Ping Xuan
ERSR: An Ellipse-constrained pseudo-label refinement and symmetric regularization framework for semi-supervised fetal head segmentation in ultrasound images
Aug 27, 2025
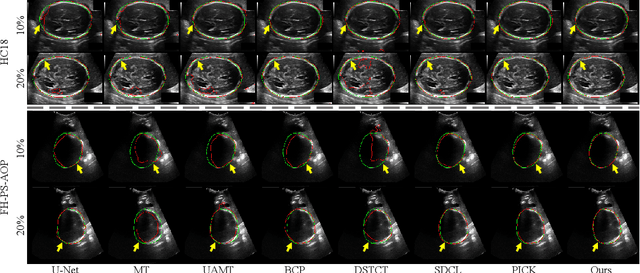

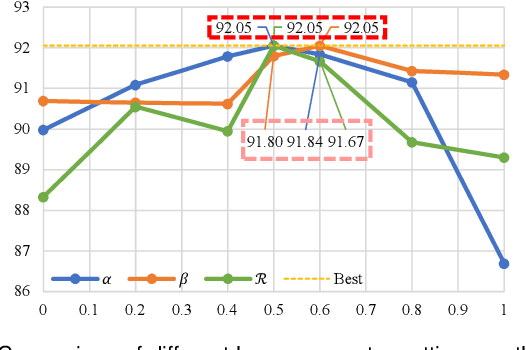
Abstract:Automated segmentation of the fetal head in ultrasound images is critical for prenatal monitoring. However, achieving robust segmentation remains challenging due to the poor quality of ultrasound images and the lack of annotated data. Semi-supervised methods alleviate the lack of annotated data but struggle with the unique characteristics of fetal head ultrasound images, making it challenging to generate reliable pseudo-labels and enforce effective consistency regularization constraints. To address this issue, we propose a novel semi-supervised framework, ERSR, for fetal head ultrasound segmentation. Our framework consists of the dual-scoring adaptive filtering strategy, the ellipse-constrained pseudo-label refinement, and the symmetry-based multiple consistency regularization. The dual-scoring adaptive filtering strategy uses boundary consistency and contour regularity criteria to evaluate and filter teacher outputs. The ellipse-constrained pseudo-label refinement refines these filtered outputs by fitting least-squares ellipses, which strengthens pixels near the center of the fitted ellipse and suppresses noise simultaneously. The symmetry-based multiple consistency regularization enforces multi-level consistency across perturbed images, symmetric regions, and between original predictions and pseudo-labels, enabling the model to capture robust and stable shape representations. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on two benchmarks. On the HC18 dataset, it reaches Dice scores of 92.05% and 95.36% with 10% and 20% labeled data, respectively. On the PSFH dataset, the scores are 91.68% and 93.70% under the same settings.
Iterative pseudo-labeling based adaptive copy-paste supervision for semi-supervised tumor segmentation
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has attracted considerable attention in medical image processing. The latest SSL methods use a combination of consistency regularization and pseudo-labeling to achieve remarkable success. However, most existing SSL studies focus on segmenting large organs, neglecting the challenging scenarios where there are numerous tumors or tumors of small volume. Furthermore, the extensive capabilities of data augmentation strategies, particularly in the context of both labeled and unlabeled data, have yet to be thoroughly investigated. To tackle these challenges, we introduce a straightforward yet effective approach, termed iterative pseudo-labeling based adaptive copy-paste supervision (IPA-CP), for tumor segmentation in CT scans. IPA-CP incorporates a two-way uncertainty based adaptive augmentation mechanism, aiming to inject tumor uncertainties present in the mean teacher architecture into adaptive augmentation. Additionally, IPA-CP employs an iterative pseudo-label transition strategy to generate more robust and informative pseudo labels for the unlabeled samples. Extensive experiments on both in-house and public datasets show that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art SSL methods in medical image segmentation. Ablation study results demonstrate the effectiveness of our technical contributions.
TSEML: A task-specific embedding-based method for few-shot classification of cancer molecular subtypes
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Molecular subtyping of cancer is recognized as a critical and challenging upstream task for personalized therapy. Existing deep learning methods have achieved significant performance in this domain when abundant data samples are available. However, the acquisition of densely labeled samples for cancer molecular subtypes remains a significant challenge for conventional data-intensive deep learning approaches. In this work, we focus on the few-shot molecular subtype prediction problem in heterogeneous and small cancer datasets, aiming to enhance precise diagnosis and personalized treatment. We first construct a new few-shot dataset for cancer molecular subtype classification and auxiliary cancer classification, named TCGA Few-Shot, from existing publicly available datasets. To effectively leverage the relevant knowledge from both tasks, we introduce a task-specific embedding-based meta-learning framework (TSEML). TSEML leverages the synergistic strengths of a model-agnostic meta-learning (MAML) approach and a prototypical network (ProtoNet) to capture diverse and fine-grained features. Comparative experiments conducted on the TCGA Few-Shot dataset demonstrate that our TSEML framework achieves superior performance in addressing the problem of few-shot molecular subtype classification.
Location embedding based pairwise distance learning for fine-grained diagnosis of urinary stones
Jun 29, 2024Abstract:The precise diagnosis of urinary stones is crucial for devising effective treatment strategies. The diagnostic process, however, is often complicated by the low contrast between stones and surrounding tissues, as well as the variability in stone locations across different patients. To address this issue, we propose a novel location embedding based pairwise distance learning network (LEPD-Net) that leverages low-dose abdominal X-ray imaging combined with location information for the fine-grained diagnosis of urinary stones. LEPD-Net enhances the representation of stone-related features through context-aware region enhancement, incorporates critical location knowledge via stone location embedding, and achieves recognition of fine-grained objects with our innovative fine-grained pairwise distance learning. Additionally, we have established an in-house dataset on urinary tract stones to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach. Comprehensive experiments conducted on this dataset reveal that our framework significantly surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge