Mark Neerincx
Modelling prospective memory and resilient situated communications via Wizard of Oz
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:This abstract presents a scenario for human-robot action in a home setting involving an older adult and a robot. The scenario is designed to explore the envisioned modelling of memory for communication with a socially assistive robots (SAR). The scenario will enable the gathering of data on failures of speech technology and human-robot communication involving shared memory that may occur during daily activities such as a music-listening activity.
Designing for Meaningful Human Control in Military Human-Machine Teams
May 12, 2023



Abstract:We propose methods for analysis, design, and evaluation of Meaningful Human Control (MHC) for defense technologies from the perspective of military human-machine teaming (HMT). Our approach is based on three principles. Firstly, MHC should be regarded as a core objective that guides all phases of analysis, design and evaluation. Secondly, MHC affects all parts of the socio-technical system, including humans, machines, AI, interactions, and context. Lastly, MHC should be viewed as a property that spans longer periods of time, encompassing both prior and realtime control by multiple actors. To describe macrolevel design options for achieving MHC, we propose various Team Design Patterns. Furthermore, we present a case study, where we applied some of these methods to envision HMT, involving robots and soldiers in a search and rescue task in a military context.
A Machine with Short-Term, Episodic, and Semantic Memory Systems
Dec 05, 2022Abstract:Inspired by the cognitive science theory of the explicit human memory systems, we have modeled an agent with short-term, episodic, and semantic memory systems, each of which is modeled with a knowledge graph. To evaluate this system and analyze the behavior of this agent, we designed and released our own reinforcement learning agent environment, "the Room", where an agent has to learn how to encode, store, and retrieve memories to maximize its return by answering questions. We show that our deep Q-learning based agent successfully learns whether a short-term memory should be forgotten, or rather be stored in the episodic or semantic memory systems. Our experiments indicate that an agent with human-like memory systems can outperform an agent without this memory structure in the environment.
A Machine With Human-Like Memory Systems
Apr 04, 2022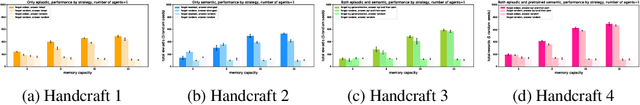
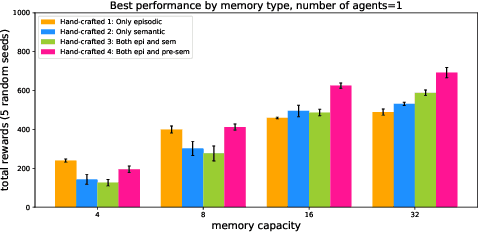
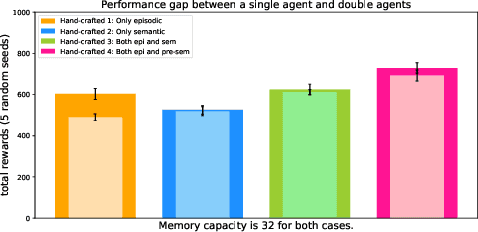
Abstract:Inspired by the cognitive science theory, we explicitly model an agent with both semantic and episodic memory systems, and show that it is better than having just one of the two memory systems. In order to show this, we have designed and released our own challenging environment, "the Room", compatible with OpenAI Gym, where an agent has to properly learn how to encode, store, and retrieve memories to maximize its rewards. The Room environment allows for a hybrid intelligence setup where machines and humans can collaborate. We show that two agents collaborating with each other results in better performance than one agent acting alone. We have open-sourced our code and models at https://github.com/tae898/explicit-memory.
A Blast From the Past: Personalizing Predictions of Video-Induced Emotions using Personal Memories as Context
Aug 27, 2020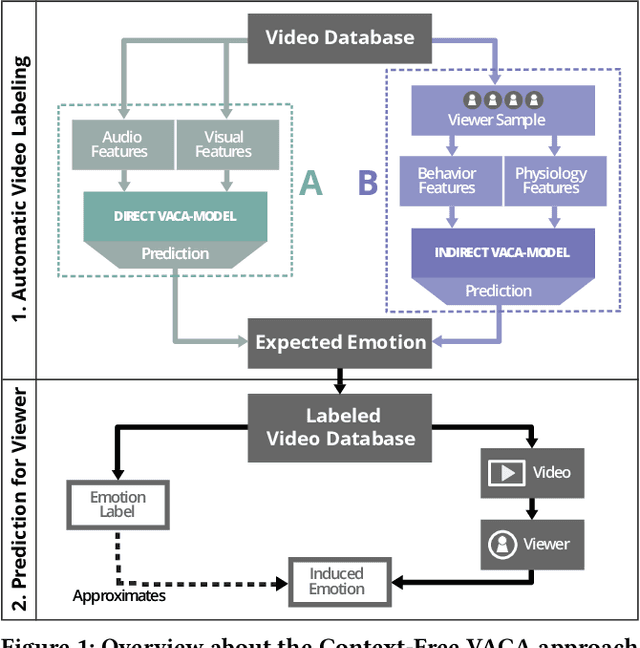
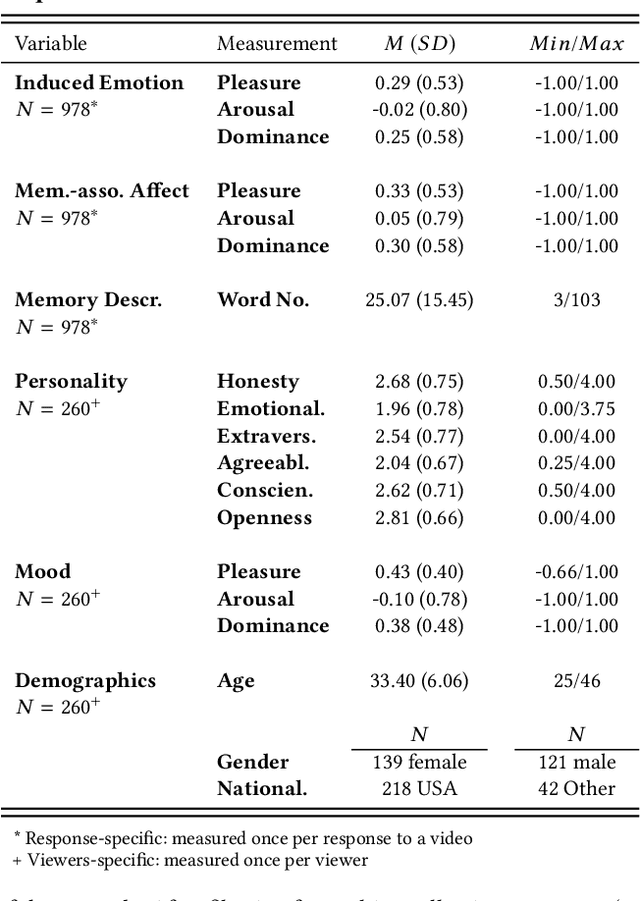
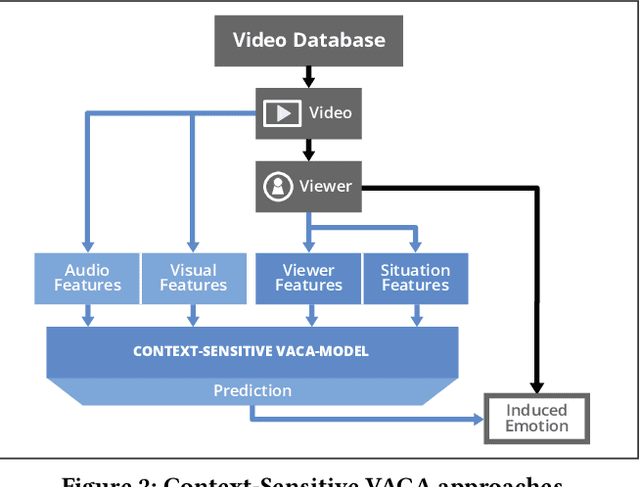

Abstract:A key challenge in the accurate prediction of viewers' emotional responses to video stimuli in real-world applications is accounting for person- and situation-specific variation. An important contextual influence shaping individuals' subjective experience of a video is the personal memories that it triggers in them. Prior research has found that this memory influence explains more variation in video-induced emotions than other contextual variables commonly used for personalizing predictions, such as viewers' demographics or personality. In this article, we show that (1) automatic analysis of text describing their video-triggered memories can account for variation in viewers' emotional responses, and (2) that combining such an analysis with that of a video's audiovisual content enhances the accuracy of automatic predictions. We discuss the relevance of these findings for improving on state of the art approaches to automated affective video analysis in personalized contexts.
Contrastive Explanations for Reinforcement Learning in terms of Expected Consequences
Jul 23, 2018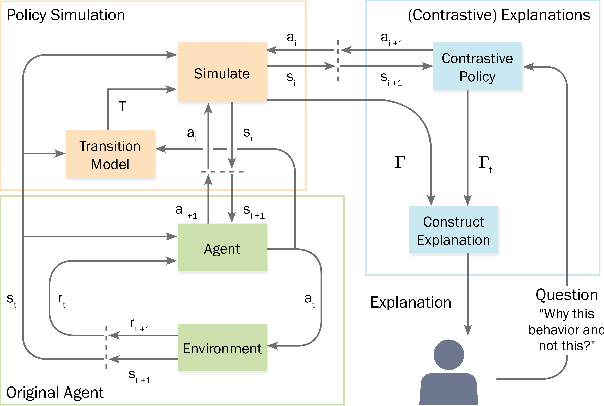

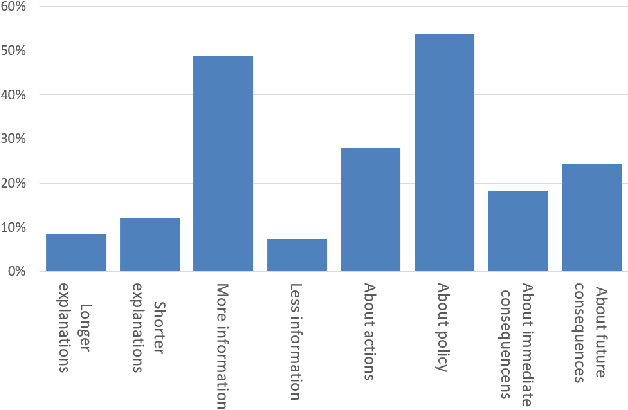
Abstract:Machine Learning models become increasingly proficient in complex tasks. However, even for experts in the field, it can be difficult to understand what the model learned. This hampers trust and acceptance, and it obstructs the possibility to correct the model. There is therefore a need for transparency of machine learning models. The development of transparent classification models has received much attention, but there are few developments for achieving transparent Reinforcement Learning (RL) models. In this study we propose a method that enables a RL agent to explain its behavior in terms of the expected consequences of state transitions and outcomes. First, we define a translation of states and actions to a description that is easier to understand for human users. Second, we developed a procedure that enables the agent to obtain the consequences of a single action, as well as its entire policy. The method calculates contrasts between the consequences of a policy derived from a user query, and of the learned policy of the agent. Third, a format for generating explanations was constructed. A pilot survey study was conducted to explore preferences of users for different explanation properties. Results indicate that human users tend to favor explanations about policy rather than about single actions.
* XAI workshop on the IJCAI conference 2018, Stockholm, Sweden
Contrastive Explanations with Local Foil Trees
Jun 19, 2018
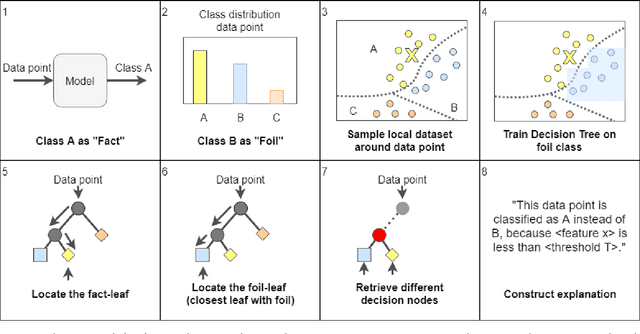
Abstract:Recent advances in interpretable Machine Learning (iML) and eXplainable AI (XAI) construct explanations based on the importance of features in classification tasks. However, in a high-dimensional feature space this approach may become unfeasible without restraining the set of important features. We propose to utilize the human tendency to ask questions like "Why this output (the fact) instead of that output (the foil)?" to reduce the number of features to those that play a main role in the asked contrast. Our proposed method utilizes locally trained one-versus-all decision trees to identify the disjoint set of rules that causes the tree to classify data points as the foil and not as the fact. In this study we illustrate this approach on three benchmark classification tasks.
A New UGV Teleoperation Interface for Improved Awareness of Network Connectivity and Physical Surroundings
Nov 07, 2017

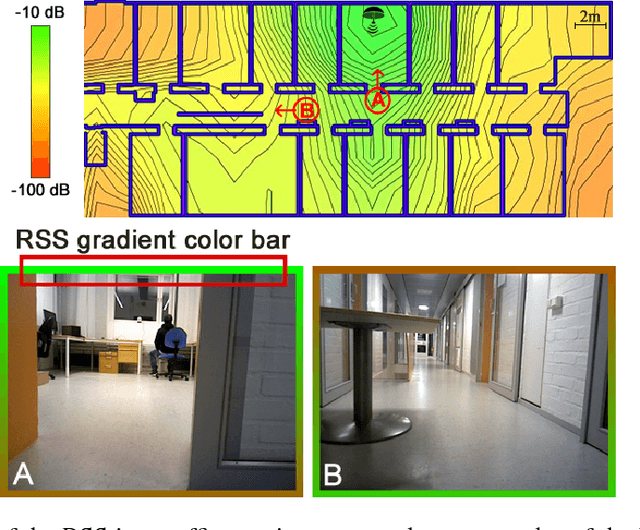
Abstract:A reliable wireless connection between the operator and the teleoperated Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV) is critical in many Urban Search and Rescue (USAR) missions. Unfortunately, as was seen in e.g. the Fukushima disaster, the networks available in areas where USAR missions take place are often severely limited in range and coverage. Therefore, during mission execution, the operator needs to keep track of not only the physical parts of the mission, such as navigating through an area or searching for victims, but also the variations in network connectivity across the environment. In this paper, we propose and evaluate a new teleoperation User Interface (UI) that includes a way of estimating the Direction of Arrival (DoA) of the Radio Signal Strength (RSS) and integrating the DoA information in the interface. The evaluation shows that using the interface results in more objects found, and less aborted missions due to connectivity problems, as compared to a standard interface. The proposed interface is an extension to an existing interface centered around the video stream captured by the UGV. But instead of just showing the network signal strength in terms of percent and a set of bars, the additional information of DoA is added in terms of a color bar surrounding the video feed. With this information, the operator knows what movement directions are safe, even when moving in regions close to the connectivity threshold.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge