Leyi Wei
DeepDR: an integrated deep-learning model web server for drug repositioning
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Background: Identifying new indications for approved drugs is a complex and time-consuming process that requires extensive knowledge of pharmacology, clinical data, and advanced computational methods. Recently, deep learning (DL) methods have shown their capability for the accurate prediction of drug repositioning. However, implementing DL-based modeling requires in-depth domain knowledge and proficient programming skills. Results: In this application, we introduce DeepDR, the first integrated platform that combines a variety of established DL-based models for disease- and target-specific drug repositioning tasks. DeepDR leverages invaluable experience to recommend candidate drugs, which covers more than 15 networks and a comprehensive knowledge graph that includes 5.9 million edges across 107 types of relationships connecting drugs, diseases, proteins/genes, pathways, and expression from six existing databases and a large scientific corpus of 24 million PubMed publications. Additionally, the recommended results include detailed descriptions of the recommended drugs and visualize key patterns with interpretability through a knowledge graph. Conclusion: DeepDR is free and open to all users without the requirement of registration. We believe it can provide an easy-to-use, systematic, highly accurate, and computationally automated platform for both experimental and computational scientists.
ERSR: An Ellipse-constrained pseudo-label refinement and symmetric regularization framework for semi-supervised fetal head segmentation in ultrasound images
Aug 27, 2025
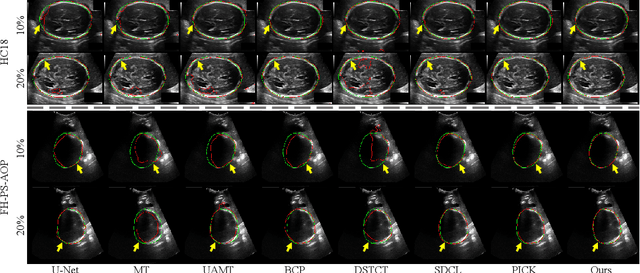

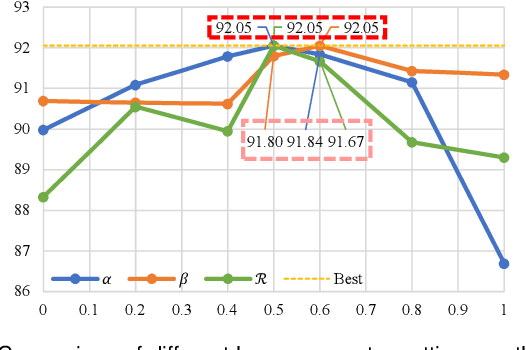
Abstract:Automated segmentation of the fetal head in ultrasound images is critical for prenatal monitoring. However, achieving robust segmentation remains challenging due to the poor quality of ultrasound images and the lack of annotated data. Semi-supervised methods alleviate the lack of annotated data but struggle with the unique characteristics of fetal head ultrasound images, making it challenging to generate reliable pseudo-labels and enforce effective consistency regularization constraints. To address this issue, we propose a novel semi-supervised framework, ERSR, for fetal head ultrasound segmentation. Our framework consists of the dual-scoring adaptive filtering strategy, the ellipse-constrained pseudo-label refinement, and the symmetry-based multiple consistency regularization. The dual-scoring adaptive filtering strategy uses boundary consistency and contour regularity criteria to evaluate and filter teacher outputs. The ellipse-constrained pseudo-label refinement refines these filtered outputs by fitting least-squares ellipses, which strengthens pixels near the center of the fitted ellipse and suppresses noise simultaneously. The symmetry-based multiple consistency regularization enforces multi-level consistency across perturbed images, symmetric regions, and between original predictions and pseudo-labels, enabling the model to capture robust and stable shape representations. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on two benchmarks. On the HC18 dataset, it reaches Dice scores of 92.05% and 95.36% with 10% and 20% labeled data, respectively. On the PSFH dataset, the scores are 91.68% and 93.70% under the same settings.
Iterative pseudo-labeling based adaptive copy-paste supervision for semi-supervised tumor segmentation
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has attracted considerable attention in medical image processing. The latest SSL methods use a combination of consistency regularization and pseudo-labeling to achieve remarkable success. However, most existing SSL studies focus on segmenting large organs, neglecting the challenging scenarios where there are numerous tumors or tumors of small volume. Furthermore, the extensive capabilities of data augmentation strategies, particularly in the context of both labeled and unlabeled data, have yet to be thoroughly investigated. To tackle these challenges, we introduce a straightforward yet effective approach, termed iterative pseudo-labeling based adaptive copy-paste supervision (IPA-CP), for tumor segmentation in CT scans. IPA-CP incorporates a two-way uncertainty based adaptive augmentation mechanism, aiming to inject tumor uncertainties present in the mean teacher architecture into adaptive augmentation. Additionally, IPA-CP employs an iterative pseudo-label transition strategy to generate more robust and informative pseudo labels for the unlabeled samples. Extensive experiments on both in-house and public datasets show that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art SSL methods in medical image segmentation. Ablation study results demonstrate the effectiveness of our technical contributions.
Location embedding based pairwise distance learning for fine-grained diagnosis of urinary stones
Jun 29, 2024Abstract:The precise diagnosis of urinary stones is crucial for devising effective treatment strategies. The diagnostic process, however, is often complicated by the low contrast between stones and surrounding tissues, as well as the variability in stone locations across different patients. To address this issue, we propose a novel location embedding based pairwise distance learning network (LEPD-Net) that leverages low-dose abdominal X-ray imaging combined with location information for the fine-grained diagnosis of urinary stones. LEPD-Net enhances the representation of stone-related features through context-aware region enhancement, incorporates critical location knowledge via stone location embedding, and achieves recognition of fine-grained objects with our innovative fine-grained pairwise distance learning. Additionally, we have established an in-house dataset on urinary tract stones to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach. Comprehensive experiments conducted on this dataset reveal that our framework significantly surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods.
Inter- and intra-uncertainty based feature aggregation model for semi-supervised histopathology image segmentation
Mar 19, 2024Abstract:Acquiring pixel-level annotations is often limited in applications such as histology studies that require domain expertise. Various semi-supervised learning approaches have been developed to work with limited ground truth annotations, such as the popular teacher-student models. However, hierarchical prediction uncertainty within the student model (intra-uncertainty) and image prediction uncertainty (inter-uncertainty) have not been fully utilized by existing methods. To address these issues, we first propose a novel inter- and intra-uncertainty regularization method to measure and constrain both inter- and intra-inconsistencies in the teacher-student architecture. We also propose a new two-stage network with pseudo-mask guided feature aggregation (PG-FANet) as the segmentation model. The two-stage structure complements with the uncertainty regularization strategy to avoid introducing extra modules in solving uncertainties and the aggregation mechanisms enable multi-scale and multi-stage feature integration. Comprehensive experimental results over the MoNuSeg and CRAG datasets show that our PG-FANet outperforms other state-of-the-art methods and our semi-supervised learning framework yields competitive performance with a limited amount of labeled data.
MolCAP: Molecular Chemical reActivity pretraining and prompted-finetuning enhanced molecular representation learning
Jun 13, 2023Abstract:Molecular representation learning (MRL) is a fundamental task for drug discovery. However, previous deep-learning (DL) methods focus excessively on learning robust inner-molecular representations by mask-dominated pretraining framework, neglecting abundant chemical reactivity molecular relationships that have been demonstrated as the determining factor for various molecular property prediction tasks. Here, we present MolCAP to promote MRL, a graph pretraining Transformer based on chemical reactivity (IMR) knowledge with prompted finetuning. Results show that MolCAP outperforms comparative methods based on traditional molecular pretraining framework, in 13 publicly available molecular datasets across a diversity of biomedical tasks. Prompted by MolCAP, even basic graph neural networks are capable of achieving surprising performance that outperforms previous models, indicating the promising prospect of applying reactivity information for MRL. In addition, manual designed molecular templets are potential to uncover the dataset bias. All in all, we expect our MolCAP to gain more chemical meaningful insights for the entire process of drug discovery.
Multi-view deep learning based molecule design and structural optimization accelerates the SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor discovery
Dec 03, 2022Abstract:In this work, we propose MEDICO, a Multi-viEw Deep generative model for molecule generation, structural optimization, and the SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitor disCOvery. To the best of our knowledge, MEDICO is the first-of-this-kind graph generative model that can generate molecular graphs similar to the structure of targeted molecules, with a multi-view representation learning framework to sufficiently and adaptively learn comprehensive structural semantics from targeted molecular topology and geometry. We show that our MEDICO significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in generating valid, unique, and novel molecules under benchmarking comparisons. In particular, we showcase the multi-view deep learning model enables us to generate not only the molecules structurally similar to the targeted molecules but also the molecules with desired chemical properties, demonstrating the strong capability of our model in exploring the chemical space deeply. Moreover, case study results on targeted molecule generation for the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) show that by integrating molecule docking into our model as chemical priori, we successfully generate new small molecules with desired drug-like properties for the Mpro, potentially accelerating the de novo design of Covid-19 drugs. Further, we apply MEDICO to the structural optimization of three well-known Mpro inhibitors (N3, 11a, and GC376) and achieve ~88% improvement in their binding affinity to Mpro, demonstrating the application value of our model for the development of therapeutics for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
MSMG-Net: Multi-scale Multi-grained Supervised Metworks for Multi-task Image Manipulation Detection and Localization
Nov 06, 2022



Abstract:With the rapid advances of image editing techniques in recent years, image manipulation detection has attracted considerable attention since the increasing security risks posed by tampered images. To address these challenges, a novel multi-scale multi-grained deep network (MSMG-Net) is proposed to automatically identify manipulated regions. In our MSMG-Net, a parallel multi-scale feature extraction structure is used to extract multi-scale features. Then the multi-grained feature learning is utilized to perceive object-level semantics relation of multi-scale features by introducing the shunted self-attention. To fuse multi-scale multi-grained features, global and local feature fusion block are designed for manipulated region segmentation by a bottom-up approach and multi-level feature aggregation block is designed for edge artifacts detection by a top-down approach. Thus, MSMG-Net can effectively perceive the object-level semantics and encode the edge artifact. Experimental results on five benchmark datasets justify the superior performance of the proposed method, outperforming state-of-the-art manipulation detection and localization methods. Extensive ablation experiments and feature visualization demonstrate the multi-scale multi-grained learning can present effective visual representations of manipulated regions. In addition, MSMG-Net shows better robustness when various post-processing methods further manipulate images.
EOCSA: Predicting Prognosis of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer with Whole Slide Histopathological Images
Oct 11, 2022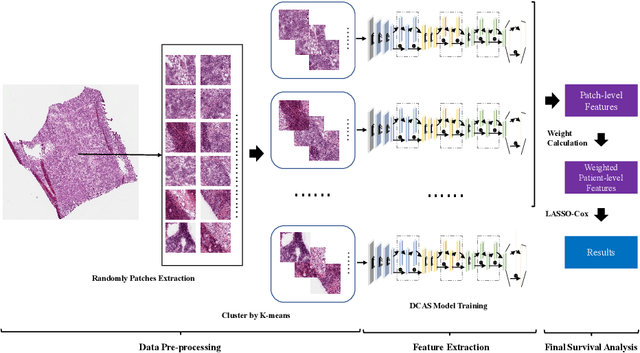
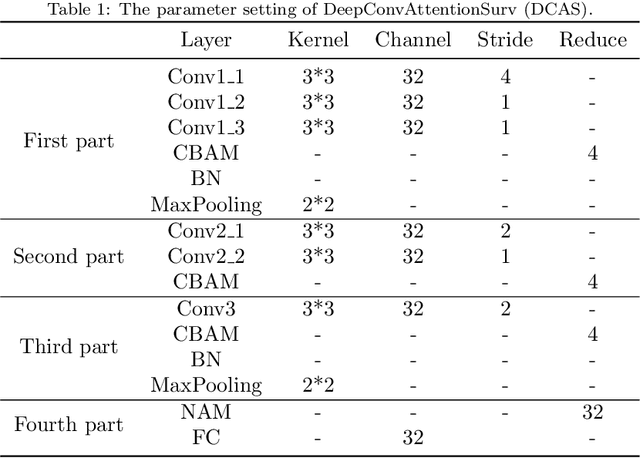
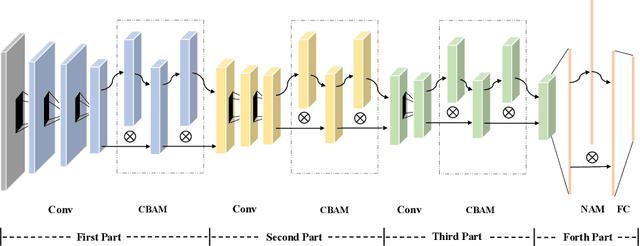
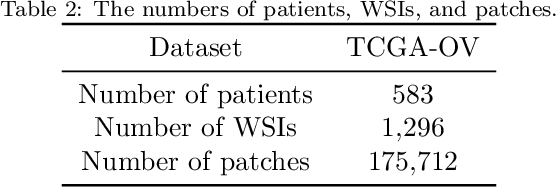
Abstract:Ovarian cancer is one of the most serious cancers that threaten women around the world. Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), as the most commonly seen subtype of ovarian cancer, has rather high mortality rate and poor prognosis among various gynecological cancers. Survival analysis outcome is able to provide treatment advices to doctors. In recent years, with the development of medical imaging technology, survival prediction approaches based on pathological images have been proposed. In this study, we designed a deep framework named EOCSA which analyzes the prognosis of EOC patients based on pathological whole slide images (WSIs). Specifically, we first randomly extracted patches from WSIs and grouped them into multiple clusters. Next, we developed a survival prediction model, named DeepConvAttentionSurv (DCAS), which was able to extract patch-level features, removed less discriminative clusters and predicted the EOC survival precisely. Particularly, channel attention, spatial attention, and neuron attention mechanisms were used to improve the performance of feature extraction. Then patient-level features were generated from our weight calculation method and the survival time was finally estimated using LASSO-Cox model. The proposed EOCSA is efficient and effective in predicting prognosis of EOC and the DCAS ensures more informative and discriminative features can be extracted. As far as we know, our work is the first to analyze the survival of EOC based on WSIs and deep neural network technologies. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed framework has achieved state-of-the-art performance of 0.980 C-index. The implementation of the approach can be found at https://github.com/RanSuLab/EOCprognosis.
MechRetro is a chemical-mechanism-driven graph learning framework for interpretable retrosynthesis prediction and pathway planning
Oct 06, 2022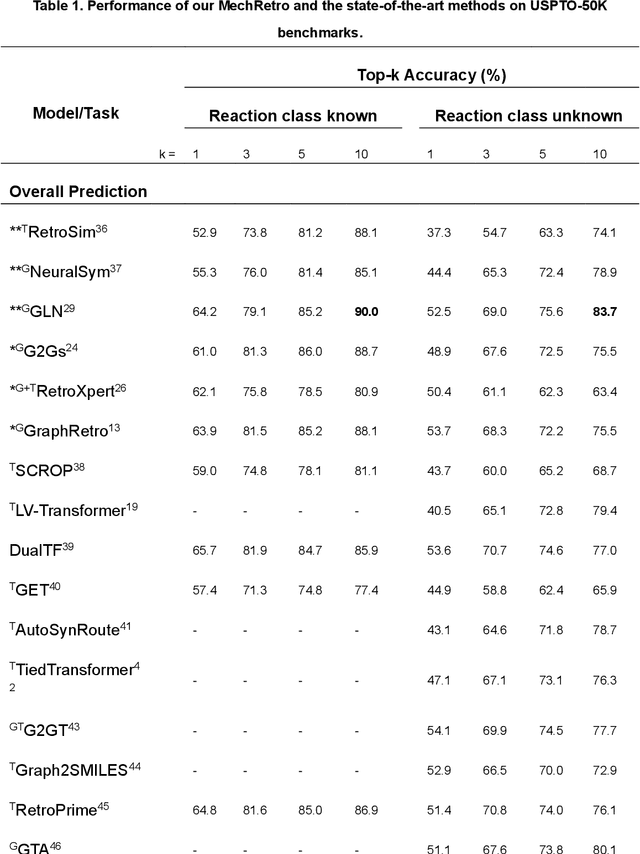
Abstract:Leveraging artificial intelligence for automatic retrosynthesis speeds up organic pathway planning in digital laboratories. However, existing deep learning approaches are unexplainable, like "black box" with few insights, notably limiting their applications in real retrosynthesis scenarios. Here, we propose MechRetro, a chemical-mechanism-driven graph learning framework for interpretable retrosynthetic prediction and pathway planning, which learns several retrosynthetic actions to simulate a reverse reaction via elaborate self-adaptive joint learning. By integrating chemical knowledge as prior information, we design a novel Graph Transformer architecture to adaptively learn discriminative and chemically meaningful molecule representations, highlighting the strong capacity in molecule feature representation learning. We demonstrate that MechRetro outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches for retrosynthetic prediction with a large margin on large-scale benchmark datasets. Extending MechRetro to the multi-step retrosynthesis analysis, we identify efficient synthetic routes via an interpretable reasoning mechanism, leading to a better understanding in the realm of knowledgeable synthetic chemists. We also showcase that MechRetro discovers a novel pathway for protokylol, along with energy scores for uncertainty assessment, broadening the applicability for practical scenarios. Overall, we expect MechRetro to provide meaningful insights for high-throughput automated organic synthesis in drug discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge