Fabien Bernier
Leveraging External Factors in Household-Level Electrical Consumption Forecasting using Hypernetworks
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Accurate electrical consumption forecasting is crucial for efficient energy management and resource allocation. While traditional time series forecasting relies on historical patterns and temporal dependencies, incorporating external factors -- such as weather indicators -- has shown significant potential for improving prediction accuracy in complex real-world applications. However, the inclusion of these additional features often degrades the performance of global predictive models trained on entire populations, despite improving individual household-level models. To address this challenge, we found that a hypernetwork architecture can effectively leverage external factors to enhance the accuracy of global electrical consumption forecasting models, by specifically adjusting the model weights to each consumer. We collected a comprehensive dataset spanning two years, comprising consumption data from over 6000 luxembourgish households and corresponding external factors such as weather indicators, holidays, and major local events. By comparing various forecasting models, we demonstrate that a hypernetwork approach outperforms existing methods when associated to external factors, reducing forecasting errors and achieving the best accuracy while maintaining the benefits of a global model.
Constraint-Guided Prediction Refinement via Deterministic Diffusion Trajectories
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Many real-world machine learning tasks require outputs that satisfy hard constraints, such as physical conservation laws, structured dependencies in graphs, or column-level relationships in tabular data. Existing approaches rely either on domain-specific architectures and losses or on strong assumptions on the constraint space, restricting their applicability to linear or convex constraints. We propose a general-purpose framework for constraint-aware refinement that leverages denoising diffusion implicit models (DDIMs). Starting from a coarse prediction, our method iteratively refines it through a deterministic diffusion trajectory guided by a learned prior and augmented by constraint gradient corrections. The approach accommodates a wide class of non-convex and nonlinear equality constraints and can be applied post hoc to any base model. We demonstrate the method in two representative domains: constrained adversarial attack generation on tabular data with column-level dependencies and in AC power flow prediction under Kirchhoff's laws. Across both settings, our diffusion-guided refinement improves both constraint satisfaction and performance while remaining lightweight and model-agnostic.
SafePowerGraph-LLM: Novel Power Grid Graph Embedding and Optimization with Large Language Models
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:Efficiently solving Optimal Power Flow (OPF) problems in power systems is crucial for operational planning and grid management. There is a growing need for scalable algorithms capable of handling the increasing variability, constraints, and uncertainties in modern power networks while providing accurate and fast solutions. To address this, machine learning techniques, particularly Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as promising approaches. This letter introduces SafePowerGraph-LLM, the first framework explicitly designed for solving OPF problems using Large Language Models (LLM)s. The proposed approach combines graph and tabular representations of power grids to effectively query LLMs, capturing the complex relationships and constraints in power systems. A new implementation of in-context learning and fine-tuning protocols for LLMs is introduced, tailored specifically for the OPF problem. SafePowerGraph-LLM demonstrates reliable performances using off-the-shelf LLM. Our study reveals the impact of LLM architecture, size, and fine-tuning and demonstrates our framework's ability to handle realistic grid components and constraints.
Survey on Fairness Notions and Related Tensions
Sep 16, 2022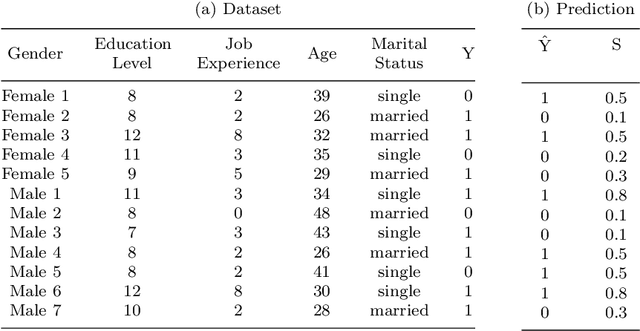

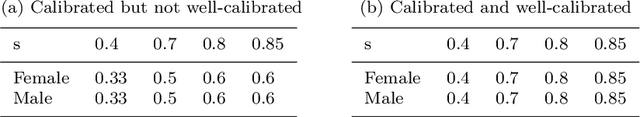
Abstract:Automated decision systems are increasingly used to take consequential decisions in problems such as job hiring and loan granting with the hope of replacing subjective human decisions with objective machine learning (ML) algorithms. ML-based decision systems, however, are found to be prone to bias which result in yet unfair decisions. Several notions of fairness have been defined in the literature to capture the different subtleties of this ethical and social concept (e.g. statistical parity, equal opportunity, etc.). Fairness requirements to be satisfied while learning models created several types of tensions among the different notions of fairness, but also with other desirable properties such as privacy and classification accuracy. This paper surveys the commonly used fairness notions and discusses the tensions that exist among them and with privacy and accuracy. Different methods to address the fairness-accuracy trade-off (classified into four approaches, namely, pre-processing, in-processing, post-processing, and hybrid) are reviewed. The survey is consolidated with experimental analysis carried out on fairness benchmark datasets to illustrate the relationship between fairness measures and accuracy on real-world scenarios.
Reducing Unintended Bias of ML Models on Tabular and Textual Data
Aug 05, 2021



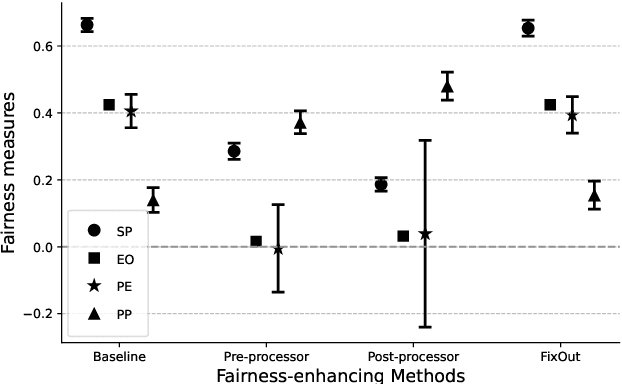
Abstract:Unintended biases in machine learning (ML) models are among the major concerns that must be addressed to maintain public trust in ML. In this paper, we address process fairness of ML models that consists in reducing the dependence of models on sensitive features, without compromising their performance. We revisit the framework FixOut that is inspired in the approach "fairness through unawareness" to build fairer models. We introduce several improvements such as automating the choice of FixOut's parameters. Also, FixOut was originally proposed to improve fairness of ML models on tabular data. We also demonstrate the feasibility of FixOut's workflow for models on textual data. We present several experimental results that illustrate the fact that FixOut improves process fairness on different classification settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge