Liyue Chen
STContext: A Multifaceted Dataset for Developing Context-aware Spatio-temporal Crowd Mobility Prediction Models
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:In smart cities, context-aware spatio-temporal crowd flow prediction (STCFP) models leverage contextual features (e.g., weather) to identify unusual crowd mobility patterns and enhance prediction accuracy. However, the best practice for incorporating contextual features remains unclear due to inconsistent usage of contextual features in different papers. Developing a multifaceted dataset with rich types of contextual features and STCFP scenarios is crucial for establishing a principled context modeling paradigm. Existing open crowd flow datasets lack an adequate range of contextual features, which poses an urgent requirement to build a multifaceted dataset to fill these research gaps. To this end, we create STContext, a multifaceted dataset for developing context-aware STCFP models. Specifically, STContext provides nine spatio-temporal datasets across five STCFP scenarios and includes ten contextual features, including weather, air quality index, holidays, points of interest, road networks, etc. Besides, we propose a unified workflow for incorporating contextual features into deep STCFP methods, with steps including feature transformation, dependency modeling, representation fusion, and training strategies. Through extensive experiments, we have obtained several useful guidelines for effective context modeling and insights for future research. The STContext is open-sourced at https://github.com/Liyue-Chen/STContext.
Efficient User Sequence Learning for Online Services via Compressed Graph Neural Networks
Jun 05, 2024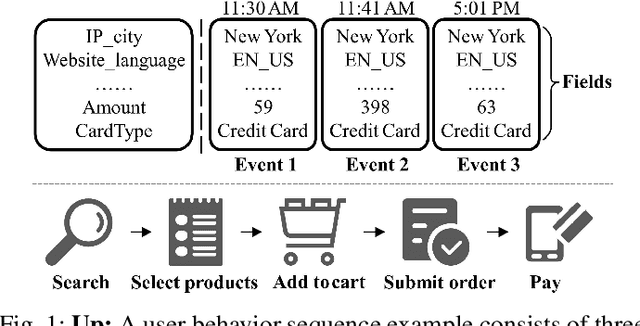
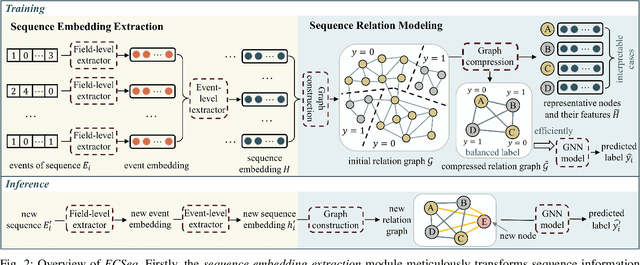
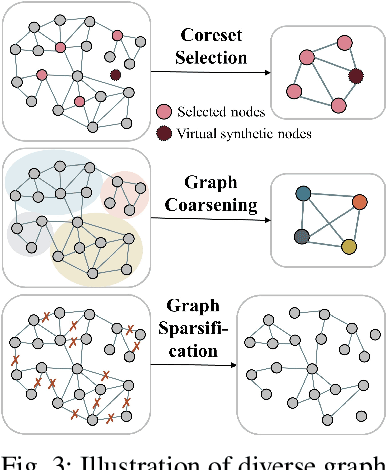
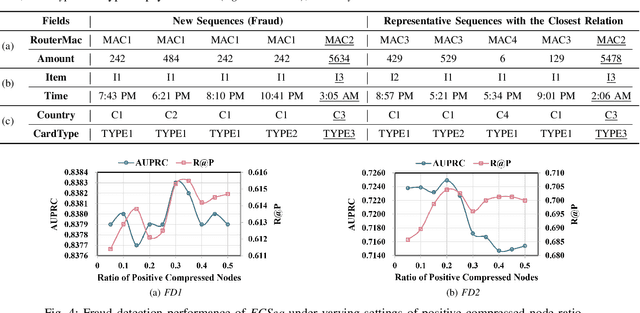
Abstract:Learning representations of user behavior sequences is crucial for various online services, such as online fraudulent transaction detection mechanisms. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have been extensively applied to model sequence relationships, and extract information from similar sequences. While user behavior sequence data volume is usually huge for online applications, directly applying GNN models may lead to substantial computational overhead during both the training and inference stages and make it challenging to meet real-time requirements for online services. In this paper, we leverage graph compression techniques to alleviate the efficiency issue. Specifically, we propose a novel unified framework called ECSeq, to introduce graph compression techniques into relation modeling for user sequence representation learning. The key module of ECSeq is sequence relation modeling, which explores relationships among sequences to enhance sequence representation learning, and employs graph compression algorithms to achieve high efficiency and scalability. ECSeq also exhibits plug-and-play characteristics, seamlessly augmenting pre-trained sequence representation models without modifications. Empirical experiments on both sequence classification and regression tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of ECSeq. Specifically, with an additional training time of tens of seconds in total on 100,000+ sequences and inference time preserved within $10^{-4}$ seconds/sample, ECSeq improves the prediction R@P$_{0.9}$ of the widely used LSTM by $\sim 5\%$.
A Unified Model for Spatio-Temporal Prediction Queries with Arbitrary Modifiable Areal Units
Mar 10, 2024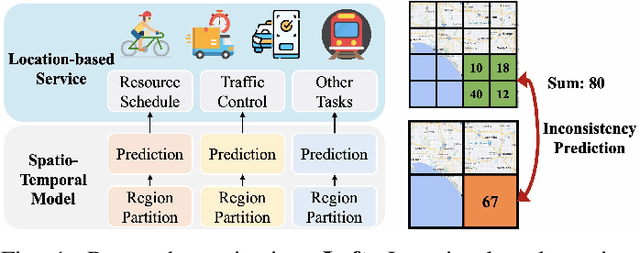
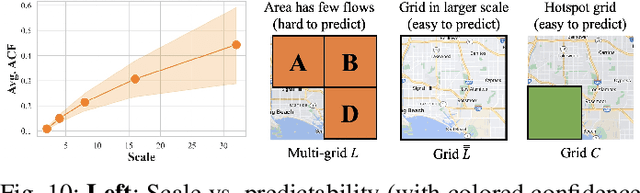
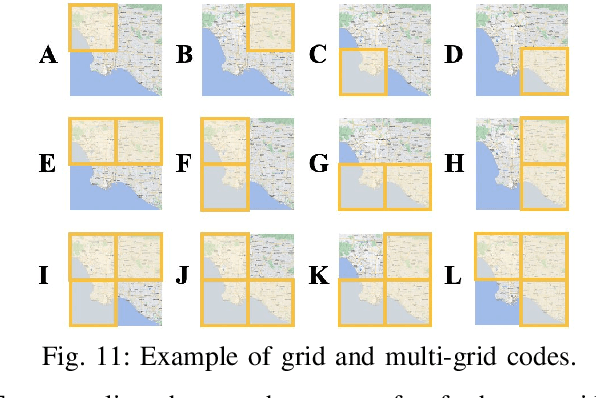
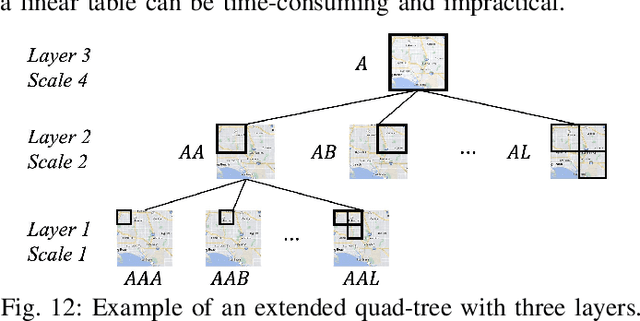
Abstract:Spatio-Temporal (ST) prediction is crucial for making informed decisions in urban location-based applications like ride-sharing. However, existing ST models often require region partition as a prerequisite, resulting in two main pitfalls. Firstly, location-based services necessitate ad-hoc regions for various purposes, requiring multiple ST models with varying scales and zones, which can be costly to support. Secondly, different ST models may produce conflicting outputs, resulting in confusing predictions. In this paper, we propose One4All-ST, a framework that can conduct ST prediction for arbitrary modifiable areal units using only one model. To reduce the cost of getting multi-scale predictions, we design an ST network with hierarchical spatial modeling and scale normalization modules to efficiently and equally learn multi-scale representations. To address prediction inconsistencies across scales, we propose a dynamic programming scheme to solve the formulated optimal combination problem, minimizing predicted error through theoretical analysis. Besides, we suggest using an extended quad-tree to index the optimal combinations for quick response to arbitrary modifiable areal units in practical online scenarios. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets verify the efficiency and effectiveness of One4All-ST in ST prediction for arbitrary modifiable areal units. The source codes and data of this work are available at https://github.com/uctb/One4All-ST.
Knowledge-inspired Subdomain Adaptation for Cross-Domain Knowledge Transfer
Aug 17, 2023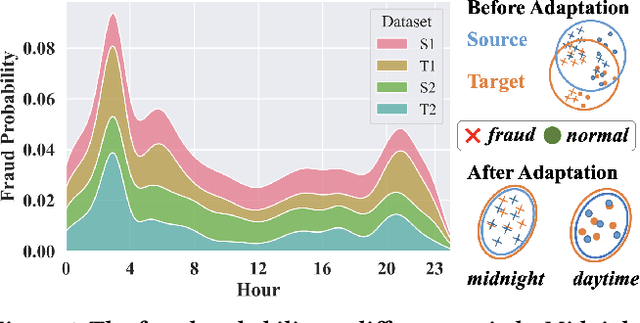
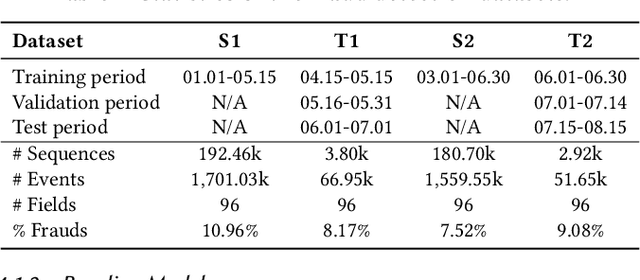
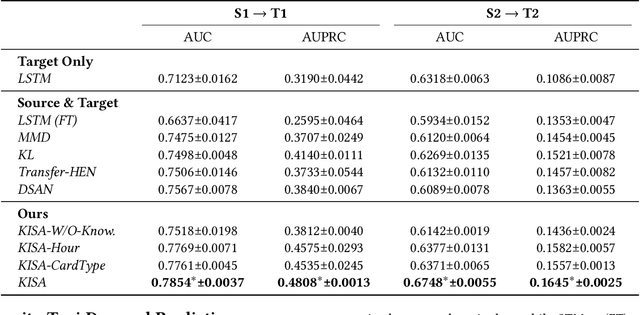
Abstract:Most state-of-the-art deep domain adaptation techniques align source and target samples in a global fashion. That is, after alignment, each source sample is expected to become similar to any target sample. However, global alignment may not always be optimal or necessary in practice. For example, consider cross-domain fraud detection, where there are two types of transactions: credit and non-credit. Aligning credit and non-credit transactions separately may yield better performance than global alignment, as credit transactions are unlikely to exhibit patterns similar to non-credit transactions. To enable such fine-grained domain adaption, we propose a novel Knowledge-Inspired Subdomain Adaptation (KISA) framework. In particular, (1) We provide the theoretical insight that KISA minimizes the shared expected loss which is the premise for the success of domain adaptation methods. (2) We propose the knowledge-inspired subdomain division problem that plays a crucial role in fine-grained domain adaption. (3) We design a knowledge fusion network to exploit diverse domain knowledge. Extensive experiments demonstrate that KISA achieves remarkable results on fraud detection and traffic demand prediction tasks.
UCTB: An Urban Computing Tool Box for Spatiotemporal Crowd Flow Prediction
Jun 07, 2023Abstract:Spatiotemporal crowd flow prediction is one of the key technologies in smart cities. Currently, there are two major pain points that plague related research and practitioners. Firstly, crowd flow is related to multiple domain knowledge factors; however, due to the diversity of application scenarios, it is difficult for subsequent work to make reasonable and comprehensive use of domain knowledge. Secondly, with the development of deep learning technology, the implementation of relevant techniques has become increasingly complex; reproducing advanced models has become a time-consuming and increasingly cumbersome task. To address these issues, we design and implement a spatiotemporal crowd flow prediction toolbox called UCTB (Urban Computing Tool Box), which integrates multiple spatiotemporal domain knowledge and state-of-the-art models simultaneously. The relevant code and supporting documents have been open-sourced at https://github.com/uctb/UCTB.
A Data-driven Region Generation Framework for Spatiotemporal Transportation Service Management
Jun 05, 2023Abstract:MAUP (modifiable areal unit problem) is a fundamental problem for spatial data management and analysis. As an instantiation of MAUP in online transportation platforms, region generation (i.e., specifying the areal unit for service operations) is the first and vital step for supporting spatiotemporal transportation services such as ride-sharing and freight transport. Most existing region generation methods are manually specified (e.g., fixed-size grids), suffering from poor spatial semantic meaning and inflexibility to meet service operation requirements. In this paper, we propose RegionGen, a data-driven region generation framework that can specify regions with key characteristics (e.g., good spatial semantic meaning and predictability) by modeling region generation as a multi-objective optimization problem. First, to obtain good spatial semantic meaning, RegionGen segments the whole city into atomic spatial elements based on road networks and obstacles (e.g., rivers). Then, it clusters the atomic spatial elements into regions by maximizing various operation characteristics, which is formulated as a multi-objective optimization problem. For this optimization problem, we propose a multi-objective co-optimization algorithm. Extensive experiments verify that RegionGen can generate more suitable regions than traditional methods for spatiotemporal service management.
Exploring Context Modeling Techniques on the Spatiotemporal Crowd Flow Prediction
Jun 30, 2021



Abstract:In the big data and AI era, context is widely exploited as extra information which makes it easier to learn a more complex pattern in machine learning systems. However, most of the existing related studies seldom take context into account. The difficulty lies in the unknown generalization ability of both context and its modeling techniques across different scenarios. To fill the above gaps, we conduct a large-scale analytical and empirical study on the spatiotemporal crowd prediction (STCFP) problem that is a widely-studied and hot research topic. We mainly make three efforts:(i) we develop new taxonomy about both context features and context modeling techniques based on extensive investigations in prevailing STCFP research; (ii) we conduct extensive experiments on seven datasets with hundreds of millions of records to quantitatively evaluate the generalization ability of both distinct context features and context modeling techniques; (iii) we summarize some guidelines for researchers to conveniently utilize context in diverse applications.
Exploring the Generalizability of Spatio-Temporal Crowd Flow Prediction: Meta-Modeling and an Analytic Framework
Sep 20, 2020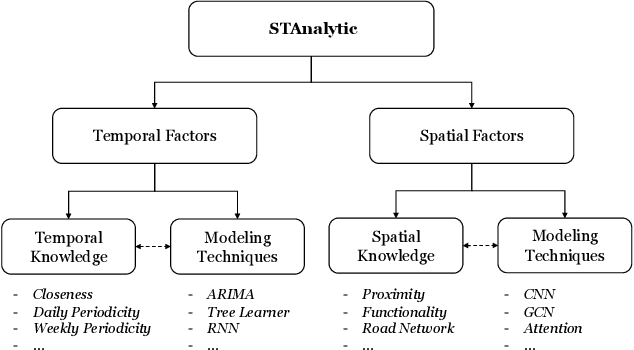
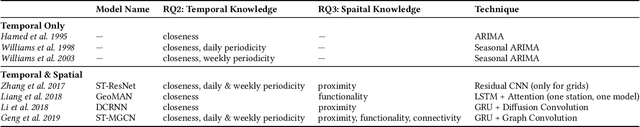
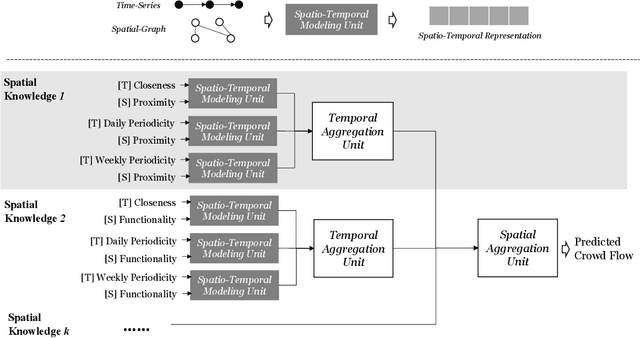
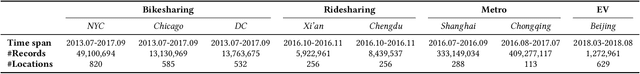
Abstract:The Spatio-Temporal Crowd Flow Prediction (STCFP) problem is a classical problem with plenty of prior research efforts that benefit from traditional statistical learning and recent deep learning approaches. While STCFP can refer to many real-world problems, most existing studies focus on quite specific applications, such as the prediction of taxi demand, ridesharing order, and so on. This hinders the STCFP research as the approaches designed for different applications are hardly comparable, and thus how an applicationdriven approach can be generalized to other scenarios is unclear. To fill in this gap, this paper makes two efforts: (i) we propose an analytic framework, called STAnalytic, to qualitatively investigate STCFP approaches regarding their design considerations on various spatial and temporal factors, aiming to make different application-driven approaches comparable; (ii) we construct an extensively large-scale STCFP benchmark datasets with four different scenarios (including ridesharing, bikesharing, metro, and electrical vehicle charging) with up to hundreds of millions of flow records, to quantitatively measure the generalizability of STCFP approaches. Furthermore, to elaborate the effectiveness of STAnalytic in helping design generalizable STCFP approaches, we propose a spatio-temporal meta-model, called STMeta, by integrating generalizable temporal and spatial knowledge identified by STAnalytic. We implement three variants of STMeta with different deep learning techniques. With the datasets, we demonstrate that STMeta variants can outperform state-of-the-art STCFP approaches by 5%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge