Lyle Palmer
Reading Race: AI Recognises Patient's Racial Identity In Medical Images
Jul 21, 2021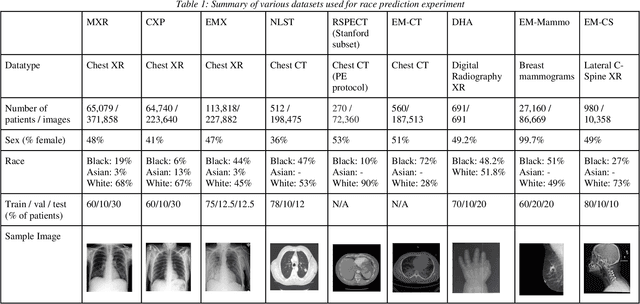
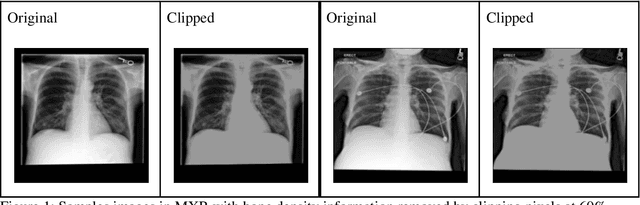
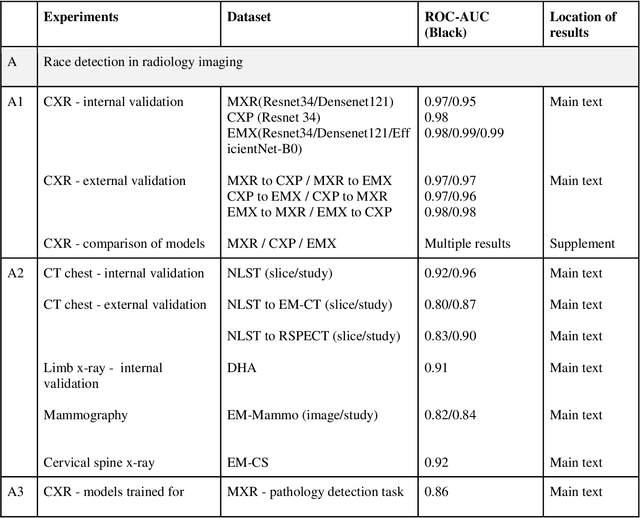
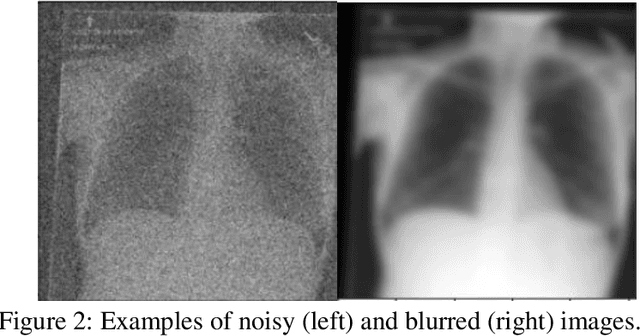
Abstract:Background: In medical imaging, prior studies have demonstrated disparate AI performance by race, yet there is no known correlation for race on medical imaging that would be obvious to the human expert interpreting the images. Methods: Using private and public datasets we evaluate: A) performance quantification of deep learning models to detect race from medical images, including the ability of these models to generalize to external environments and across multiple imaging modalities, B) assessment of possible confounding anatomic and phenotype population features, such as disease distribution and body habitus as predictors of race, and C) investigation into the underlying mechanism by which AI models can recognize race. Findings: Standard deep learning models can be trained to predict race from medical images with high performance across multiple imaging modalities. Our findings hold under external validation conditions, as well as when models are optimized to perform clinically motivated tasks. We demonstrate this detection is not due to trivial proxies or imaging-related surrogate covariates for race, such as underlying disease distribution. Finally, we show that performance persists over all anatomical regions and frequency spectrum of the images suggesting that mitigation efforts will be challenging and demand further study. Interpretation: We emphasize that model ability to predict self-reported race is itself not the issue of importance. However, our findings that AI can trivially predict self-reported race -- even from corrupted, cropped, and noised medical images -- in a setting where clinical experts cannot, creates an enormous risk for all model deployments in medical imaging: if an AI model secretly used its knowledge of self-reported race to misclassify all Black patients, radiologists would not be able to tell using the same data the model has access to.
A Bayesian Data Augmentation Approach for Learning Deep Models
Oct 29, 2017



Abstract:Data augmentation is an essential part of the training process applied to deep learning models. The motivation is that a robust training process for deep learning models depends on large annotated datasets, which are expensive to be acquired, stored and processed. Therefore a reasonable alternative is to be able to automatically generate new annotated training samples using a process known as data augmentation. The dominant data augmentation approach in the field assumes that new training samples can be obtained via random geometric or appearance transformations applied to annotated training samples, but this is a strong assumption because it is unclear if this is a reliable generative model for producing new training samples. In this paper, we provide a novel Bayesian formulation to data augmentation, where new annotated training points are treated as missing variables and generated based on the distribution learned from the training set. For learning, we introduce a theoretically sound algorithm --- generalised Monte Carlo expectation maximisation, and demonstrate one possible implementation via an extension of the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN). Classification results on MNIST, CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 show the better performance of our proposed method compared to the current dominant data augmentation approach mentioned above --- the results also show that our approach produces better classification results than similar GAN models.
Automated 5-year Mortality Prediction using Deep Learning and Radiomics Features from Chest Computed Tomography
Jul 01, 2016


Abstract:We propose new methods for the prediction of 5-year mortality in elderly individuals using chest computed tomography (CT). The methods consist of a classifier that performs this prediction using a set of features extracted from the CT image and segmentation maps of multiple anatomic structures. We explore two approaches: 1) a unified framework based on deep learning, where features and classifier are automatically learned in a single optimisation process; and 2) a multi-stage framework based on the design and selection/extraction of hand-crafted radiomics features, followed by the classifier learning process. Experimental results, based on a dataset of 48 annotated chest CTs, show that the deep learning model produces a mean 5-year mortality prediction accuracy of 68.5%, while radiomics produces a mean accuracy that varies between 56% to 66% (depending on the feature selection/extraction method and classifier). The successful development of the proposed models has the potential to make a profound impact in preventive and personalised healthcare.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge