Maja Schlereth
Department Artificial Intelligence in Biomedical Engineering, FAU Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Pattern Recognition Lab, FAU Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen
Decomposition Sampling for Efficient Region Annotations in Active Learning
Dec 08, 2025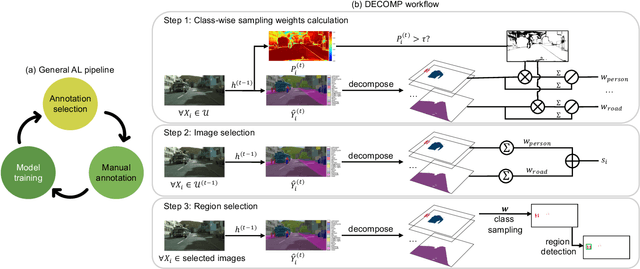
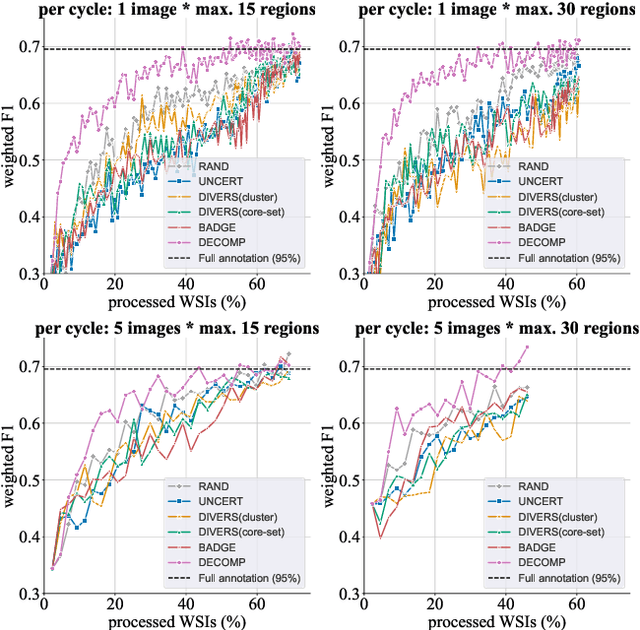
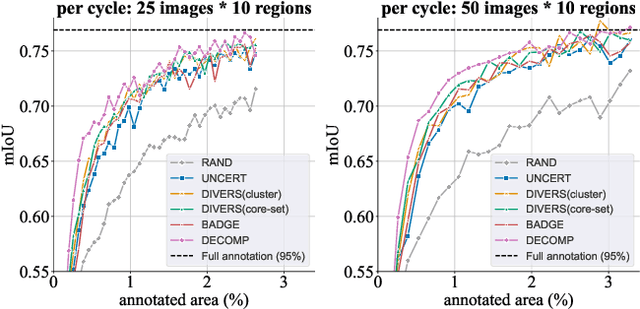
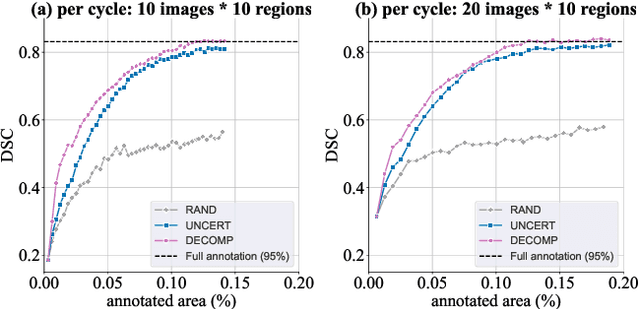
Abstract:Active learning improves annotation efficiency by selecting the most informative samples for annotation and model training. While most prior work has focused on selecting informative images for classification tasks, we investigate the more challenging setting of dense prediction, where annotations are more costly and time-intensive, especially in medical imaging. Region-level annotation has been shown to be more efficient than image-level annotation for these tasks. However, existing methods for representative annotation region selection suffer from high computational and memory costs, irrelevant region choices, and heavy reliance on uncertainty sampling. We propose decomposition sampling (DECOMP), a new active learning sampling strategy that addresses these limitations. It enhances annotation diversity by decomposing images into class-specific components using pseudo-labels and sampling regions from each class. Class-wise predictive confidence further guides the sampling process, ensuring that difficult classes receive additional annotations. Across ROI classification, 2-D segmentation, and 3-D segmentation, DECOMP consistently surpasses baseline methods by better sampling minority-class regions and boosting performance on these challenging classes. Code is in https://github.com/JingnaQiu/DECOMP.git.
Faster, Self-Supervised Super-Resolution for Anisotropic Multi-View MRI Using a Sparse Coordinate Loss
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Acquiring images in high resolution is often a challenging task. Especially in the medical sector, image quality has to be balanced with acquisition time and patient comfort. To strike a compromise between scan time and quality for Magnetic Resonance (MR) imaging, two anisotropic scans with different low-resolution (LR) orientations can be acquired. Typically, LR scans are analyzed individually by radiologists, which is time consuming and can lead to inaccurate interpretation. To tackle this, we propose a novel approach for fusing two orthogonal anisotropic LR MR images to reconstruct anatomical details in a unified representation. Our multi-view neural network is trained in a self-supervised manner, without requiring corresponding high-resolution (HR) data. To optimize the model, we introduce a sparse coordinate-based loss, enabling the integration of LR images with arbitrary scaling. We evaluate our method on MR images from two independent cohorts. Our results demonstrate comparable or even improved super-resolution (SR) performance compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) self-supervised SR methods for different upsampling scales. By combining a patient-agnostic offline and a patient-specific online phase, we achieve a substantial speed-up of up to ten times for patient-specific reconstruction while achieving similar or better SR quality. Code is available at https://github.com/MajaSchle/tripleSR.
Leveraging image captions for selective whole slide image annotation
Jul 08, 2024


Abstract:Acquiring annotations for whole slide images (WSIs)-based deep learning tasks, such as creating tissue segmentation masks or detecting mitotic figures, is a laborious process due to the extensive image size and the significant manual work involved in the annotation. This paper focuses on identifying and annotating specific image regions that optimize model training, given a limited annotation budget. While random sampling helps capture data variance by collecting annotation regions throughout the WSIs, insufficient data curation may result in an inadequate representation of minority classes. Recent studies proposed diversity sampling to select a set of regions that maximally represent unique characteristics of the WSIs. This is done by pretraining on unlabeled data through self-supervised learning and then clustering all regions in the latent space. However, establishing the optimal number of clusters can be difficult and not all clusters are task-relevant. This paper presents prototype sampling, a new method for annotation region selection. It discovers regions exhibiting typical characteristics of each task-specific class. The process entails recognizing class prototypes from extensive histopathology image-caption databases and detecting unlabeled image regions that resemble these prototypes. Our results show that prototype sampling is more effective than random and diversity sampling in identifying annotation regions with valuable training information, resulting in improved model performance in semantic segmentation and mitotic figure detection tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/DeepMicroscopy/Prototype-sampling.
Focus on Content not Noise: Improving Image Generation for Nuclei Segmentation by Suppressing Steganography in CycleGAN
Aug 03, 2023Abstract:Annotating nuclei in microscopy images for the training of neural networks is a laborious task that requires expert knowledge and suffers from inter- and intra-rater variability, especially in fluorescence microscopy. Generative networks such as CycleGAN can inverse the process and generate synthetic microscopy images for a given mask, thereby building a synthetic dataset. However, past works report content inconsistencies between the mask and generated image, partially due to CycleGAN minimizing its loss by hiding shortcut information for the image reconstruction in high frequencies rather than encoding the desired image content and learning the target task. In this work, we propose to remove the hidden shortcut information, called steganography, from generated images by employing a low pass filtering based on the DCT. We show that this increases coherence between generated images and cycled masks and evaluate synthetic datasets on a downstream nuclei segmentation task. Here we achieve an improvement of 5.4 percentage points in the F1-score compared to a vanilla CycleGAN. Integrating advanced regularization techniques into the CycleGAN architecture may help mitigate steganography-related issues and produce more accurate synthetic datasets for nuclei segmentation.
Adaptive Region Selection for Active Learning in Whole Slide Image Semantic Segmentation
Jul 14, 2023



Abstract:The process of annotating histological gigapixel-sized whole slide images (WSIs) at the pixel level for the purpose of training a supervised segmentation model is time-consuming. Region-based active learning (AL) involves training the model on a limited number of annotated image regions instead of requesting annotations of the entire images. These annotation regions are iteratively selected, with the goal of optimizing model performance while minimizing the annotated area. The standard method for region selection evaluates the informativeness of all square regions of a specified size and then selects a specific quantity of the most informative regions. We find that the efficiency of this method highly depends on the choice of AL step size (i.e., the combination of region size and the number of selected regions per WSI), and a suboptimal AL step size can result in redundant annotation requests or inflated computation costs. This paper introduces a novel technique for selecting annotation regions adaptively, mitigating the reliance on this AL hyperparameter. Specifically, we dynamically determine each region by first identifying an informative area and then detecting its optimal bounding box, as opposed to selecting regions of a uniform predefined shape and size as in the standard method. We evaluate our method using the task of breast cancer metastases segmentation on the public CAMELYON16 dataset and show that it consistently achieves higher sampling efficiency than the standard method across various AL step sizes. With only 2.6\% of tissue area annotated, we achieve full annotation performance and thereby substantially reduce the costs of annotating a WSI dataset. The source code is available at https://github.com/DeepMicroscopy/AdaptiveRegionSelection.
Automatic Classification of Neuromuscular Diseases in Children Using Photoacoustic Imaging
Jan 27, 2022
Abstract:Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) cause a significant burden for both healthcare systems and society. They can lead to severe progressive muscle weakness, muscle degeneration, contracture, deformity and progressive disability. The NMDs evaluated in this study often manifest in early childhood. As subtypes of disease, e.g. Duchenne Muscular Dystropy (DMD) and Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), are difficult to differentiate at the beginning and worsen quickly, fast and reliable differential diagnosis is crucial. Photoacoustic and ultrasound imaging has shown great potential to visualize and quantify the extent of different diseases. The addition of automatic classification of such image data could further improve standard diagnostic procedures. We compare deep learning-based 2-class and 3-class classifiers based on VGG16 for differentiating healthy from diseased muscular tissue. This work shows promising results with high accuracies above 0.86 for the 3-class problem and can be used as a proof of concept for future approaches for earlier diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring of NMDs.
Initial Investigations Towards Non-invasive Monitoring of Chronic Wound Healing Using Deep Learning and Ultrasound Imaging
Jan 25, 2022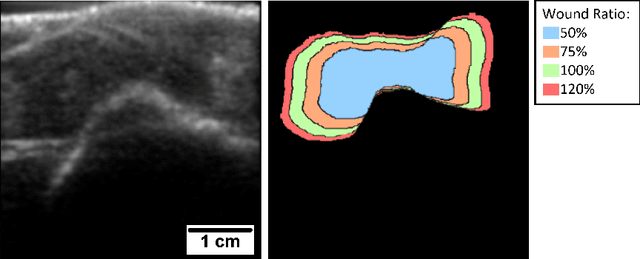

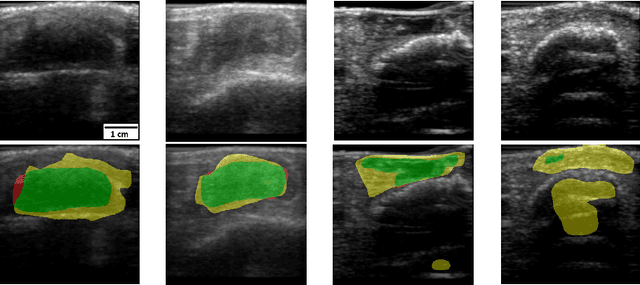
Abstract:Chronic wounds including diabetic and arterial/venous insufficiency injuries have become a major burden for healthcare systems worldwide. Demographic changes suggest that wound care will play an even bigger role in the coming decades. Predicting and monitoring response to therapy in wound care is currently largely based on visual inspection with little information on the underlying tissue. Thus, there is an urgent unmet need for innovative approaches that facilitate personalized diagnostics and treatments at the point-of-care. It has been recently shown that ultrasound imaging can monitor response to therapy in wound care, but this work required onerous manual image annotations. In this study, we present initial results of a deep learning-based automatic segmentation of cross-sectional wound size in ultrasound images and identify requirements and challenges for future research on this application. Evaluation of the segmentation results underscores the potential of the proposed deep learning approach to complement non-invasive imaging with Dice scores of 0.34 (U-Net, FCN) and 0.27 (ResNet-U-Net) but also highlights the need for improving robustness further. We conclude that deep learning-supported analysis of non-invasive ultrasound images is a promising area of research to automatically extract cross-sectional wound size and depth information with potential value in monitoring response to therapy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge