Mengli Cheng
DiffPoint: Single and Multi-view Point Cloud Reconstruction with ViT Based Diffusion Model
Feb 17, 2024



Abstract:As the task of 2D-to-3D reconstruction has gained significant attention in various real-world scenarios, it becomes crucial to be able to generate high-quality point clouds. Despite the recent success of deep learning models in generating point clouds, there are still challenges in producing high-fidelity results due to the disparities between images and point clouds. While vision transformers (ViT) and diffusion models have shown promise in various vision tasks, their benefits for reconstructing point clouds from images have not been demonstrated yet. In this paper, we first propose a neat and powerful architecture called DiffPoint that combines ViT and diffusion models for the task of point cloud reconstruction. At each diffusion step, we divide the noisy point clouds into irregular patches. Then, using a standard ViT backbone that treats all inputs as tokens (including time information, image embeddings, and noisy patches), we train our model to predict target points based on input images. We evaluate DiffPoint on both single-view and multi-view reconstruction tasks and achieve state-of-the-art results. Additionally, we introduce a unified and flexible feature fusion module for aggregating image features from single or multiple input images. Furthermore, our work demonstrates the feasibility of applying unified architectures across languages and images to improve 3D reconstruction tasks.
MuLTI: Efficient Video-and-Language Understanding with MultiWay-Sampler and Multiple Choice Modeling
Mar 10, 2023



Abstract:Video-and-language understanding has a variety of applications in the industry, such as video question answering, text-video retrieval and multi-label classification. Existing video-and-language understanding methods generally adopt heavy multi-modal encoders and feature fusion modules, which consume large amounts of GPU memory. Especially, they have difficulty dealing with dense video frames or long text that are prevalent in industrial applications. In this paper, we propose MuLTI, a highly accurate and memory-efficient video-and-language understanding model that achieves efficient and effective feature fusion through feature sampling and attention modules. Therefore, MuLTI can handle longer sequences with limited GPU memory. Then, we introduce an attention-based adapter to the encoders, which finetunes the shallow features to improve the model's performance with low GPU memory consumption. Finally, to further improve the model's performance, we introduce a new pretraining task named Multiple Choice Modeling to bridge the task gap between pretraining and downstream tasks and enhance the model's ability to align the video and the text. Benefiting from the efficient feature fusion module, the attention-based adapter and the new pretraining task, MuLTI achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple datasets. Implementation and pretrained models will be released.
EasyRec: An easy-to-use, extendable and efficient framework for building industrial recommendation systems
Sep 26, 2022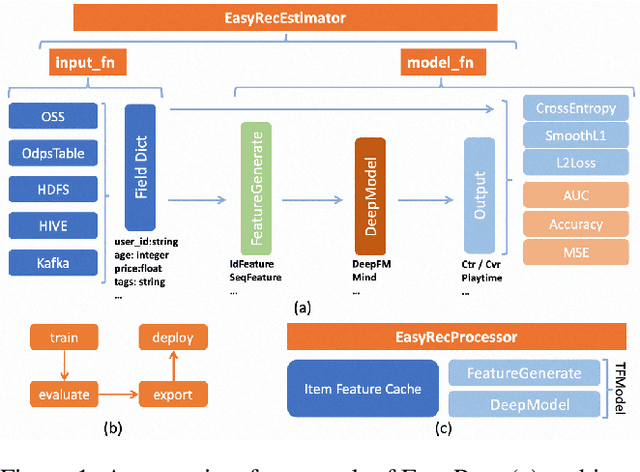
Abstract:We present EasyRec, an easy-to-use, extendable and efficient recommendation framework for building industrial recommendation systems. Our EasyRec framework is superior in the following aspects: first, EasyRec adopts a modular and pluggable design pattern to reduce the efforts to build custom models; second, EasyRec implements hyper-parameter optimization and feature selection algorithms to improve model performance automatically; third, EasyRec applies online learning to fast adapt to the ever-changing data distribution. The code is released: https://github.com/alibaba/EasyRec.
EasyASR: A Distributed Machine Learning Platform for End-to-end Automatic Speech Recognition
Sep 14, 2020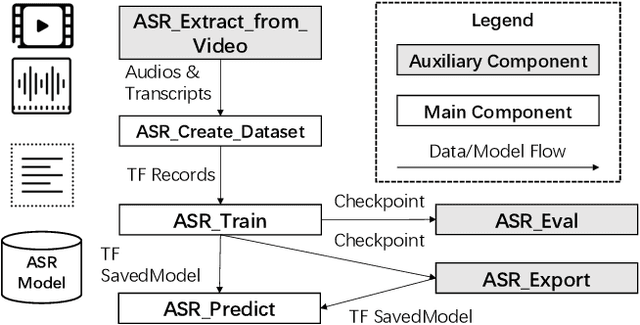
Abstract:We present EasyASR, a distributed machine learning platform for training and serving large-scale Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models, as well as collecting and processing audio data at scale. Our platform is built upon the Machine Learning Platform for AI of Alibaba Cloud. Its main functionality is to support efficient learning and inference for end-to-end ASR models on distributed GPU clusters. It allows users to learn ASR models with either pre-defined or user-customized network architectures via simple user interface. On EasyASR, we have produced state-of-the-art results over several public datasets for Mandarin speech recognition.
One-shot Text Field Labeling using Attention and Belief Propagation for Structure Information Extraction
Sep 09, 2020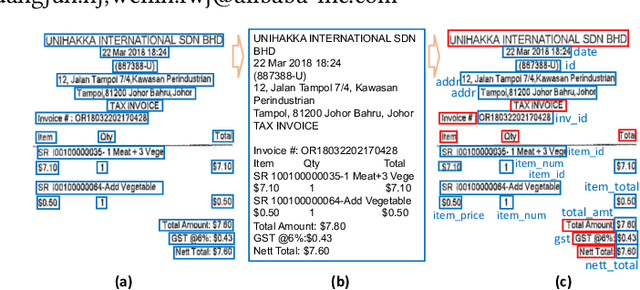
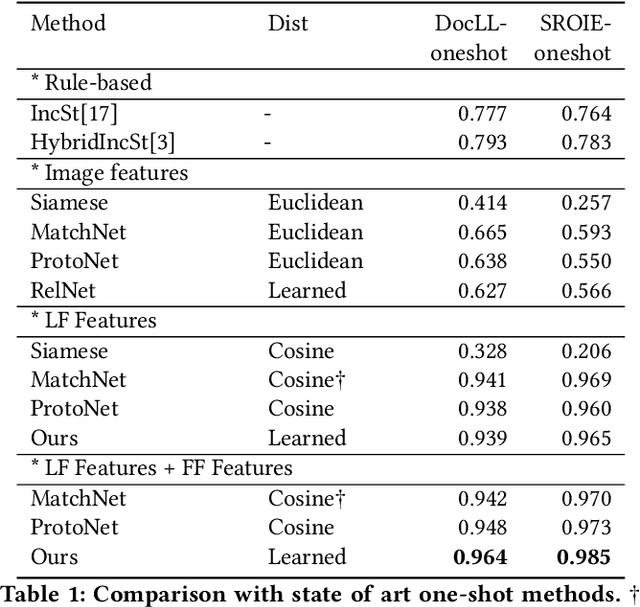
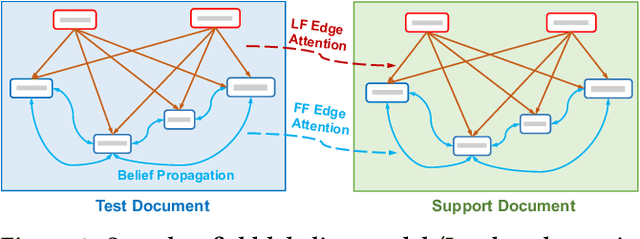
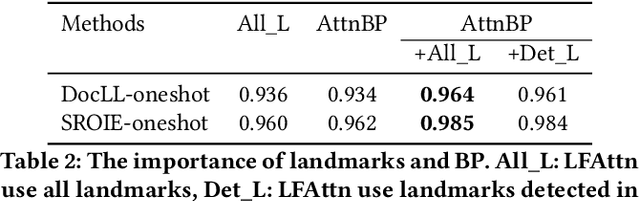
Abstract:Structured information extraction from document images usually consists of three steps: text detection, text recognition, and text field labeling. While text detection and text recognition have been heavily studied and improved a lot in literature, text field labeling is less explored and still faces many challenges. Existing learning based methods for text labeling task usually require a large amount of labeled examples to train a specific model for each type of document. However, collecting large amounts of document images and labeling them is difficult and sometimes impossible due to privacy issues. Deploying separate models for each type of document also consumes a lot of resources. Facing these challenges, we explore one-shot learning for the text field labeling task. Existing one-shot learning methods for the task are mostly rule-based and have difficulty in labeling fields in crowded regions with few landmarks and fields consisting of multiple separate text regions. To alleviate these problems, we proposed a novel deep end-to-end trainable approach for one-shot text field labeling, which makes use of attention mechanism to transfer the layout information between document images. We further applied conditional random field on the transferred layout information for the refinement of field labeling. We collected and annotated a real-world one-shot field labeling dataset with a large variety of document types and conducted extensive experiments to examine the effectiveness of the proposed model. To stimulate research in this direction, the collected dataset and the one-shot model will be released1.
* 9 pages
Weakly Supervised Construction of ASR Systems with Massive Video Data
Aug 04, 2020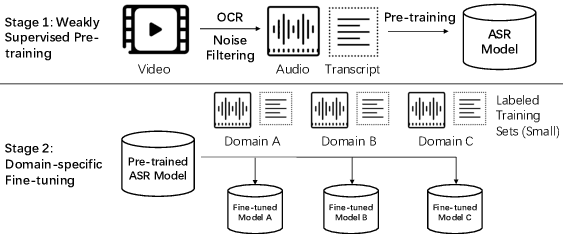
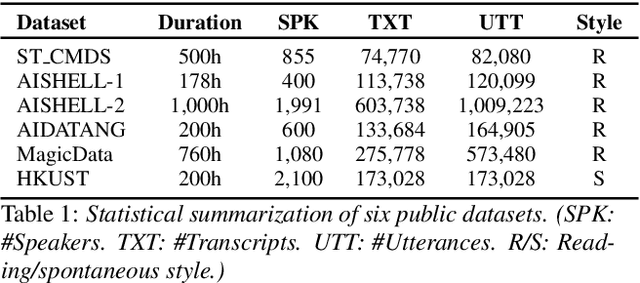
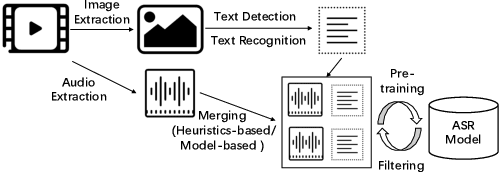
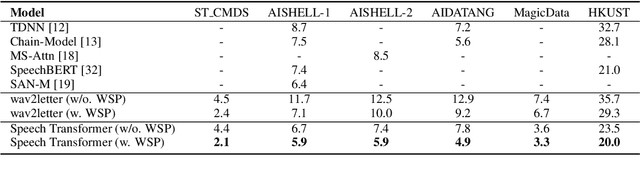
Abstract:Building Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems from scratch is significantly challenging, mostly due to the time-consuming and financially-expensive process of annotating a large amount of audio data with transcripts. Although several unsupervised pre-training models have been proposed, applying such models directly might still be sub-optimal if more labeled, training data could be obtained without a large cost. In this paper, we present a weakly supervised framework for constructing ASR systems with massive video data. As videos often contain human-speech audios aligned with subtitles, we consider videos as an important knowledge source, and propose an effective approach to extract high-quality audios aligned with transcripts from videos based on Optical Character Recognition (OCR). The underlying ASR model can be fine-tuned to fit any domain-specific target training datasets after weakly supervised pre-training. Extensive experiments show that our framework can easily produce state-of-the-art results on six public datasets for Mandarin speech recognition.
IncepText: A New Inception-Text Module with Deformable PSROI Pooling for Multi-Oriented Scene Text Detection
May 08, 2018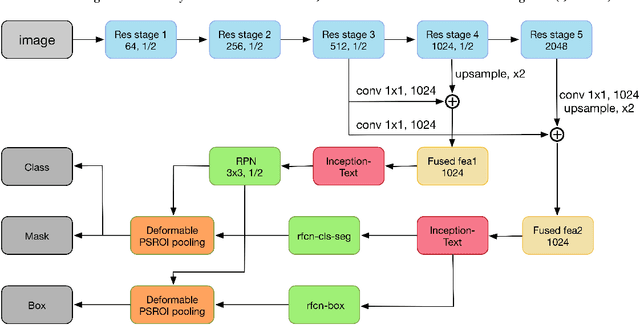
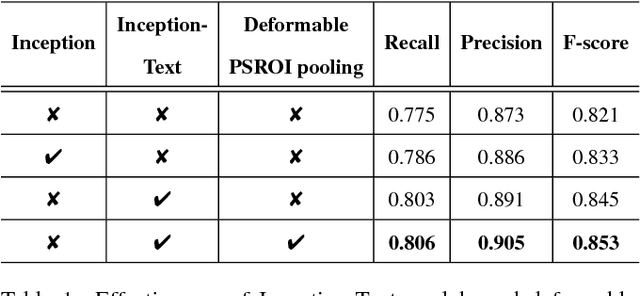
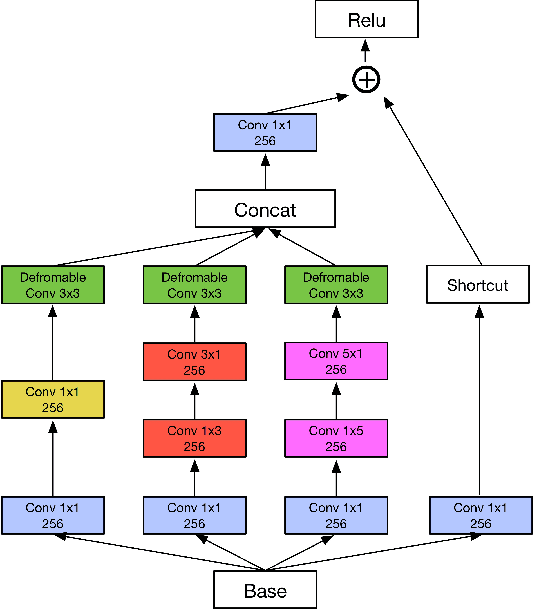
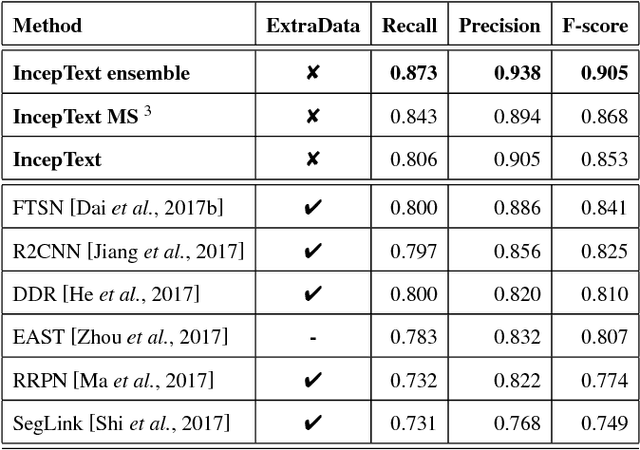
Abstract:Incidental scene text detection, especially for multi-oriented text regions, is one of the most challenging tasks in many computer vision applications. Different from the common object detection task, scene text often suffers from a large variance of aspect ratio, scale, and orientation. To solve this problem, we propose a novel end-to-end scene text detector IncepText from an instance-aware segmentation perspective. We design a novel Inception-Text module and introduce deformable PSROI pooling to deal with multi-oriented text detection. Extensive experiments on ICDAR2015, RCTW-17, and MSRA-TD500 datasets demonstrate our method's superiority in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency. Our proposed method achieves 1st place result on ICDAR2015 challenge and the state-of-the-art performance on other datasets. Moreover, we have released our implementation as an OCR product which is available for public access.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge