Lianghao Tan
An Improved Dung Beetle Optimizer for Random Forest Optimization
Nov 24, 2024



Abstract:To improve the convergence speed and optimization accuracy of the Dung Beetle Optimizer (DBO), this paper proposes an improved algorithm based on circle mapping and longitudinal-horizontal crossover strategy (CICRDBO). First, the Circle method is used to map the initial population to increase diversity. Second, the longitudinal-horizontal crossover strategy is applied to enhance the global search ability by ensuring the position updates of the dung beetle. Simulations were conducted on 10 benchmark test functions, and the results demonstrate that the improved algorithm performs well in both convergence speed and optimization accuracy. The improved algorithm is further applied to the hyperparameter selection of the Random Forest classification algorithm for binary classification prediction in the retail industry. Various combination comparisons prove the practicality of the improved algorithm, followed by SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) analysis.
CIB-SE-YOLOv8: Optimized YOLOv8 for Real-Time Safety Equipment Detection on Construction Sites
Oct 28, 2024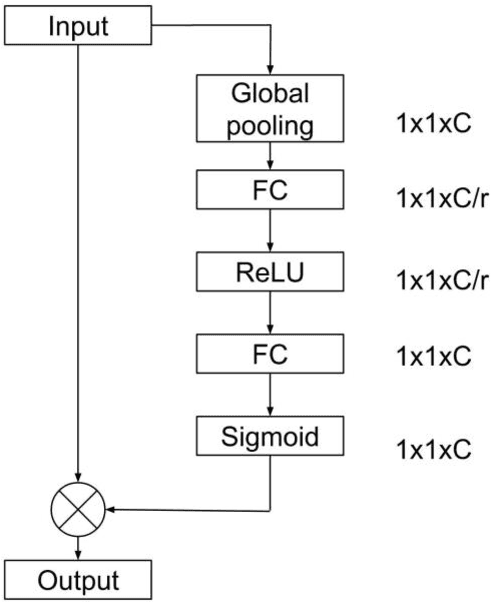
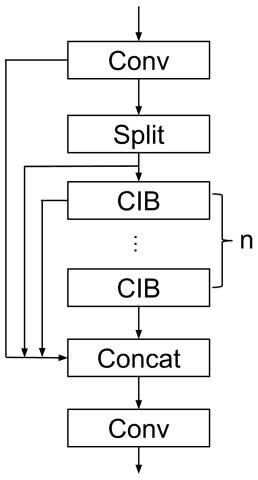
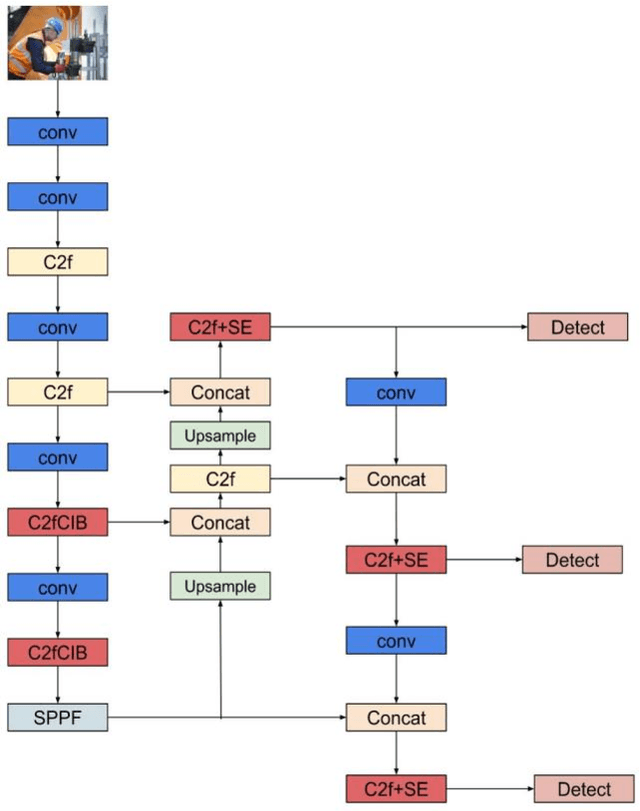

Abstract:Ensuring safety on construction sites is critical, with helmets playing a key role in reducing injuries. Traditional safety checks are labor-intensive and often insufficient. This study presents a computer vision-based solution using YOLO for real-time helmet detection, leveraging the SHEL5K dataset. Our proposed CIB-SE-YOLOv8 model incorporates SE attention mechanisms and modified C2f blocks, enhancing detection accuracy and efficiency. This model offers a more effective solution for promoting safety compliance on construction sites.
Enhancing Skin Lesion Diagnosis with Ensemble Learning
Sep 06, 2024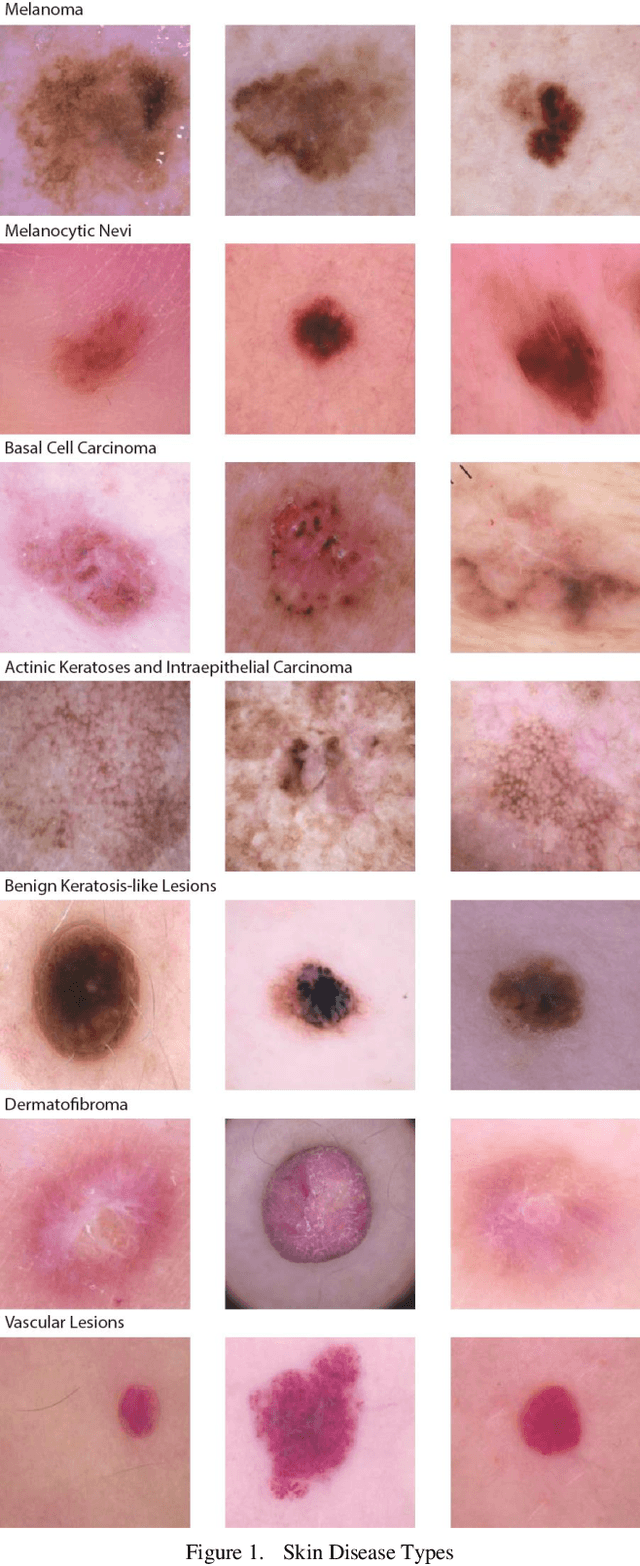
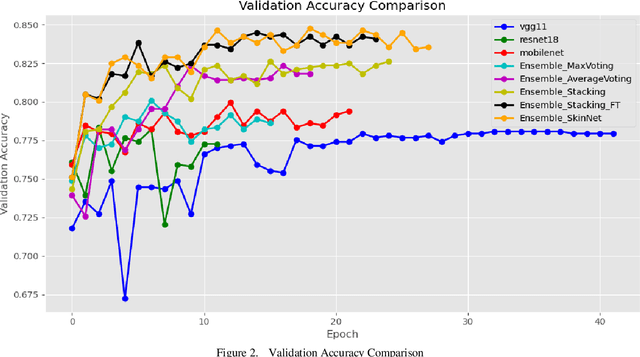
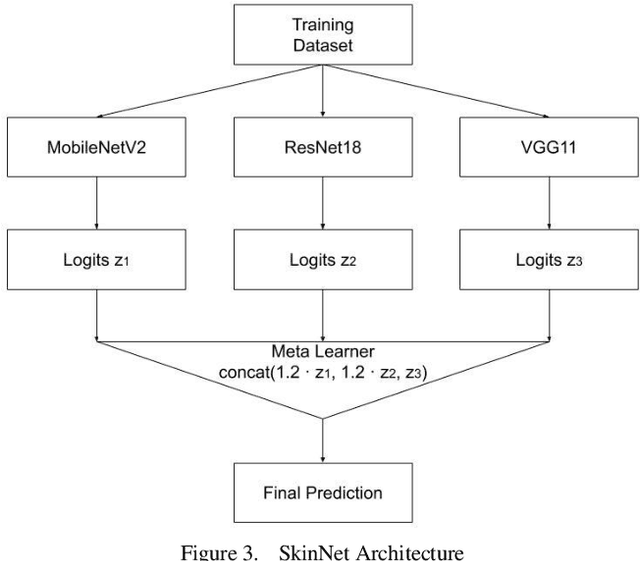
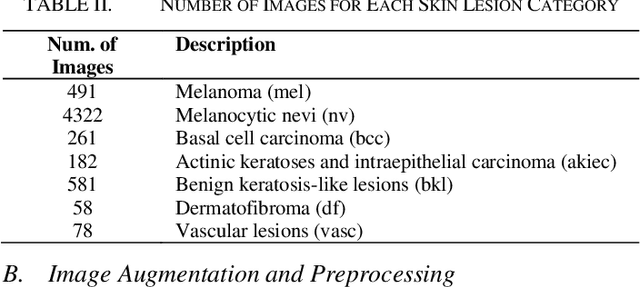
Abstract:Skin lesions are an increasingly significant medical concern, varying widely in severity from benign to cancerous. Accurate diagnosis is essential for ensuring timely and appropriate treatment. This study examines the implementation of deep learning methods to assist in the diagnosis of skin lesions using the HAM10000 dataset, which contains seven distinct types of lesions. First, we evaluated three pre-trained models: MobileNetV2, ResNet18, and VGG11, achieving accuracies of 0.798, 0.802, and 0.805, respectively. To further enhance classification accuracy, we developed ensemble models employing max voting, average voting, and stacking, resulting in accuracies of 0.803, 0.82, and 0.83. Building on the best-performing ensemble learning model, stacking, we developed our proposed model, SkinNet, which incorporates a customized architecture and fine-tuning, achieving an accuracy of 0.867 and an AUC of 0.96. This substantial improvement over individual models demonstrates the effectiveness of ensemble learning in improving skin lesion classification.
Deep Learning for Lung Disease Classification Using Transfer Learning and a Customized CNN Architecture with Attention
Aug 23, 2024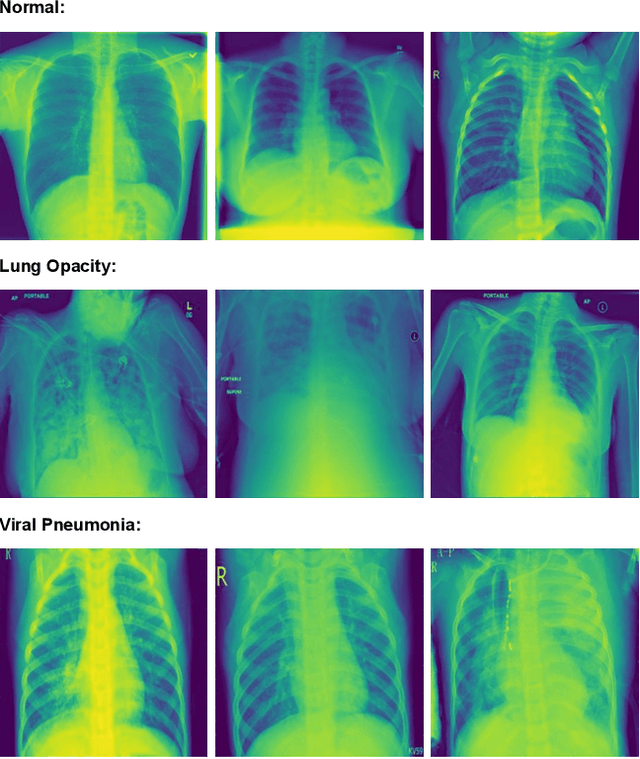
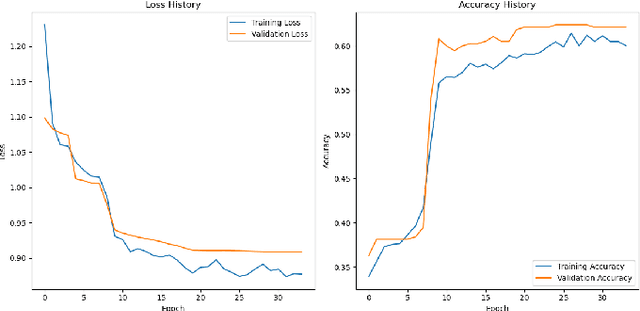
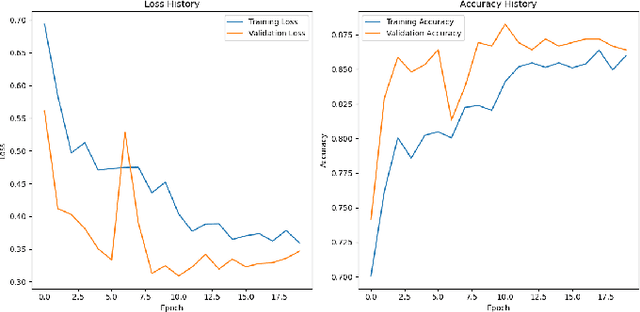
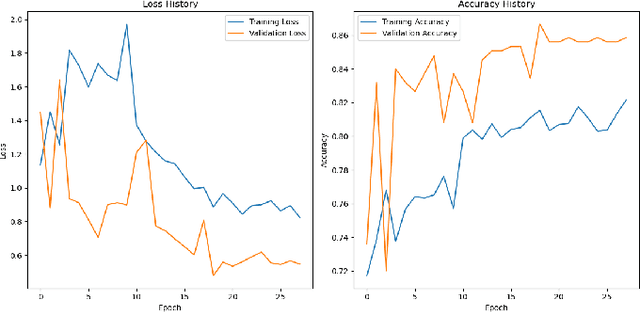
Abstract:Many people die from lung-related diseases every year. X-ray is an effective way to test if one is diagnosed with a lung-related disease or not. This study concentrates on categorizing three distinct types of lung X-rays: those depicting healthy lungs, those showing lung opacities, and those indicative of viral pneumonia. Accurately diagnosing the disease at an early phase is critical. In this paper, five different pre-trained models will be tested on the Lung X-ray Image Dataset. SqueezeNet, VGG11, ResNet18, DenseNet, and MobileNetV2 achieved accuracies of 0.64, 0.85, 0.87, 0.88, and 0.885, respectively. MobileNetV2, as the best-performing pre-trained model, will then be further analyzed as the base model. Eventually, our own model, MobileNet-Lung based on MobileNetV2, with fine-tuning and an additional layer of attention within feature layers, was invented to tackle the lung disease classification task and achieved an accuracy of 0.933. This result is significantly improved compared with all five pre-trained models.
Adaptive Friction in Deep Learning: Enhancing Optimizers with Sigmoid and Tanh Function
Aug 07, 2024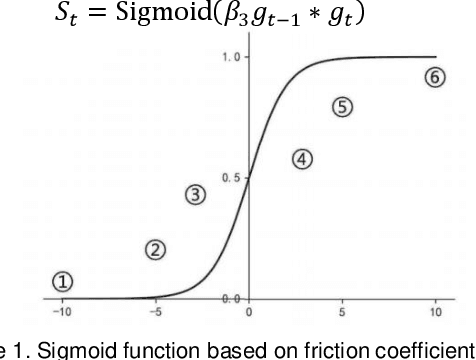
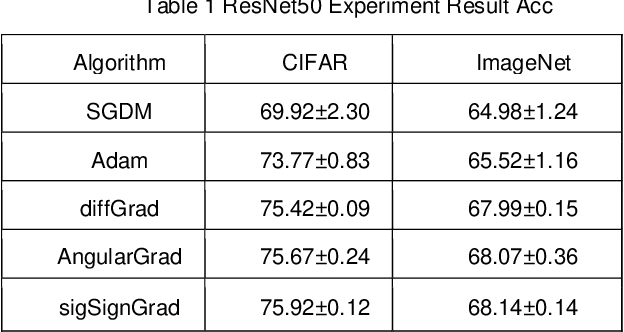
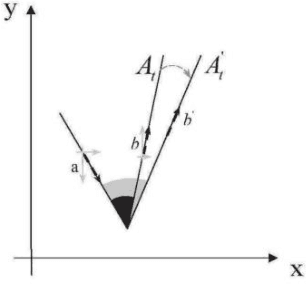
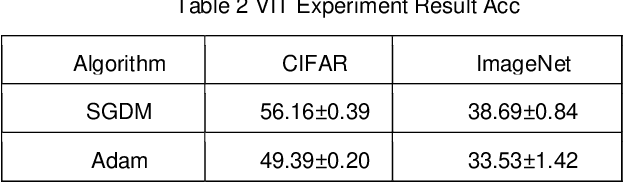
Abstract:Adaptive optimizers are pivotal in guiding the weight updates of deep neural networks, yet they often face challenges such as poor generalization and oscillation issues. To counter these, we introduce sigSignGrad and tanhSignGrad, two novel optimizers that integrate adaptive friction coefficients based on the Sigmoid and Tanh functions, respectively. These algorithms leverage short-term gradient information, a feature overlooked in traditional Adam variants like diffGrad and AngularGrad, to enhance parameter updates and convergence.Our theoretical analysis demonstrates the wide-ranging adjustment capability of the friction coefficient S, which aligns with targeted parameter update strategies and outperforms existing methods in both optimization trajectory smoothness and convergence rate. Extensive experiments on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and Mini-ImageNet datasets using ResNet50 and ViT architectures confirm the superior performance of our proposed optimizers, showcasing improved accuracy and reduced training time. The innovative approach of integrating adaptive friction coefficients as plug-ins into existing optimizers, exemplified by the sigSignAdamW and sigSignAdamP variants, presents a promising strategy for boosting the optimization performance of established algorithms. The findings of this study contribute to the advancement of optimizer design in deep learning.
Enhanced Self-Checkout System for Retail Based on Improved YOLOv10
Jul 31, 2024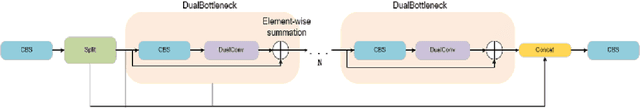
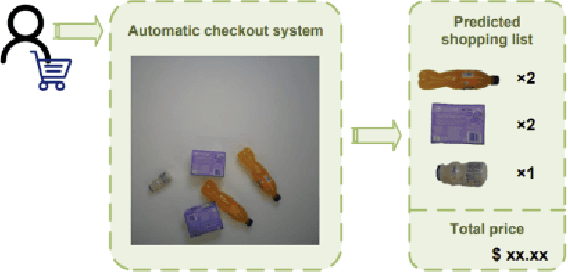
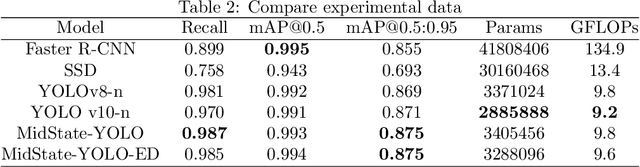
Abstract:With the rapid advancement of deep learning technologies, computer vision has shown immense potential in retail automation. This paper presents a novel self-checkout system for retail based on an improved YOLOv10 network, aimed at enhancing checkout efficiency and reducing labor costs. We propose targeted optimizations to the YOLOv10 model, by incorporating the detection head structure from YOLOv8, which significantly improves product recognition accuracy. Additionally, we develop a post-processing algorithm tailored for self-checkout scenarios, to further enhance the application of system. Experimental results demonstrate that our system outperforms existing methods in both product recognition accuracy and checkout speed. This research not only provides a new technical solution for retail automation but offers valuable insights into optimizing deep learning models for real-world applications.
Automatic News Generation and Fact-Checking System Based on Language Processing
May 17, 2024Abstract:This paper explores an automatic news generation and fact-checking system based on language processing, aimed at enhancing the efficiency and quality of news production while ensuring the authenticity and reliability of the news content. With the rapid development of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and deep learning technologies, automatic news generation systems are capable of extracting key information from massive data and generating well-structured, fluent news articles. Meanwhile, by integrating fact-checking technology, the system can effectively prevent the spread of false news and improve the accuracy and credibility of news. This study details the key technologies involved in automatic news generation and factchecking, including text generation, information extraction, and the application of knowledge graphs, and validates the effectiveness of these technologies through experiments. Additionally, the paper discusses the future development directions of automatic news generation and fact-checking systems, emphasizing the importance of further integration and innovation of technologies. The results show that with continuous technological optimization and practical application, these systems will play an increasingly important role in the future news industry, providing more efficient and reliable news services.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge