Kyungjune Baek
Multi-dimensional Preference Alignment by Conditioning Reward Itself
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback has emerged as a standard for aligning diffusion models. However, we identify a fundamental limitation in the standard DPO formulation because it relies on the Bradley-Terry model to aggregate diverse evaluation axes like aesthetic quality and semantic alignment into a single scalar reward. This aggregation creates a reward conflict where the model is forced to unlearn desirable features of a specific dimension if they appear in a globally non-preferred sample. To address this issue, we propose Multi Reward Conditional DPO (MCDPO). This method resolves reward conflicts by introducing a disentangled Bradley-Terry objective. MCDPO explicitly injects a preference outcome vector as a condition during training, which allows the model to learn the correct optimization direction for each reward axis independently within a single network. We further introduce dimensional reward dropout to ensure balanced optimization across dimensions. Extensive experiments on Stable Diffusion 1.5 and SDXL demonstrate that MCDPO achieves superior performance on benchmarks. Notably, our conditional framework enables dynamic and multiple-axis control at inference time using Classifier Free Guidance to amplify specific reward dimensions without additional training or external reward models.
Rethinking Direct Preference Optimization in Diffusion Models
May 24, 2025



Abstract:Aligning text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models with human preferences has emerged as a critical research challenge. While recent advances in this area have extended preference optimization techniques from large language models (LLMs) to the diffusion setting, they often struggle with limited exploration. In this work, we propose a novel and orthogonal approach to enhancing diffusion-based preference optimization. First, we introduce a stable reference model update strategy that relaxes the frozen reference model, encouraging exploration while maintaining a stable optimization anchor through reference model regularization. Second, we present a timestep-aware training strategy that mitigates the reward scale imbalance problem across timesteps. Our method can be integrated into various preference optimization algorithms. Experimental results show that our approach improves the performance of state-of-the-art methods on human preference evaluation benchmarks.
Toward Stable World Models: Measuring and Addressing World Instability in Generative Environments
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:We present a novel study on enhancing the capability of preserving the content in world models, focusing on a property we term World Stability. Recent diffusion-based generative models have advanced the synthesis of immersive and realistic environments that are pivotal for applications such as reinforcement learning and interactive game engines. However, while these models excel in quality and diversity, they often neglect the preservation of previously generated scenes over time--a shortfall that can introduce noise into agent learning and compromise performance in safety-critical settings. In this work, we introduce an evaluation framework that measures world stability by having world models perform a sequence of actions followed by their inverses to return to their initial viewpoint, thereby quantifying the consistency between the starting and ending observations. Our comprehensive assessment of state-of-the-art diffusion-based world models reveals significant challenges in achieving high world stability. Moreover, we investigate several improvement strategies to enhance world stability. Our results underscore the importance of world stability in world modeling and provide actionable insights for future research in this domain.
Length-Aware DETR for Robust Moment Retrieval
Dec 30, 2024Abstract:Video Moment Retrieval (MR) aims to localize moments within a video based on a given natural language query. Given the prevalent use of platforms like YouTube for information retrieval, the demand for MR techniques is significantly growing. Recent DETR-based models have made notable advances in performance but still struggle with accurately localizing short moments. Through data analysis, we identified limited feature diversity in short moments, which motivated the development of MomentMix. MomentMix employs two augmentation strategies: ForegroundMix and BackgroundMix, each enhancing the feature representations of the foreground and background, respectively. Additionally, our analysis of prediction bias revealed that short moments particularly struggle with accurately predicting their center positions of moments. To address this, we propose a Length-Aware Decoder, which conditions length through a novel bipartite matching process. Our extensive studies demonstrate the efficacy of our length-aware approach, especially in localizing short moments, leading to improved overall performance. Our method surpasses state-of-the-art DETR-based methods on benchmark datasets, achieving the highest R1 and mAP on QVHighlights and the highest R1@0.7 on TACoS and Charades-STA (such as a 2.46% gain in R1@0.7 and a 2.57% gain in mAP average for QVHighlights). The code is available at https://github.com/sjpark5800/LA-DETR.
TWLV-I: Analysis and Insights from Holistic Evaluation on Video Foundation Models
Aug 21, 2024Abstract:In this work, we discuss evaluating video foundation models in a fair and robust manner. Unlike language or image foundation models, many video foundation models are evaluated with differing parameters (such as sampling rate, number of frames, pretraining steps, etc.), making fair and robust comparisons challenging. Therefore, we present a carefully designed evaluation framework for measuring two core capabilities of video comprehension: appearance and motion understanding. Our findings reveal that existing video foundation models, whether text-supervised like UMT or InternVideo2, or self-supervised like V-JEPA, exhibit limitations in at least one of these capabilities. As an alternative, we introduce TWLV-I, a new video foundation model that constructs robust visual representations for both motion- and appearance-based videos. Based on the average top-1 accuracy of linear probing on five action recognition benchmarks, pretrained only on publicly accessible datasets, our model shows a 4.6%p improvement compared to V-JEPA (ViT-L) and a 7.7%p improvement compared to UMT (ViT-L). Even when compared to much larger models, our model demonstrates a 7.2%p improvement compared to DFN (ViT-H), a 2.7%p improvement compared to V-JEPA~(ViT-H) and a 2.8%p improvement compared to InternVideo2 (ViT-g). We provide embedding vectors obtained by TWLV-I from videos of several commonly used video benchmarks, along with evaluation source code that can directly utilize these embeddings. The code is available on "https://github.com/twelvelabs-io/video-embeddings-evaluation-framework".
Commonality in Natural Images Rescues GANs: Pretraining GANs with Generic and Privacy-free Synthetic Data
Apr 11, 2022

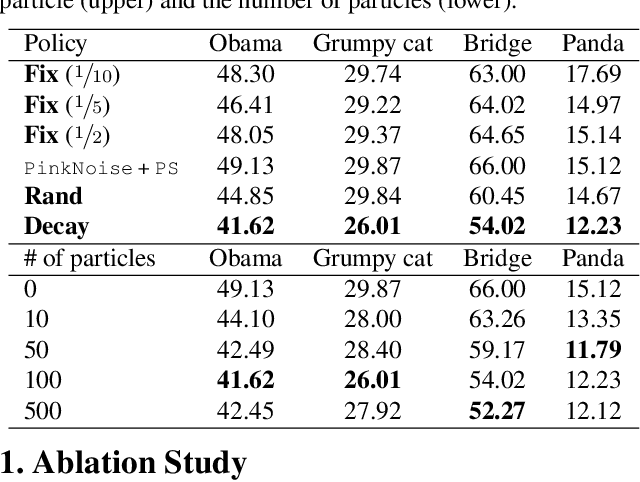
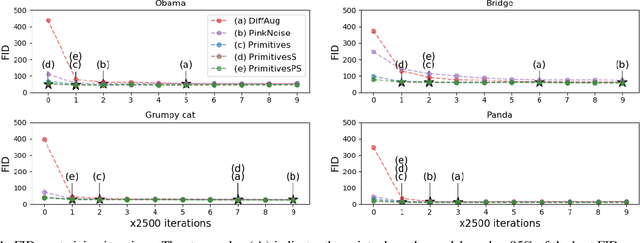
Abstract:Transfer learning for GANs successfully improves generation performance under low-shot regimes. However, existing studies show that the pretrained model using a single benchmark dataset is not generalized to various target datasets. More importantly, the pretrained model can be vulnerable to copyright or privacy risks as membership inference attack advances. To resolve both issues, we propose an effective and unbiased data synthesizer, namely Primitives-PS, inspired by the generic characteristics of natural images. Specifically, we utilize 1) the generic statistics on the frequency magnitude spectrum, 2) the elementary shape (i.e., image composition via elementary shapes) for representing the structure information, and 3) the existence of saliency as prior. Since our synthesizer only considers the generic properties of natural images, the single model pretrained on our dataset can be consistently transferred to various target datasets, and even outperforms the previous methods pretrained with the natural images in terms of Fr'echet inception distance. Extensive analysis, ablation study, and evaluations demonstrate that each component of our data synthesizer is effective, and provide insights on the desirable nature of the pretrained model for the transferability of GANs.
Rethinking the Truly Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation
Jun 11, 2020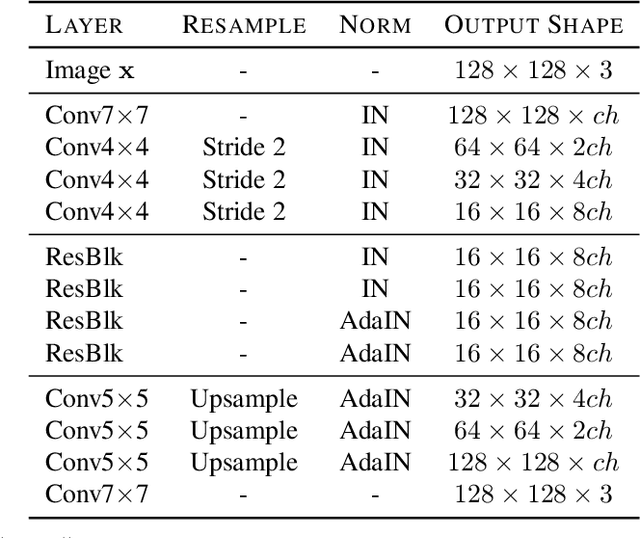

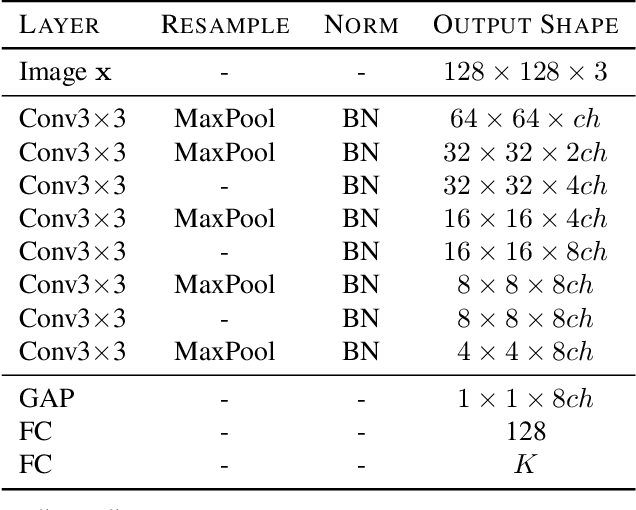
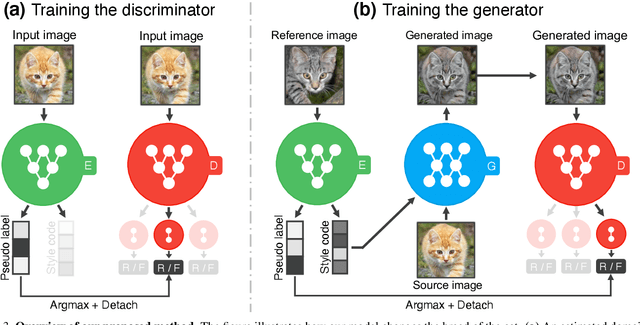
Abstract:Every recent image-to-image translation model uses either image-level (i.e. input-output pairs) or set-level (i.e. domain labels) supervision at minimum. However, even the set-level supervision can be a serious bottleneck for data collection in practice. In this paper, we tackle image-to-image translation in a fully unsupervised setting, i.e., neither paired images nor domain labels. To this end, we propose the truly unsupervised image-to-image translation method (TUNIT) that simultaneously learns to separate image domains via an information-theoretic approach and generate corresponding images using the estimated domain labels. Experimental results on various datasets show that the proposed method successfully separates domains and translates images across those domains. In addition, our model outperforms existing set-level supervised methods under a semi-supervised setting, where a subset of domain labels is provided. The source code is available at https://github.com/clovaai/tunit
Editable Generative Adversarial Networks: Generating and Editing Faces Simultaneously
Jul 20, 2018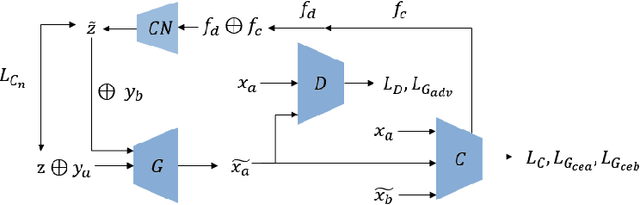
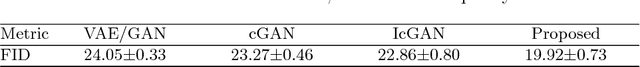

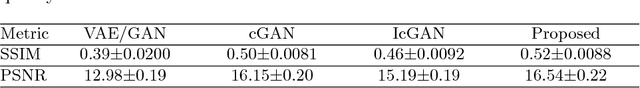
Abstract:We propose a novel framework for simultaneously generating and manipulating the face images with desired attributes. While the state-of-the-art attribute editing technique has achieved the impressive performance for creating realistic attribute effects, they only address the image editing problem, using the input image as the condition of model. Recently, several studies attempt to tackle both novel face generation and attribute editing problem using a single solution. However, their image quality is still unsatisfactory. Our goal is to develop a single unified model that can simultaneously create and edit high quality face images with desired attributes. A key idea of our work is that we decompose the image into the latent and attribute vector in low dimensional representation, and then utilize the GAN framework for mapping the low dimensional representation to the image. In this way, we can address both the generation and editing problem by learning the generator. For qualitative and quantitative evaluations, the proposed algorithm outperforms recent algorithms addressing the same problem. Also, we show that our model can achieve the competitive performance with the state-of-the-art attribute editing technique in terms of attribute editing quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge