baselines by an average of 1.0%. This highlights that TADS significantly enhances data efficiency by curating a high-utility subset that yields a much higher performance ceiling within the same computational constraints.
E2PL: Effective and Efficient Prompt Learning for Incomplete Multi-view Multi-Label Class Incremental Learning
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Multi-view multi-label classification (MvMLC) is indispensable for modern web applications aggregating information from diverse sources. However, real-world web-scale settings are rife with missing views and continuously emerging classes, which pose significant obstacles to robust learning. Prevailing methods are ill-equipped for this reality, as they either lack adaptability to new classes or incur exponential parameter growth when handling all possible missing-view patterns, severely limiting their scalability in web environments. To systematically address this gap, we formally introduce a novel task, termed \emph{incomplete multi-view multi-label class incremental learning} (IMvMLCIL), which requires models to simultaneously address heterogeneous missing views and dynamic class expansion. To tackle this task, we propose \textsf{E2PL}, an Effective and Efficient Prompt Learning framework for IMvMLCIL. \textsf{E2PL} unifies two novel prompt designs: \emph{task-tailored prompts} for class-incremental adaptation and \emph{missing-aware prompts} for the flexible integration of arbitrary view-missing scenarios. To fundamentally address the exponential parameter explosion inherent in missing-aware prompts, we devise an \emph{efficient prototype tensorization} module, which leverages atomic tensor decomposition to elegantly reduce the prompt parameter complexity from exponential to linear w.r.t. the number of views. We further incorporate a \emph{dynamic contrastive learning} strategy explicitly model the complex dependencies among diverse missing-view patterns, thus enhancing the model's robustness. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks demonstrate that \textsf{E2PL} consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both effectiveness and efficiency. The codes and datasets are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/code-for-E2PL.
TermGPT: Multi-Level Contrastive Fine-Tuning for Terminology Adaptation in Legal and Financial Domain
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance in text generation tasks; however, their embedding spaces often suffer from the isotropy problem, resulting in poor discrimination of domain-specific terminology, particularly in legal and financial contexts. This weakness in terminology-level representation can severely hinder downstream tasks such as legal judgment prediction or financial risk analysis, where subtle semantic distinctions are critical. To address this problem, we propose TermGPT, a multi-level contrastive fine-tuning framework designed for terminology adaptation. We first construct a sentence graph to capture semantic and structural relations, and generate semantically consistent yet discriminative positive and negative samples based on contextual and topological cues. We then devise a multi-level contrastive learning approach at both the sentence and token levels, enhancing global contextual understanding and fine-grained terminology discrimination. To support robust evaluation, we construct the first financial terminology dataset derived from official regulatory documents. Experiments show that TermGPT outperforms existing baselines in term discrimination tasks within the finance and legal domains.
Modeling Orders of User Behaviors via Differentiable Sorting: A Multi-task Framework to Predicting User Post-click Conversion
Jul 18, 2023Abstract:User post-click conversion prediction is of high interest to researchers and developers. Recent studies employ multi-task learning to tackle the selection bias and data sparsity problem, two severe challenges in post-click behavior prediction, by incorporating click data. However, prior works mainly focused on pointwise learning and the orders of labels (i.e., click and post-click) are not well explored, which naturally poses a listwise learning problem. Inspired by recent advances on differentiable sorting, in this paper, we propose a novel multi-task framework that leverages orders of user behaviors to predict user post-click conversion in an end-to-end approach. Specifically, we define an aggregation operator to combine predicted outputs of different tasks to a unified score, then we use the computed scores to model the label relations via differentiable sorting. Extensive experiments on public and industrial datasets show the superiority of our proposed model against competitive baselines.
HCFRec: Hash Collaborative Filtering via Normalized Flow with Structural Consensus for Efficient Recommendation
May 24, 2022



Abstract:The ever-increasing data scale of user-item interactions makes it challenging for an effective and efficient recommender system. Recently, hash-based collaborative filtering (Hash-CF) approaches employ efficient Hamming distance of learned binary representations of users and items to accelerate recommendations. However, Hash-CF often faces two challenging problems, i.e., optimization on discrete representations and preserving semantic information in learned representations. To address the above two challenges, we propose HCFRec, a novel Hash-CF approach for effective and efficient recommendations. Specifically, HCFRec not only innovatively introduces normalized flow to learn the optimal hash code by efficiently fit a proposed approximate mixture multivariate normal distribution, a continuous but approximately discrete distribution, but also deploys a cluster consistency preserving mechanism to preserve the semantic structure in representations for more accurate recommendations. Extensive experiments conducted on six real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of our HCFRec compared to the state-of-art methods in terms of effectiveness and efficiency.
Adaptive Portfolio by Solving Multi-armed Bandit via Thompson Sampling
Nov 14, 2019



Abstract:As the cornerstone of modern portfolio theory, Markowitz's mean-variance optimization is considered a major model adopted in portfolio management. However, due to the difficulty of estimating its parameters, it cannot be applied to all periods. In some cases, naive strategies such as Equally-weighted and Value-weighted portfolios can even get better performance. Under these circumstances, we can use multiple classic strategies as multiple strategic arms in multi-armed bandit to naturally establish a connection with the portfolio selection problem. This can also help to maximize the rewards in the bandit algorithm by the trade-off between exploration and exploitation. In this paper, we present a portfolio bandit strategy through Thompson sampling which aims to make online portfolio choices by effectively exploiting the performances among multiple arms. Also, by constructing multiple strategic arms, we can obtain the optimal investment portfolio to adapt different investment periods. Moreover, we devise a novel reward function based on users' different investment risk preferences, which can be adaptive to various investment styles. Our experimental results demonstrate that our proposed portfolio strategy has marked superiority across representative real-world market datasets in terms of extensive evaluation criteria.
FinBrain: When Finance Meets AI 2.0
Aug 26, 2018
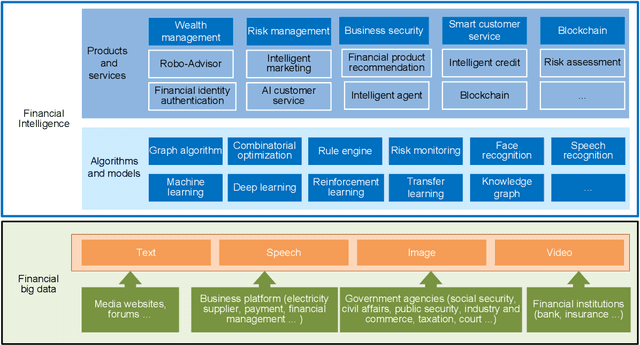
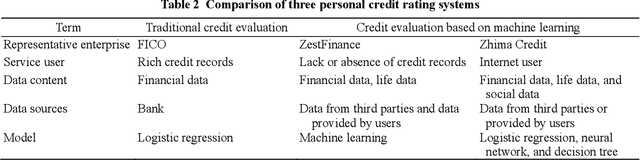
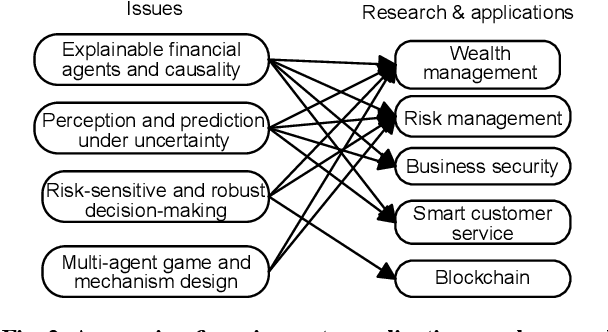
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is the core technology of technological revolution and industrial transformation. As one of the new intelligent needs in the AI 2.0 era, financial intelligence has elicited much attention from the academia and industry. In our current dynamic capital market, financial intelligence demonstrates a fast and accurate machine learning capability to handle complex data and has gradually acquired the potential to become a "financial brain". In this work, we survey existing studies on financial intelligence. First, we describe the concept of financial intelligence and elaborate on its position in the financial technology field. Second, we introduce the development of financial intelligence and review state-of-the-art techniques in wealth management, risk management, financial security, financial consulting, and blockchain. Finally, we propose a research framework called FinBrain and summarize four open issues, namely, explainable financial agents and causality, perception and prediction under uncertainty, risk-sensitive and robust decision making, and multi-agent game and mechanism design. We believe that these research directions can lay the foundation for the development of AI 2.0 in the finance field.
* 11 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge