Maxime Amblard
SEMAGRAMME, LORIA
"Wait, did you mean the doctor?": Collecting a Dialogue Corpus for Topical Analysis
Jan 14, 2025
Abstract:Dialogue is at the core of human behaviour and being able to identify the topic at hand is crucial to take part in conversation. Yet, there are few accounts of the topical organisation in casual dialogue and of how people recognise the current topic in the literature. Moreover, analysing topics in dialogue requires conversations long enough to contain several topics and types of topic shifts. Such data is complicated to collect and annotate. In this paper we present a dialogue collection experiment which aims to build a corpus suitable for topical analysis. We will carry out the collection with a messaging tool we developed.
With a Little Help from my Friends: Topic Segmentation of Multi-party Casual Conversations
Feb 05, 2024



Abstract:Topics play an important role in the global organisation of a conversation as what is currently discussed constrains the possible contributions of the participant. Understanding the way topics are organised in interaction would provide insight on the structure of dialogue beyond the sequence of utterances. However, studying this high-level structure is a complex task that we try to approach by first segmenting dialogues into smaller topically coherent sets of utterances. Understanding the interactions between these segments would then enable us to propose a model of topic organisation at a dialogue level. In this paper we work with open-domain conversations and try to reach a comparable level of accuracy as recent machine learning based topic segmentation models but with a formal approach. The features we identify as meaningful for this task help us understand better the topical structure of a conversation.
Discourse Structure Extraction from Pre-Trained and Fine-Tuned Language Models in Dialogues
Feb 12, 2023
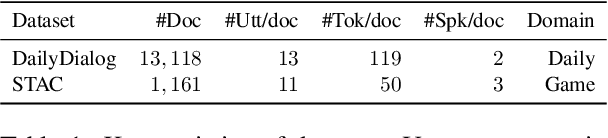
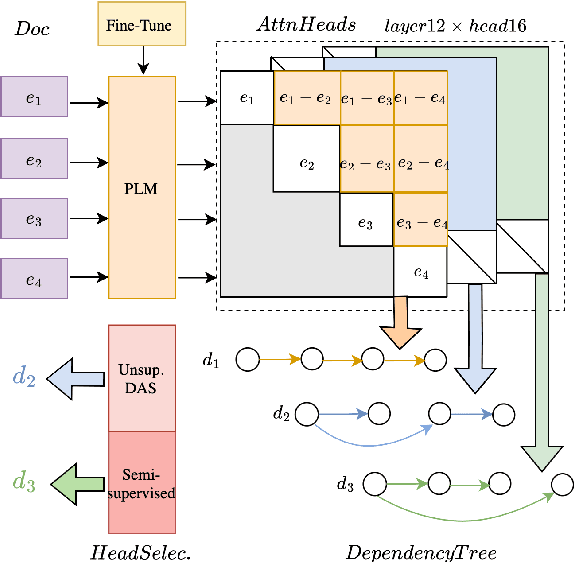
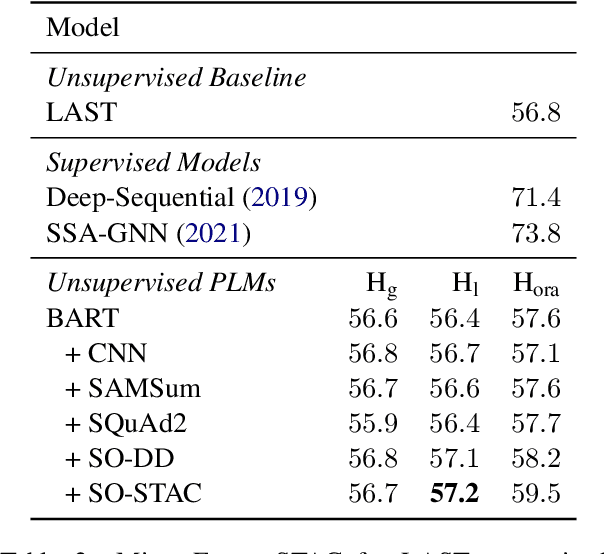
Abstract:Discourse processing suffers from data sparsity, especially for dialogues. As a result, we explore approaches to build discourse structures for dialogues, based on attention matrices from Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs). We investigate multiple tasks for fine-tuning and show that the dialogue-tailored Sentence Ordering task performs best. To locate and exploit discourse information in PLMs, we propose an unsupervised and a semi-supervised method. Our proposals achieve encouraging results on the STAC corpus, with F1 scores of 57.2 and 59.3 for unsupervised and semi-supervised methods, respectively. When restricted to projective trees, our scores improved to 63.3 and 68.1.
How much of UCCA can be predicted from AMR?
Jul 25, 2022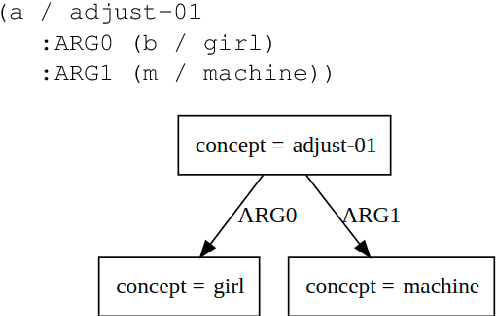
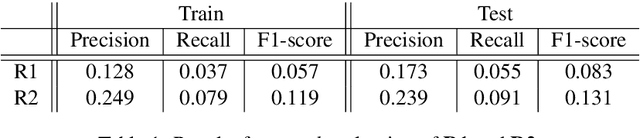


Abstract:In this paper, we consider two of the currently popular semantic frameworks: Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR)a more abstract framework, and Universal Conceptual Cognitive Annotation (UCCA)-an anchored framework. We use a corpus-based approach to build two graph rewriting systems, a deterministic and a non-deterministic one, from the former to the latter framework. We present their evaluation and a number of ambiguities that we discovered while building our rules. Finally, we provide a discussion and some future work directions in relation to comparing semantic frameworks of different flavors.
Graph Querying for Semantic Annotations
Jul 25, 2022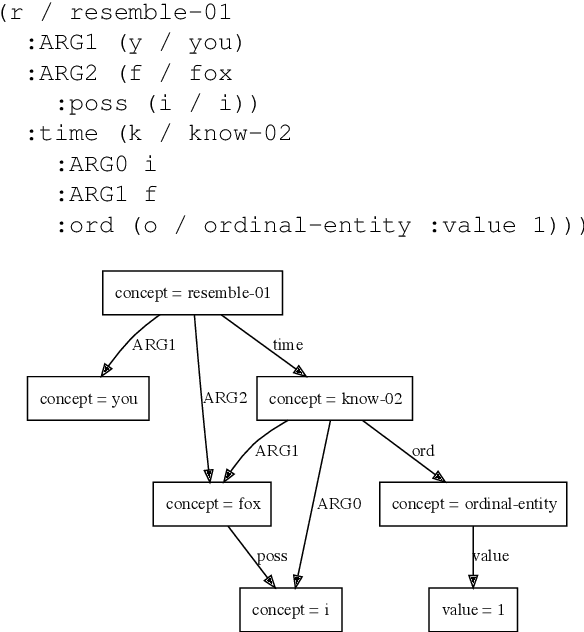
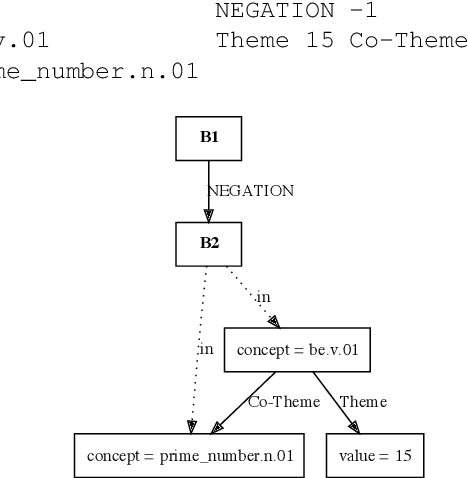
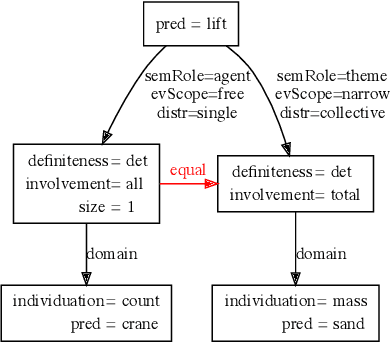
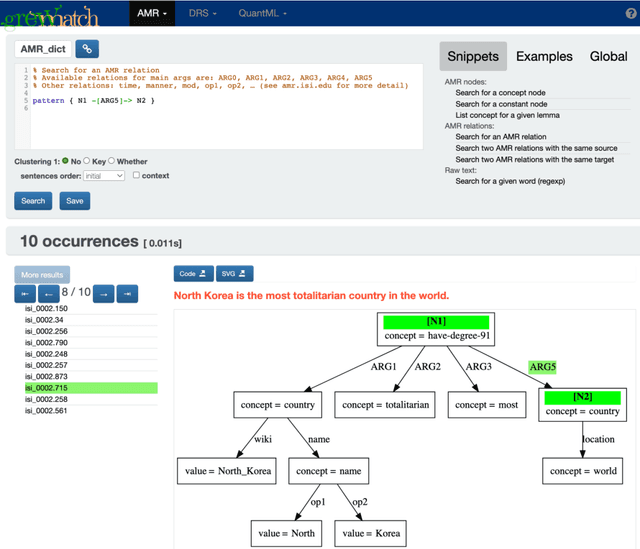
Abstract:This paper presents how the online tool GREW-MATCH can be used to make queries and visualise data from existing semantically annotated corpora. A dedicated syntax is available to construct simple to complex queries and execute them against a corpus. Such queries give transverse views of the annotated data, these views can help for checking the consistency of annotations in one corpus or across several corpora. GREW-MATCH can then be seen as an error mining tool: when inconsistencies are detected, it helps finding the sentences which should be fixed. Finally, GREW-MATCH can also be used as a side tool to assist annotation tasks helping to find annotation examples in existing corpora to be compared to the data to be annotated.
A Multi-Party Dialogue Ressource in French
Jul 25, 2022
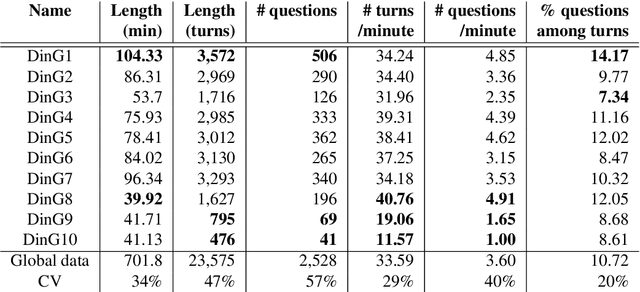
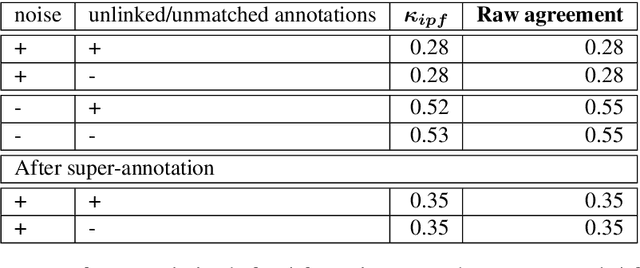
Abstract:We present Dialogues in Games (DinG), a corpus of manual transcriptions of real-life, oral, spontaneous multi-party dialogues between French-speaking players of the board game Catan. Our objective is to make available a quality resource for French, composed of long dialogues, to facilitate their study in the style of (Asher et al., 2016). In a general dialogue setting, participants share personal information, which makes it impossible to disseminate the resource freely and openly. In DinG, the attention of the participants is focused on the game, which prevents them from talking about themselves. In addition, we are conducting a study on the nature of the questions in dialogue, through annotation (Cruz Blandon et al., 2019), in order to develop more natural automatic dialogue systems.
Reducing Unintended Bias of ML Models on Tabular and Textual Data
Aug 05, 2021



Abstract:Unintended biases in machine learning (ML) models are among the major concerns that must be addressed to maintain public trust in ML. In this paper, we address process fairness of ML models that consists in reducing the dependence of models on sensitive features, without compromising their performance. We revisit the framework FixOut that is inspired in the approach "fairness through unawareness" to build fairer models. We introduce several improvements such as automating the choice of FixOut's parameters. Also, FixOut was originally proposed to improve fairness of ML models on tabular data. We also demonstrate the feasibility of FixOut's workflow for models on textual data. We present several experimental results that illustrate the fact that FixOut improves process fairness on different classification settings.
Toward Dialogue Modeling: A Semantic Annotation Scheme for Questions and Answers
Aug 23, 2019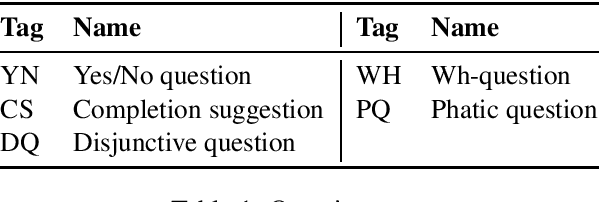
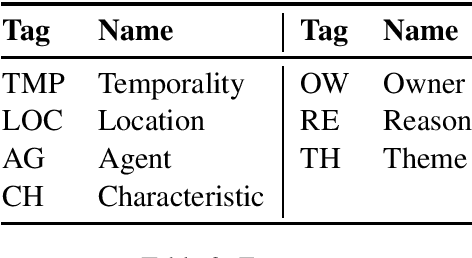
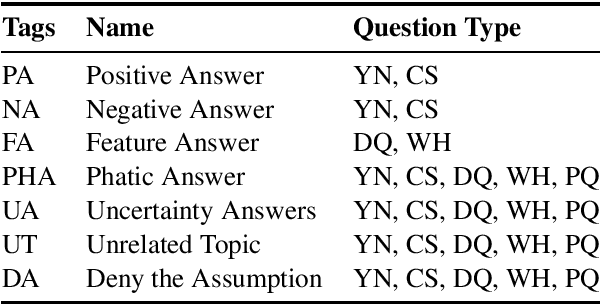
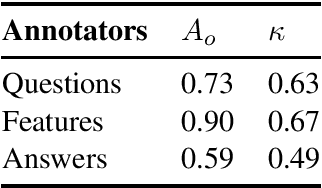
Abstract:The present study proposes an annotation scheme for classifying the content and discourse contribution of question-answer pairs. We propose detailed guidelines for using the scheme and apply them to dialogues in English, Spanish, and Dutch. Finally, we report on initial machine learning experiments for automatic annotation.
Introducing a Calculus of Effects and Handlers for Natural Language Semantics
Jul 08, 2016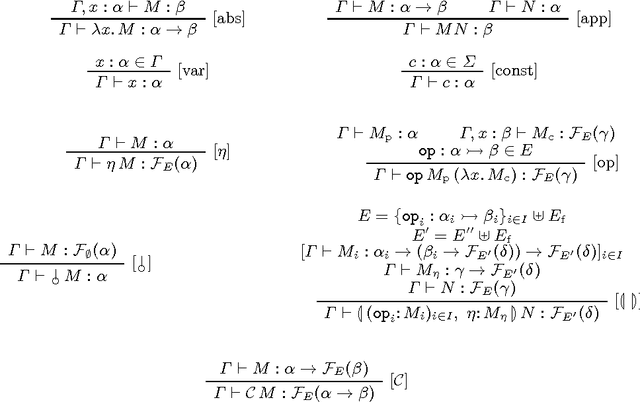
Abstract:In compositional model-theoretic semantics, researchers assemble truth-conditions or other kinds of denotations using the lambda calculus. It was previously observed that the lambda terms and/or the denotations studied tend to follow the same pattern: they are instances of a monad. In this paper, we present an extension of the simply-typed lambda calculus that exploits this uniformity using the recently discovered technique of effect handlers. We prove that our calculus exhibits some of the key formal properties of the lambda calculus and we use it to construct a modular semantics for a small fragment that involves multiple distinct semantic phenomena.
Pragmatic Side Effects
Jun 17, 2015Abstract:In the quest to give a formal compositional semantics to natural languages, semanticists have started turning their attention to phenomena that have been also considered as parts of pragmatics (e.g., discourse anaphora and presupposition projection). To account for these phenomena, the very kinds of meanings assigned to words and phrases are often revisited. To be more specific, in the prevalent paradigm of modeling natural language denotations using the simply-typed lambda calculus (higher-order logic) this means revisiting the types of denotations assigned to individual parts of speech. However, the lambda calculus also serves as a fundamental theory of computation, and in the study of computation, similar type shifts have been employed to give a meaning to side effects. Side effects in programming languages correspond to actions that go beyond the lexical scope of an expression (a thrown exception might propagate throughout a program, a variable modified at one point might later be read at an another) or even beyond the scope of the program itself (a program might interact with the outside world by e.g., printing documents, making sounds, operating robotic limbs...).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge