Guy Perrier
SEMAGRAMME, LORIA
Graph Querying for Semantic Annotations
Jul 25, 2022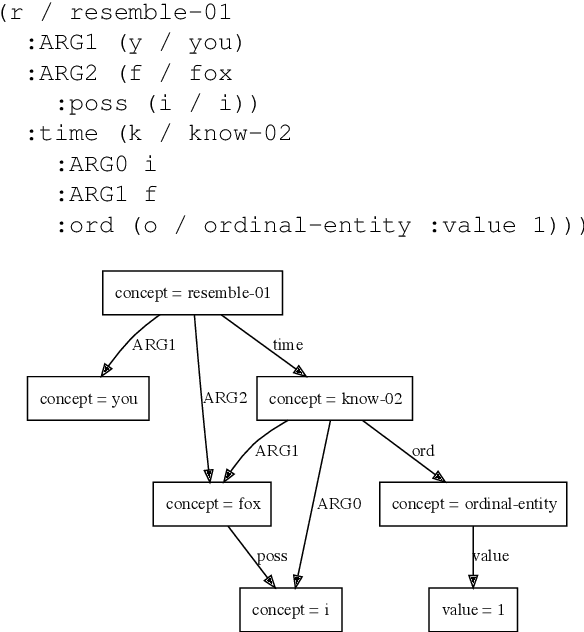
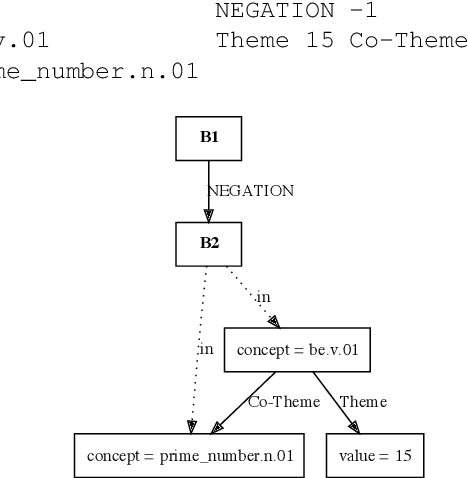
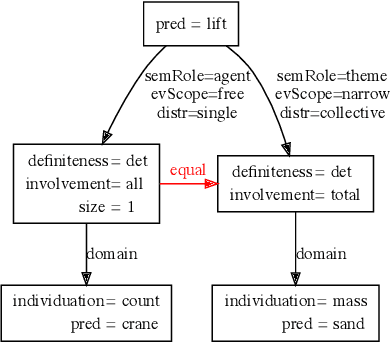
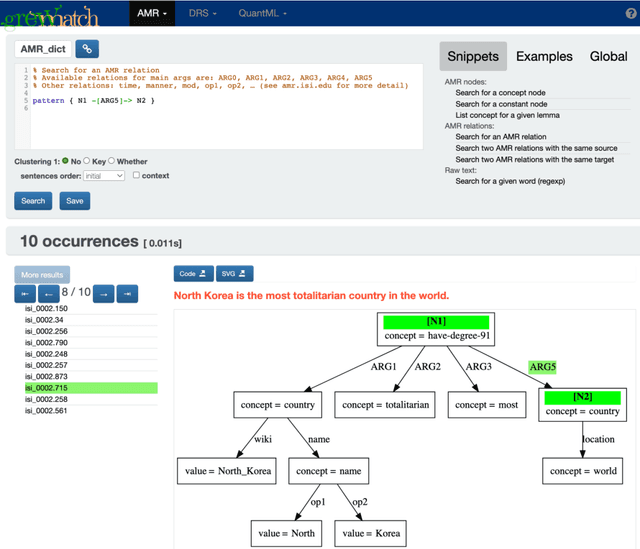
Abstract:This paper presents how the online tool GREW-MATCH can be used to make queries and visualise data from existing semantically annotated corpora. A dedicated syntax is available to construct simple to complex queries and execute them against a corpus. Such queries give transverse views of the annotated data, these views can help for checking the consistency of annotations in one corpus or across several corpora. GREW-MATCH can then be seen as an error mining tool: when inconsistencies are detected, it helps finding the sentences which should be fixed. Finally, GREW-MATCH can also be used as a side tool to assist annotation tasks helping to find annotation examples in existing corpora to be compared to the data to be annotated.
Motifs de graphe pour le calcul de dépendances syntaxiques complètes
Nov 18, 2010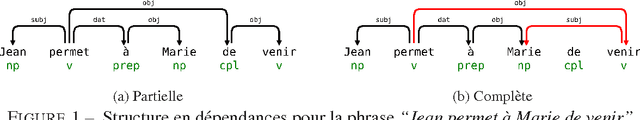
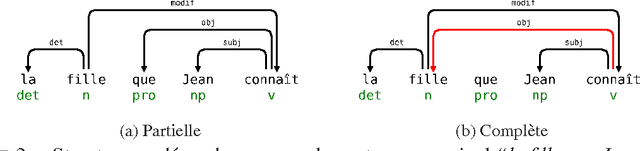
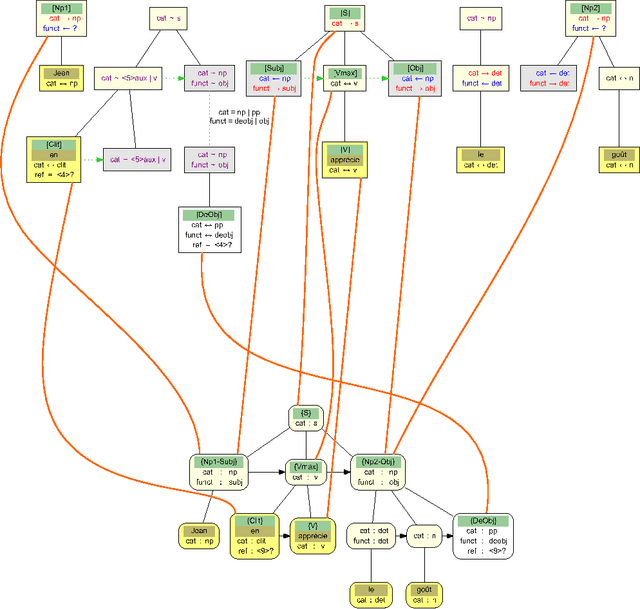
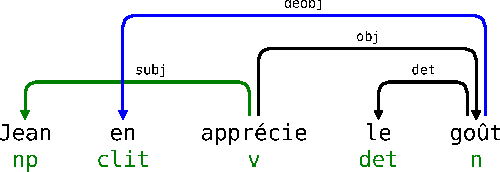
Abstract:This article describes a method to build syntactical dependencies starting from the phrase structure parsing process. The goal is to obtain all the information needed for a detailled semantical analysis. Interaction Grammars are used for parsing; the saturation of polarities which is the core of this formalism can be mapped to dependency relation. Formally, graph patterns are used to express the set of constraints which control dependency creations.
Analyse en dépendances à l'aide des grammaires d'interaction
Sep 18, 2009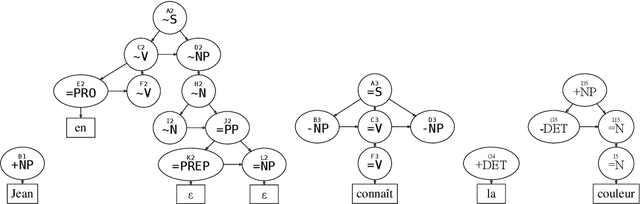
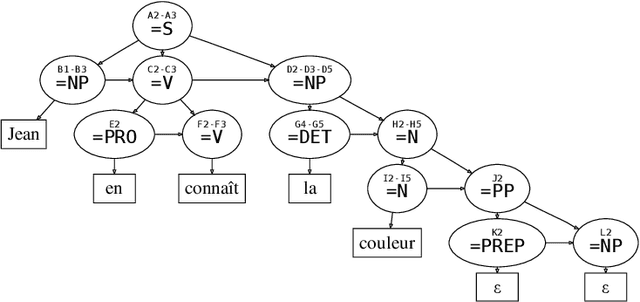


Abstract:This article proposes a method to extract dependency structures from phrase-structure level parsing with Interaction Grammars. Interaction Grammars are a formalism which expresses interactions among words using a polarity system. Syntactical composition is led by the saturation of polarities. Interactions take place between constituents, but as grammars are lexicalized, these interactions can be translated at the level of words. Dependency relations are extracted from the parsing process: every dependency is the consequence of a polarity saturation. The dependency relations we obtain can be seen as a refinement of the usual dependency tree. Generally speaking, this work sheds new light on links between phrase structure and dependency parsing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge