Amandine Decker
LORIA, UL, CNRS, SEMAGRAMME, GU
"Wait, did you mean the doctor?": Collecting a Dialogue Corpus for Topical Analysis
Jan 14, 2025
Abstract:Dialogue is at the core of human behaviour and being able to identify the topic at hand is crucial to take part in conversation. Yet, there are few accounts of the topical organisation in casual dialogue and of how people recognise the current topic in the literature. Moreover, analysing topics in dialogue requires conversations long enough to contain several topics and types of topic shifts. Such data is complicated to collect and annotate. In this paper we present a dialogue collection experiment which aims to build a corpus suitable for topical analysis. We will carry out the collection with a messaging tool we developed.
With a Little Help from my Friends: Topic Segmentation of Multi-party Casual Conversations
Feb 05, 2024



Abstract:Topics play an important role in the global organisation of a conversation as what is currently discussed constrains the possible contributions of the participant. Understanding the way topics are organised in interaction would provide insight on the structure of dialogue beyond the sequence of utterances. However, studying this high-level structure is a complex task that we try to approach by first segmenting dialogues into smaller topically coherent sets of utterances. Understanding the interactions between these segments would then enable us to propose a model of topic organisation at a dialogue level. In this paper we work with open-domain conversations and try to reach a comparable level of accuracy as recent machine learning based topic segmentation models but with a formal approach. The features we identify as meaningful for this task help us understand better the topical structure of a conversation.
Topic and genre in dialogue
Dec 06, 2023Abstract:In this paper we argue that topic plays a fundamental role in conversations, and that the concept is needed in addition to that of genre to define interactions. In particular, the concepts of genre and topic need to be separated and orthogonally defined. This would enable modular, reliable and controllable flexible-domain dialogue systems.
Tackling Morphological Analogies Using Deep Learning -- Extended Version
Nov 09, 2021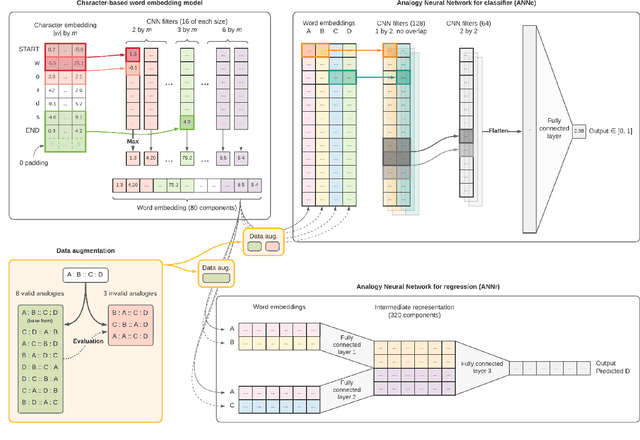
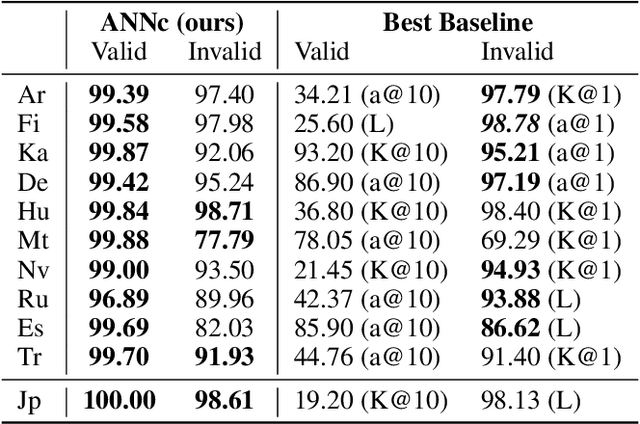
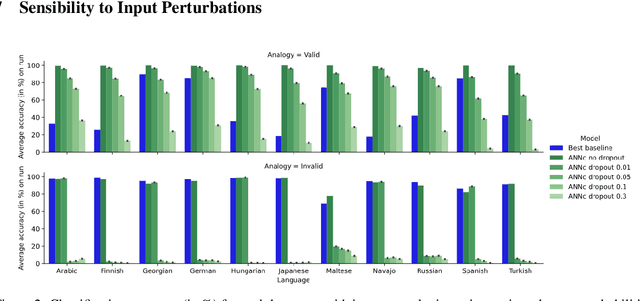
Abstract:Analogical proportions are statements of the form "A is to B as C is to D". They constitute an inference tool that provides a logical framework to address learning, transfer, and explainability concerns and that finds useful applications in artificial intelligence and natural language processing. In this paper, we address two problems, namely, analogy detection and resolution in morphology. Multiple symbolic approaches tackle the problem of analogies in morphology and achieve competitive performance. We show that it is possible to use a data-driven strategy to outperform those models. We propose an approach using deep learning to detect and solve morphological analogies. It encodes structural properties of analogical proportions and relies on a specifically designed embedding model capturing morphological characteristics of words. We demonstrate our model's competitive performance on analogy detection and resolution over multiple languages. We provide an empirical study to analyze the impact of balancing training data and evaluate the robustness of our approach to input perturbation.
A Neural Approach for Detecting Morphological Analogies
Aug 09, 2021
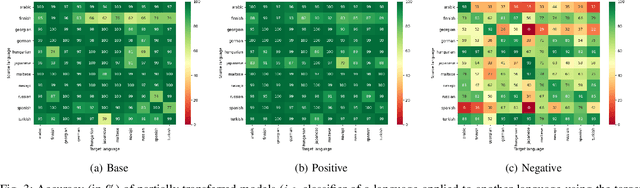
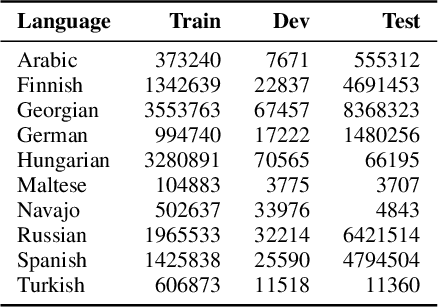
Abstract:Analogical proportions are statements of the form "A is to B as C is to D" that are used for several reasoning and classification tasks in artificial intelligence and natural language processing (NLP). For instance, there are analogy based approaches to semantics as well as to morphology. In fact, symbolic approaches were developed to solve or to detect analogies between character strings, e.g., the axiomatic approach as well as that based on Kolmogorov complexity. In this paper, we propose a deep learning approach to detect morphological analogies, for instance, with reinflexion or conjugation. We present empirical results that show that our framework is competitive with the above-mentioned state of the art symbolic approaches. We also explore empirically its transferability capacity across languages, which highlights interesting similarities between them.
On the Transferability of Neural Models of Morphological Analogies
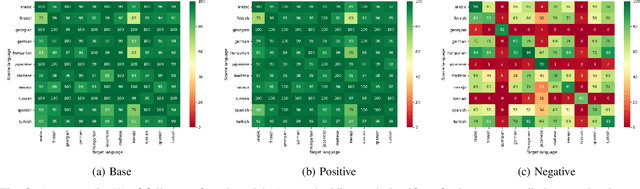
Aug 09, 2021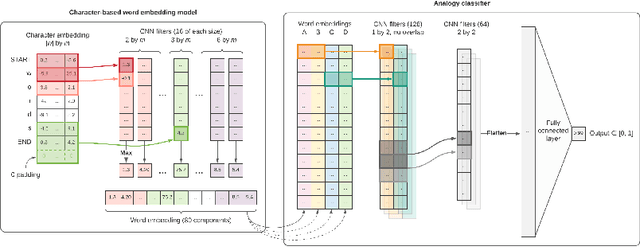
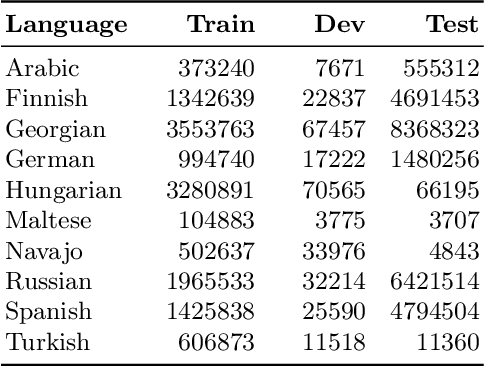
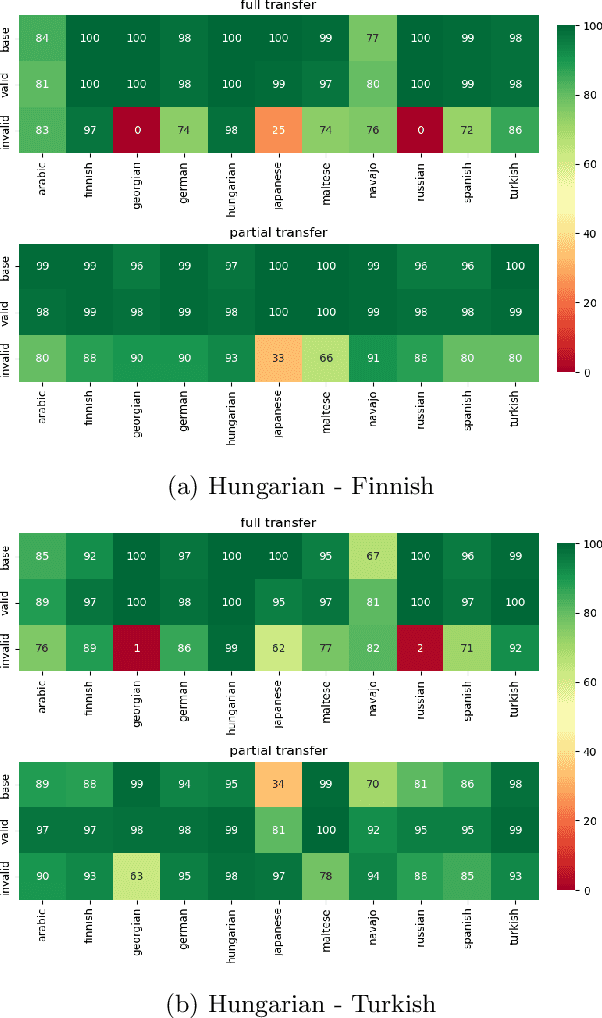
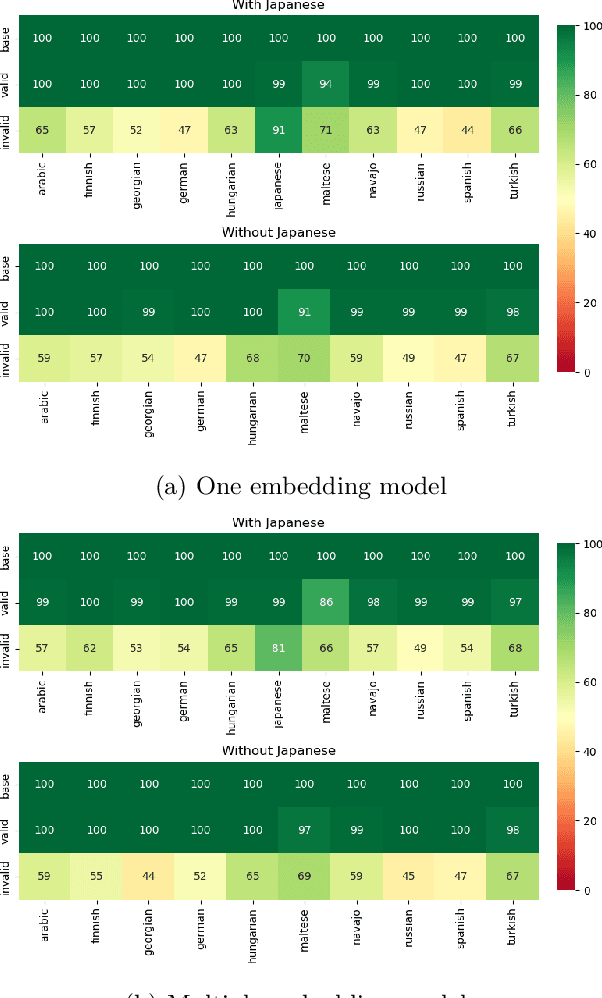
Abstract:Analogical proportions are statements expressed in the form "A is to B as C is to D" and are used for several reasoning and classification tasks in artificial intelligence and natural language processing (NLP). In this paper, we focus on morphological tasks and we propose a deep learning approach to detect morphological analogies. We present an empirical study to see how our framework transfers across languages, and that highlights interesting similarities and differences between these languages. In view of these results, we also discuss the possibility of building a multilingual morphological model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge