Kuan Zhu
Improving Generalization in LLM Structured Pruning via Function-Aware Neuron Grouping
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive performance across natural language tasks but incur substantial computational and storage costs due to their scale. Post-training structured pruning offers an efficient solution. However, when few-shot calibration sets fail to adequately reflect the pretraining data distribution, existing methods exhibit limited generalization to downstream tasks. To address this issue, we propose Function-Aware Neuron Grouping (FANG), a post-training pruning framework that alleviates calibration bias by identifying and preserving neurons critical to specific function. FANG groups neurons with similar function based on the type of semantic context they process and prunes each group independently. During importance estimation within each group, tokens that strongly correlate with the functional role of the neuron group are given higher weighting. Additionally, FANG also preserves neurons that contribute across multiple context types. To achieve a better trade-off between sparsity and performance, it allocates sparsity to each block adaptively based on its functional complexity. Experiments show that FANG improves downstream accuracy while preserving language modeling performance. It achieves the state-of-the-art (SOTA) results when combined with FLAP and OBC, two representative pruning methods. Specifically, FANG outperforms FLAP and OBC by 1.5%--8.5% in average accuracy under 30% and 40% sparsity.
Seedance 1.5 pro: A Native Audio-Visual Joint Generation Foundation Model
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Recent strides in video generation have paved the way for unified audio-visual generation. In this work, we present Seedance 1.5 pro, a foundational model engineered specifically for native, joint audio-video generation. Leveraging a dual-branch Diffusion Transformer architecture, the model integrates a cross-modal joint module with a specialized multi-stage data pipeline, achieving exceptional audio-visual synchronization and superior generation quality. To ensure practical utility, we implement meticulous post-training optimizations, including Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) on high-quality datasets and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) with multi-dimensional reward models. Furthermore, we introduce an acceleration framework that boosts inference speed by over 10X. Seedance 1.5 pro distinguishes itself through precise multilingual and dialect lip-syncing, dynamic cinematic camera control, and enhanced narrative coherence, positioning it as a robust engine for professional-grade content creation. Seedance 1.5 pro is now accessible on Volcano Engine at https://console.volcengine.com/ark/region:ark+cn-beijing/experience/vision?type=GenVideo.
UniFGVC: Universal Training-Free Few-Shot Fine-Grained Vision Classification via Attribute-Aware Multimodal Retrieval
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Few-shot fine-grained visual classification (FGVC) aims to leverage limited data to enable models to discriminate subtly distinct categories. Recent works mostly finetuned the pre-trained visual language models to achieve performance gain, yet suffering from overfitting and weak generalization. To deal with this, we introduce UniFGVC, a universal training-free framework that reformulates few-shot FGVC as multimodal retrieval. First, we propose the Category-Discriminative Visual Captioner (CDV-Captioner) to exploit the open-world knowledge of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to generate a structured text description that captures the fine-grained attribute features distinguishing closely related classes. CDV-Captioner uses chain-of-thought prompting and visually similar reference images to reduce hallucination and enhance discrimination of generated captions. Using it we can convert each image into an image-description pair, enabling more comprehensive feature representation, and construct the multimodal category templates using few-shot samples for the subsequent retrieval pipeline. Then, off-the-shelf vision and text encoders embed query and template pairs, and FGVC is accomplished by retrieving the nearest template in the joint space. UniFGVC ensures broad compatibility with diverse MLLMs and encoders, offering reliable generalization and adaptability across few-shot FGVC scenarios. Extensive experiments on 12 FGVC benchmarks demonstrate its consistent superiority over prior few-shot CLIP-based methods and even several fully-supervised MLLMs-based approaches.
Cracking the Code of Hallucination in LVLMs with Vision-aware Head Divergence
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) have made substantial progress in integrating large language models (LLMs) with visual inputs, enabling advanced multimodal reasoning. Despite their success, a persistent challenge is hallucination-where generated text fails to accurately reflect visual content-undermining both accuracy and reliability. Existing methods focus on alignment training or decoding refinements but primarily address symptoms at the generation stage without probing the underlying causes. In this work, we investigate the internal mechanisms driving hallucination in LVLMs, with an emphasis on the multi-head attention module. Specifically, we introduce Vision-aware Head Divergence (VHD), a metric that quantifies the sensitivity of attention head outputs to visual context. Based on this, our findings reveal the presence of vision-aware attention heads that are more attuned to visual information; however, the model's overreliance on its prior language patterns is closely related to hallucinations. Building on these insights, we propose Vision-aware Head Reinforcement (VHR), a training-free approach to mitigate hallucination by enhancing the role of vision-aware attention heads. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance compared to state-of-the-art approaches in mitigating hallucinations, while maintaining high efficiency with negligible additional time overhead.
Monocular Lane Detection Based on Deep Learning: A Survey
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Lane detection plays an important role in autonomous driving perception systems. As deep learning algorithms gain popularity, monocular lane detection methods based on deep learning have demonstrated superior performance and emerged as a key research direction in autonomous driving perception. The core design of these algorithmic frameworks can be summarized as follows: (1) Task paradigm, focusing on lane instance-level discrimination; (2) Lane modeling, representing lanes as a set of learnable parameters in the neural network; (3) Global context supplementation, enhancing the detection of obscure lanes; (4) Perspective effect elimination, providing 3D lanes usable for downstream applications. From these perspectives, this paper presents a comprehensive overview of existing methods, encompassing both the increasingly mature 2D lane detection approaches and the developing 3D lane detection works. For a relatively fair comparison, in addition to comparing the performance of mainstream methods on different benchmarks, their inference speed is also investigated under a unified setting. Moreover, we present some extended works on lane detection, including multi-task perception, video lane detection, online high-definition map construction, and lane topology reasoning, to offer readers a comprehensive roadmap for the evolution of lane detection. Finally, we point out some potential future research directions in this field. We exhaustively collect the papers and codes of existing works at https://github.com/Core9724/Awesome-Lane-Detection and will keep tracing the research.
SEEKR: Selective Attention-Guided Knowledge Retention for Continual Learning of Large Language Models
Nov 09, 2024Abstract:Continual learning (CL) is crucial for language models to dynamically adapt to the evolving real-world demands. To mitigate the catastrophic forgetting problem in CL, data replay has been proven a simple and effective strategy, and the subsequent data-replay-based distillation can further enhance the performance. However, existing methods fail to fully exploit the knowledge embedded in models from previous tasks, resulting in the need for a relatively large number of replay samples to achieve good results. In this work, we first explore and emphasize the importance of attention weights in knowledge retention, and then propose a SElective attEntion-guided Knowledge Retention method (SEEKR) for data-efficient replay-based continual learning of large language models (LLMs). Specifically, SEEKR performs attention distillation on the selected attention heads for finer-grained knowledge retention, where the proposed forgettability-based and task-sensitivity-based measures are used to identify the most valuable attention heads. Experimental results on two continual learning benchmarks for LLMs demonstrate the superiority of SEEKR over the existing methods on both performance and efficiency. Explicitly, SEEKR achieves comparable or even better performance with only 1/10 of the replayed data used by other methods, and reduces the proportion of replayed data to 1%.
Plug-and-Play Pseudo Label Correction Network for Unsupervised Person Re-identification
Jun 14, 2022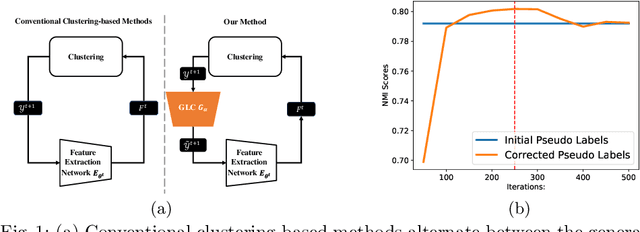
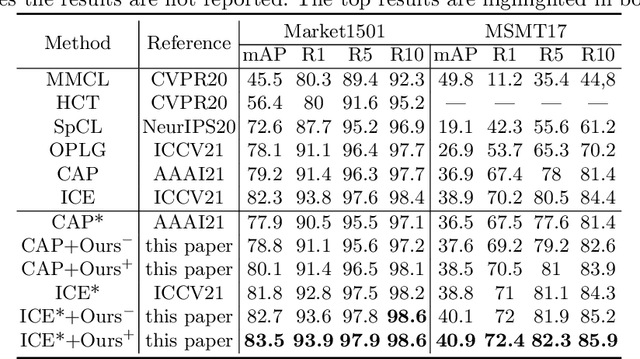
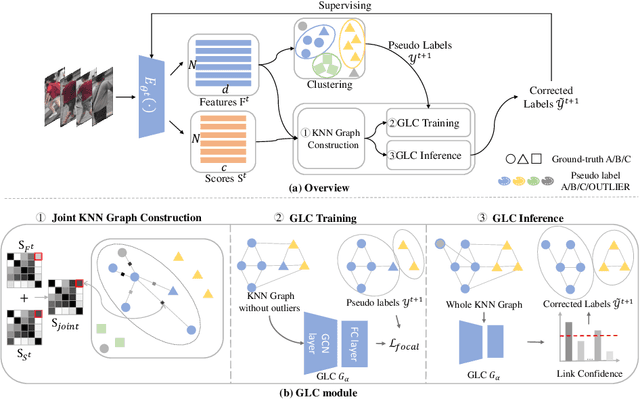
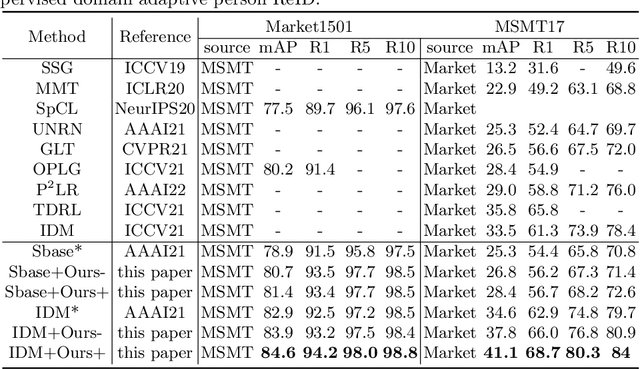
Abstract:Clustering-based methods, which alternate between the generation of pseudo labels and the optimization of the feature extraction network, play a dominant role in both unsupervised learning (USL) and unsupervised domain adaptive (UDA) person re-identification (Re-ID). To alleviate the adverse effect of noisy pseudo labels, the existing methods either abandon unreliable labels or refine the pseudo labels via mutual learning or label propagation. However, a great many erroneous labels are still accumulated because these methods mostly adopt traditional unsupervised clustering algorithms which rely on certain assumptions on data distribution and fail to capture the distribution of complex real-world data. In this paper, we propose the plug-and-play graph-based pseudo label correction network (GLC) to refine the pseudo labels in the manner of supervised clustering. GLC is trained to perceive the varying data distribution at each epoch of the self-training with the supervision of initial pseudo labels generated by any clustering method. It can learn to rectify the initial noisy labels by means of the relationship constraints between samples on the k Nearest Neighbor (kNN) graph and early-stop training strategy. Specifically, GLC learns to aggregate node features from neighbors and predict whether the nodes should be linked on the graph. Besides, GLC is optimized with 'early stop' before the noisy labels are severely memorized to prevent overfitting to noisy pseudo labels. Consequently, GLC improves the quality of pseudo labels though the supervision signals contain some noise, leading to better Re-ID performance. Extensive experiments in USL and UDA person Re-ID on Market-1501 and MSMT17 show that our method is widely compatible with various clustering-based methods and promotes the state-of-the-art performance consistently.
Part-Aware Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Person Re-Identification
Mar 08, 2022



Abstract:In person re-identification (ReID), very recent researches have validated pre-training the models on unlabelled person images is much better than on ImageNet. However, these researches directly apply the existing self-supervised learning (SSL) methods designed for image classification to ReID without any adaption in the framework. These SSL methods match the outputs of local views (e.g., red T-shirt, blue shorts) to those of the global views at the same time, losing lots of details. In this paper, we propose a ReID-specific pre-training method, Part-Aware Self-Supervised pre-training (PASS), which can generate part-level features to offer fine-grained information and is more suitable for ReID. PASS divides the images into several local areas, and the local views randomly cropped from each area are assigned with a specific learnable [PART] token. On the other hand, the [PART]s of all local areas are also appended to the global views. PASS learns to match the output of the local views and global views on the same [PART]. That is, the learned [PART] of the local views from a local area is only matched with the corresponding [PART] learned from the global views. As a result, each [PART] can focus on a specific local area of the image and extracts fine-grained information of this area. Experiments show PASS sets the new state-of-the-art performances on Market1501 and MSMT17 on various ReID tasks, e.g., vanilla ViT-S/16 pre-trained by PASS achieves 92.2\%/90.2\%/88.5\% mAP accuracy on Market1501 for supervised/UDA/USL ReID. Our codes are available at https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/PASS-reID.
AAformer: Auto-Aligned Transformer for Person Re-Identification
Apr 02, 2021



Abstract:Transformer is showing its superiority over convolutional architectures in many vision tasks like image classification and object detection. However, the lacking of an explicit alignment mechanism limits its capability in person re-identification (re-ID), in which there are inevitable misalignment issues caused by pose/viewpoints variations, etc. On the other hand, the alignment paradigm of convolutional neural networks does not perform well in Transformer in our experiments. To address this problem, we develop a novel alignment framework for Transformer through adding the learnable vectors of "part tokens" to learn the part representations and integrating the part alignment into the self-attention. A part token only interacts with a subset of patch embeddings and learns to represent this subset. Based on the framework, we design an online Auto-Aligned Transformer (AAformer) to adaptively assign the patch embeddings of the same semantics to the identical part token in the running time. The part tokens can be regarded as the part prototypes, and a fast variant of Sinkhorn-Knopp algorithm is employed to cluster the patch embeddings to part tokens online. AAformer can be viewed as a new principled formulation for simultaneously learning both part alignment and part representations. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of part tokens and the superiority of AAformer over various state-of-the-art CNN-based methods. Our codes will be released.
Identity-Guided Human Semantic Parsing for Person Re-Identification
Jul 27, 2020



Abstract:Existing alignment-based methods have to employ the pretrained human parsing models to achieve the pixel-level alignment, and cannot identify the personal belongings (e.g., backpacks and reticule) which are crucial to person re-ID. In this paper, we propose the identity-guided human semantic parsing approach (ISP) to locate both the human body parts and personal belongings at pixel-level for aligned person re-ID only with person identity labels. We design the cascaded clustering on feature maps to generate the pseudo-labels of human parts. Specifically, for the pixels of all images of a person, we first group them to foreground or background and then group the foreground pixels to human parts. The cluster assignments are subsequently used as pseudo-labels of human parts to supervise the part estimation and ISP iteratively learns the feature maps and groups them. Finally, local features of both human body parts and personal belongings are obtained according to the selflearned part estimation, and only features of visible parts are utilized for the retrieval. Extensive experiments on three widely used datasets validate the superiority of ISP over lots of state-of-the-art methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/ISP-reID.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge