Li Qian
SparkRA: A Retrieval-Augmented Knowledge Service System Based on Spark Large Language Model
Aug 13, 2024
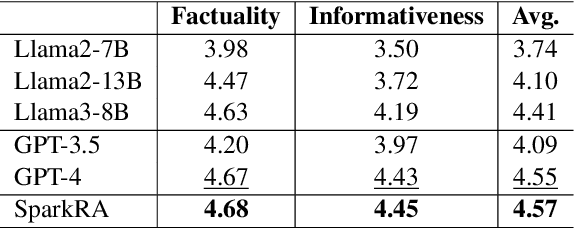

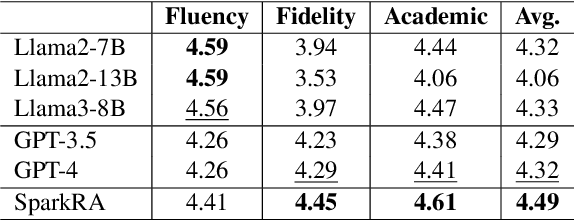
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable achievements across various language tasks.To enhance the performance of LLMs in scientific literature services, we developed the scientific literature LLM (SciLit-LLM) through pre-training and supervised fine-tuning on scientific literature, building upon the iFLYTEK Spark LLM. Furthermore, we present a knowledge service system Spark Research Assistant (SparkRA) based on our SciLit-LLM. SparkRA is accessible online and provides three primary functions: literature investigation, paper reading, and academic writing. As of July 30, 2024, SparkRA has garnered over 50,000 registered users, with a total usage count exceeding 1.3 million.
UniMC: A Unified Framework for Long-Term Memory Conversation via Relevance Representation Learning
Jun 18, 2023



Abstract:Open-domain long-term memory conversation can establish long-term intimacy with humans, and the key is the ability to understand and memorize long-term dialogue history information. Existing works integrate multiple models for modelling through a pipeline, which ignores the coupling between different stages. In this paper, we propose a Unified framework for Long-term Memory Conversations (UniMC), which increases the connection between different stages by learning relevance representation. Specifically, we decompose the main task into three subtasks based on probability graphs: 1) conversation summarization, 2) memory retrieval, 3) memory-augmented generation. Each subtask involves learning a representation for calculating the relevance between the query and memory, which is modelled by inserting a special token at the beginning of the decoder input. The relevance representation learning strengthens the connection across subtasks through parameter sharing and joint training. Extensive experimental results show that the proposed method consistently improves over strong baselines and yields better dialogue consistency and engagingness.
Distinguishability Calibration to In-Context Learning
Feb 13, 2023Abstract:Recent years have witnessed increasing interests in prompt-based learning in which models can be trained on only a few annotated instances, making them suitable in low-resource settings. When using prompt-based learning for text classification, the goal is to use a pre-trained language model (PLM) to predict a missing token in a pre-defined template given an input text, which can be mapped to a class label. However, PLMs built on the transformer architecture tend to generate similar output embeddings, making it difficult to discriminate between different class labels. The problem is further exacerbated when dealing with classification tasks involving many fine-grained class labels. In this work, we alleviate this information diffusion issue, i.e., different tokens share a large proportion of similar information after going through stacked multiple self-attention layers in a transformer, by proposing a calibration method built on feature transformations through rotation and scaling to map a PLM-encoded embedding into a new metric space to guarantee the distinguishability of the resulting embeddings. Furthermore, we take the advantage of hyperbolic embeddings to capture the hierarchical relations among fine-grained class-associated token embedding by a coarse-to-fine metric learning strategy to enhance the distinguishability of the learned output embeddings. Extensive experiments on the three datasets under various settings demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Our code can be found at https://github.com/donttal/TARA.
Transfer Learning for Scientific Data Chain Extraction in Small Chemical Corpus with BERT-CRF Model
May 13, 2019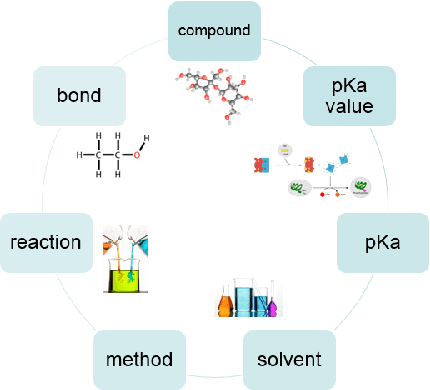
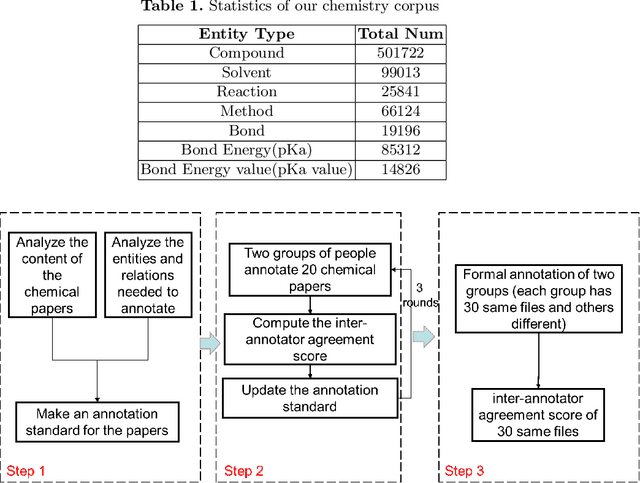
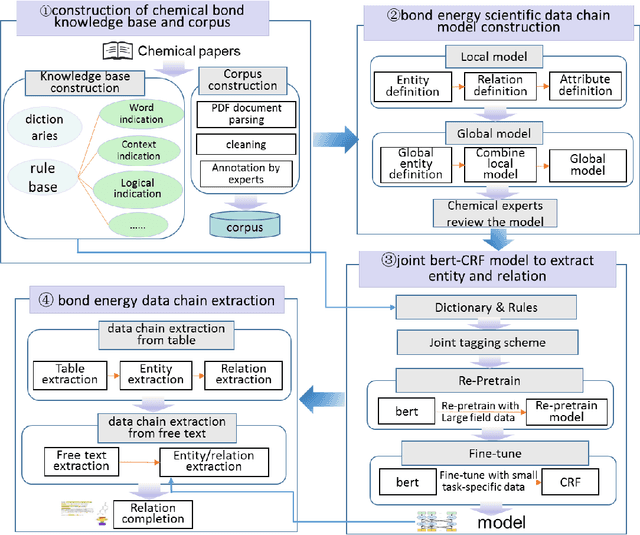
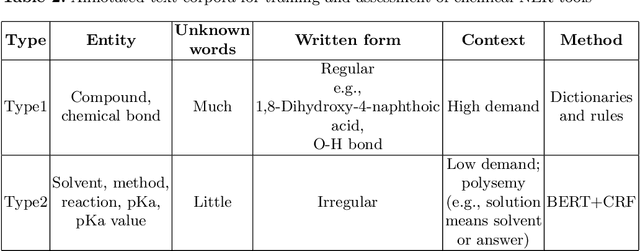
Abstract:Computational chemistry develops fast in recent years due to the rapid growth and breakthroughs in AI. Thanks for the progress in natural language processing, researchers can extract more fine-grained knowledge in publications to stimulate the development in computational chemistry. While the works and corpora in chemical entity extraction have been restricted in the biomedicine or life science field instead of the chemistry field, we build a new corpus in chemical bond field annotated for 7 types of entities: compound, solvent, method, bond, reaction, pKa and pKa value. This paper presents a novel BERT-CRF model to build scientific chemical data chains by extracting 7 chemical entities and relations from publications. And we propose a joint model to extract the entities and relations simultaneously. Experimental results on our Chemical Special Corpus demonstrate that we achieve state-of-art and competitive NER performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge