Lauren Gillespie
On the Opportunities and Risks of Foundation Models
Aug 18, 2021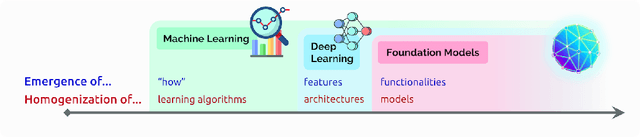
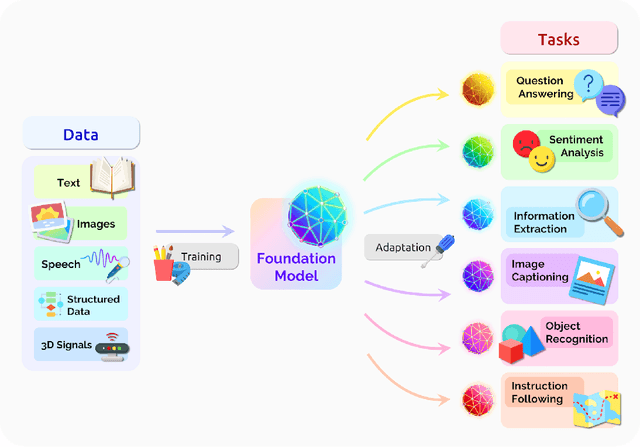
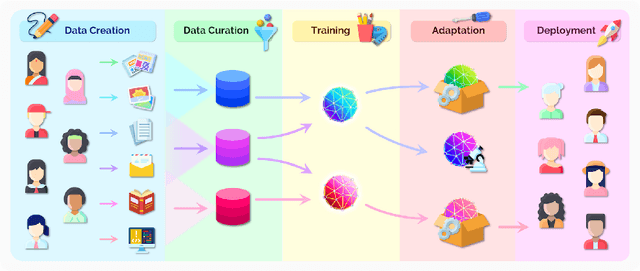
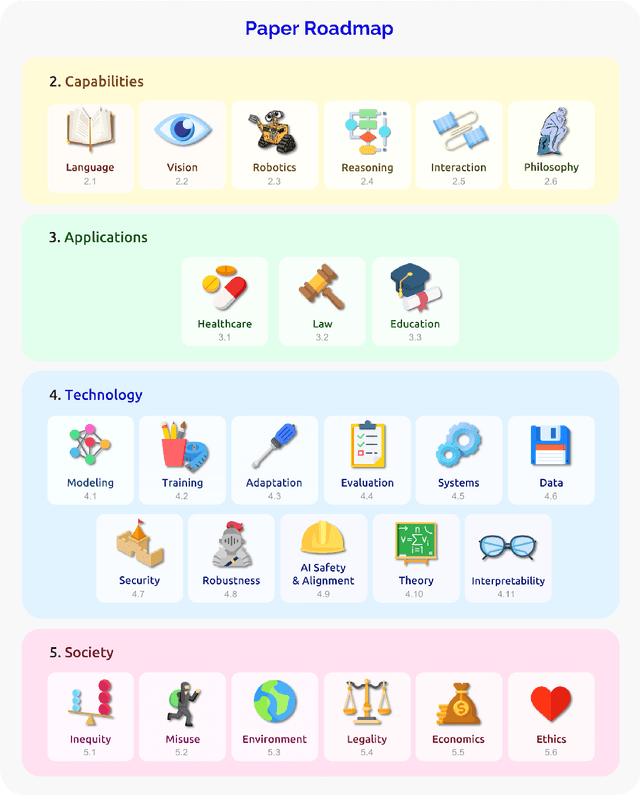
Abstract:AI is undergoing a paradigm shift with the rise of models (e.g., BERT, DALL-E, GPT-3) that are trained on broad data at scale and are adaptable to a wide range of downstream tasks. We call these models foundation models to underscore their critically central yet incomplete character. This report provides a thorough account of the opportunities and risks of foundation models, ranging from their capabilities (e.g., language, vision, robotics, reasoning, human interaction) and technical principles(e.g., model architectures, training procedures, data, systems, security, evaluation, theory) to their applications (e.g., law, healthcare, education) and societal impact (e.g., inequity, misuse, economic and environmental impact, legal and ethical considerations). Though foundation models are based on standard deep learning and transfer learning, their scale results in new emergent capabilities,and their effectiveness across so many tasks incentivizes homogenization. Homogenization provides powerful leverage but demands caution, as the defects of the foundation model are inherited by all the adapted models downstream. Despite the impending widespread deployment of foundation models, we currently lack a clear understanding of how they work, when they fail, and what they are even capable of due to their emergent properties. To tackle these questions, we believe much of the critical research on foundation models will require deep interdisciplinary collaboration commensurate with their fundamentally sociotechnical nature.
Rethinking the limiting dynamics of SGD: modified loss, phase space oscillations, and anomalous diffusion
Jul 19, 2021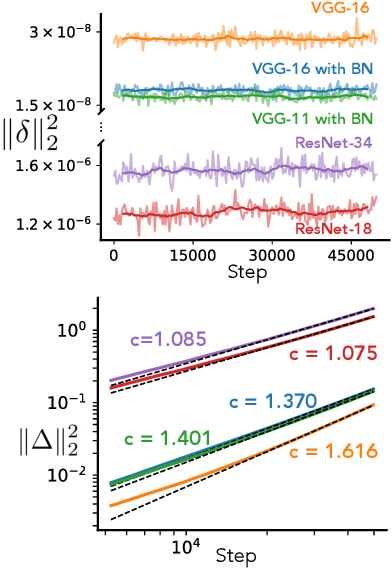
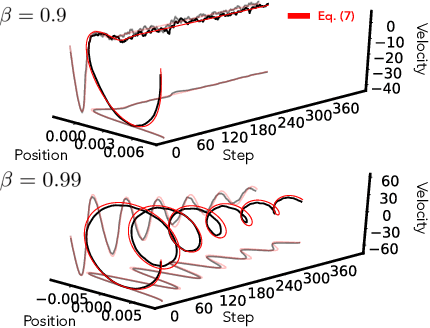
Abstract:In this work we explore the limiting dynamics of deep neural networks trained with stochastic gradient descent (SGD). We find empirically that long after performance has converged, networks continue to move through parameter space by a process of anomalous diffusion in which distance travelled grows as a power law in the number of gradient updates with a nontrivial exponent. We reveal an intricate interaction between the hyperparameters of optimization, the structure in the gradient noise, and the Hessian matrix at the end of training that explains this anomalous diffusion. To build this understanding, we first derive a continuous-time model for SGD with finite learning rates and batch sizes as an underdamped Langevin equation. We study this equation in the setting of linear regression, where we can derive exact, analytic expressions for the phase space dynamics of the parameters and their instantaneous velocities from initialization to stationarity. Using the Fokker-Planck equation, we show that the key ingredient driving these dynamics is not the original training loss, but rather the combination of a modified loss, which implicitly regularizes the velocity, and probability currents, which cause oscillations in phase space. We identify qualitative and quantitative predictions of this theory in the dynamics of a ResNet-18 model trained on ImageNet. Through the lens of statistical physics, we uncover a mechanistic origin for the anomalous limiting dynamics of deep neural networks trained with SGD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge