Kevin Maik Jablonka
Beyond Learning on Molecules by Weakly Supervising on Molecules
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Molecular representations are inherently task-dependent, yet most pre-trained molecular encoders are not. Task conditioning promises representations that reorganize based on task descriptions, but existing approaches rely on expensive labeled data. We show that weak supervision on programmatically derived molecular motifs is sufficient. Our Adaptive Chemical Embedding Model (ACE-Mol) learns from hundreds of motifs paired with natural language descriptors that are cheap to compute, trivial to scale. Conventional encoders slowly search the embedding space for task-relevant structure, whereas ACE-Mol immediately aligns its representations with the task. ACE-Mol achieves state-of-the-art performance across molecular property prediction benchmarks with interpretable, chemically meaningful representations.
Semantic Content Determines Algorithmic Performance
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Counting should not depend on what is being counted; more generally, any algorithm's behavior should be invariant to the semantic content of its arguments. We introduce WhatCounts to test this property in isolation. Unlike prior work that conflates semantic sensitivity with reasoning complexity or prompt variation, WhatCounts is atomic: count items in an unambiguous, delimited list with no duplicates, distractors, or reasoning steps for different semantic types. Frontier LLMs show over 40% accuracy variation depending solely on what is being counted - cities versus chemicals, names versus symbols. Controlled ablations rule out confounds. The gap is semantic, and it shifts unpredictably with small amounts of unrelated fine-tuning. LLMs do not implement algorithms; they approximate them, and the approximation is argument-dependent. As we show with an agentic example, this has implications beyond counting: any LLM function may carry hidden dependencies on the meaning of its inputs.
An autonomous living database for perovskite photovoltaics
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Scientific discovery is severely bottlenecked by the inability of manual curation to keep pace with exponential publication rates. This creates a widening knowledge gap. This is especially stark in photovoltaics, where the leading database for perovskite solar cells has been stagnant since 2021 despite massive ongoing research output. Here, we resolve this challenge by establishing an autonomous, self-updating living database (PERLA). Our pipeline integrates large language models with physics-aware validation to extract complex device data from the continuous literature stream, achieving human-level precision (>90%) and eliminating annotator variance. By employing this system on the previously inaccessible post-2021 literature, we uncover critical evolutionary trends hidden by data lag: the field has decisively shifted toward inverted architectures employing self-assembled monolayers and formamidinium-rich compositions, driving a clear trajectory of sustained voltage loss reduction. PERLA transforms static publications into dynamic knowledge resources that enable data-driven discovery to operate at the speed of publication.
General purpose models for the chemical sciences
Jul 10, 2025



Abstract:Data-driven techniques have a large potential to transform and accelerate the chemical sciences. However, chemical sciences also pose the unique challenge of very diverse, small, fuzzy datasets that are difficult to leverage in conventional machine learning approaches completely. A new class of models, general-purpose models (GPMs) such as large language models, have shown the ability to solve tasks they have not been directly trained on, and to flexibly operate with low amounts of data in different formats. In this review, we discuss fundamental building principles of GPMs and review recent applications of those models in the chemical sciences across the entire scientific process. While many of these applications are still in the prototype phase, we expect that the increasing interest in GPMs will make many of them mature in the coming years.
ChemPile: A 250GB Diverse and Curated Dataset for Chemical Foundation Models
May 18, 2025



Abstract:Foundation models have shown remarkable success across scientific domains, yet their impact in chemistry remains limited due to the absence of diverse, large-scale, high-quality datasets that reflect the field's multifaceted nature. We present the ChemPile, an open dataset containing over 75 billion tokens of curated chemical data, specifically built for training and evaluating general-purpose models in the chemical sciences. The dataset mirrors the human learning journey through chemistry -- from educational foundations to specialized expertise -- spanning multiple modalities and content types including structured data in diverse chemical representations (SMILES, SELFIES, IUPAC names, InChI, molecular renderings), scientific and educational text, executable code, and chemical images. ChemPile integrates foundational knowledge (textbooks, lecture notes), specialized expertise (scientific articles and language-interfaced data), visual understanding (molecular structures, diagrams), and advanced reasoning (problem-solving traces and code) -- mirroring how human chemists develop expertise through diverse learning materials and experiences. Constructed through hundreds of hours of expert curation, the ChemPile captures both foundational concepts and domain-specific complexity. We provide standardized training, validation, and test splits, enabling robust benchmarking. ChemPile is openly released via HuggingFace with a consistent API, permissive license, and detailed documentation. We hope the ChemPile will serve as a catalyst for chemical AI, enabling the development of the next generation of chemical foundation models.
Lessons from the trenches on evaluating machine-learning systems in materials science
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Measurements are fundamental to knowledge creation in science, enabling consistent sharing of findings and serving as the foundation for scientific discovery. As machine learning systems increasingly transform scientific fields, the question of how to effectively evaluate these systems becomes crucial for ensuring reliable progress. In this review, we examine the current state and future directions of evaluation frameworks for machine learning in science. We organize the review around a broadly applicable framework for evaluating machine learning systems through the lens of statistical measurement theory, using materials science as our primary context for examples and case studies. We identify key challenges common across machine learning evaluation such as construct validity, data quality issues, metric design limitations, and benchmark maintenance problems that can lead to phantom progress when evaluation frameworks fail to capture real-world performance needs. By examining both traditional benchmarks and emerging evaluation approaches, we demonstrate how evaluation choices fundamentally shape not only our measurements but also research priorities and scientific progress. These findings reveal the critical need for transparency in evaluation design and reporting, leading us to propose evaluation cards as a structured approach to documenting measurement choices and limitations. Our work highlights the importance of developing a more diverse toolbox of evaluation techniques for machine learning in materials science, while offering insights that can inform evaluation practices in other scientific domains where similar challenges exist.
Probing the limitations of multimodal language models for chemistry and materials research
Nov 25, 2024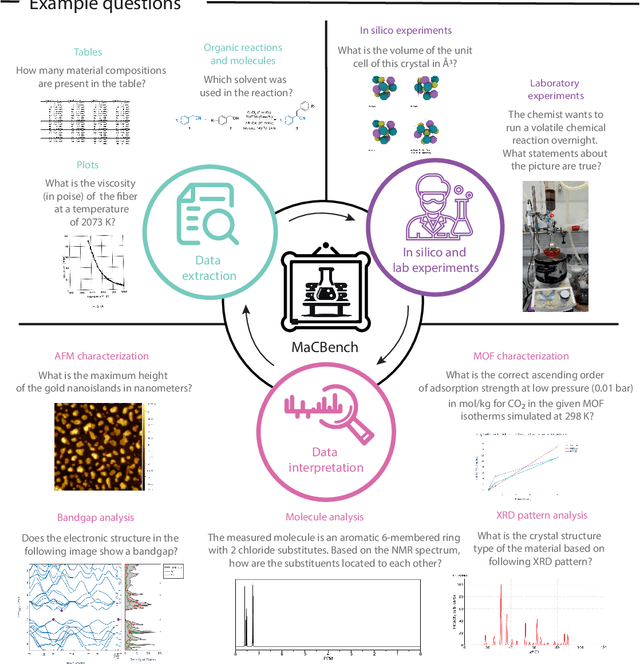
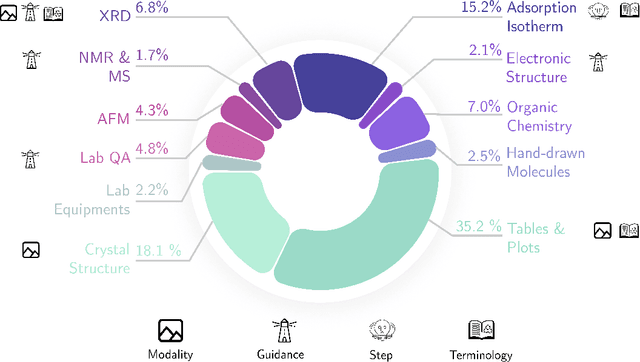
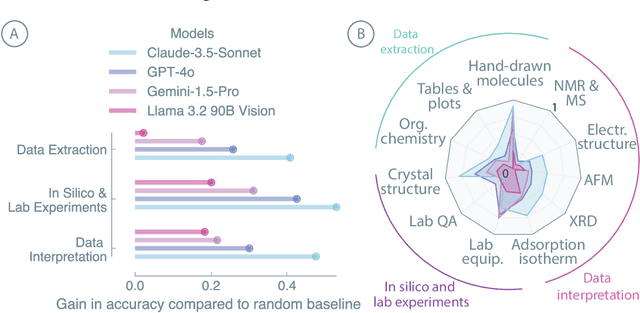
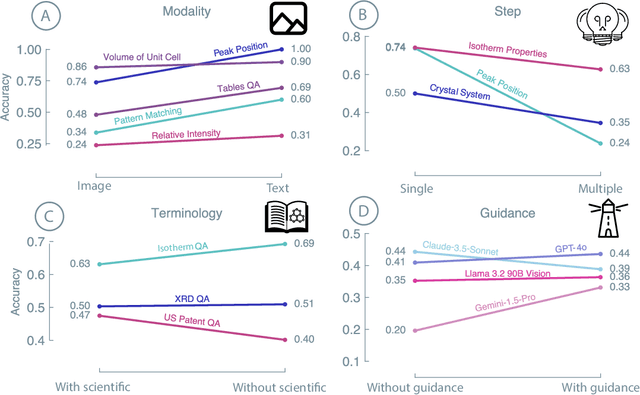
Abstract:Recent advancements in artificial intelligence have sparked interest in scientific assistants that could support researchers across the full spectrum of scientific workflows, from literature review to experimental design and data analysis. A key capability for such systems is the ability to process and reason about scientific information in both visual and textual forms - from interpreting spectroscopic data to understanding laboratory setups. Here, we introduce MaCBench, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating how vision-language models handle real-world chemistry and materials science tasks across three core aspects: data extraction, experimental understanding, and results interpretation. Through a systematic evaluation of leading models, we find that while these systems show promising capabilities in basic perception tasks - achieving near-perfect performance in equipment identification and standardized data extraction - they exhibit fundamental limitations in spatial reasoning, cross-modal information synthesis, and multi-step logical inference. Our insights have important implications beyond chemistry and materials science, suggesting that developing reliable multimodal AI scientific assistants may require advances in curating suitable training data and approaches to training those models.
Reflections from the 2024 Large Language Model (LLM) Hackathon for Applications in Materials Science and Chemistry
Nov 20, 2024
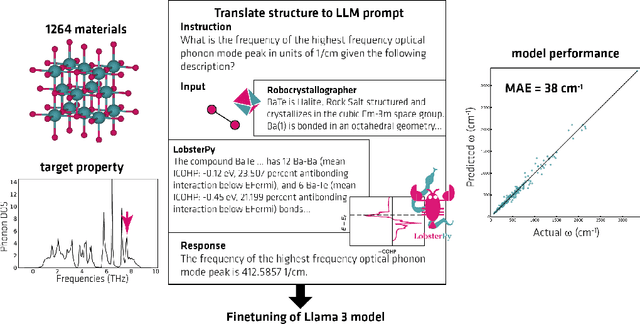
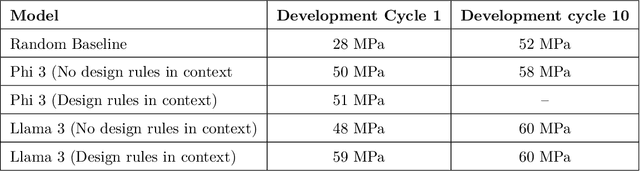
Abstract:Here, we present the outcomes from the second Large Language Model (LLM) Hackathon for Applications in Materials Science and Chemistry, which engaged participants across global hybrid locations, resulting in 34 team submissions. The submissions spanned seven key application areas and demonstrated the diverse utility of LLMs for applications in (1) molecular and material property prediction; (2) molecular and material design; (3) automation and novel interfaces; (4) scientific communication and education; (5) research data management and automation; (6) hypothesis generation and evaluation; and (7) knowledge extraction and reasoning from scientific literature. Each team submission is presented in a summary table with links to the code and as brief papers in the appendix. Beyond team results, we discuss the hackathon event and its hybrid format, which included physical hubs in Toronto, Montreal, San Francisco, Berlin, Lausanne, and Tokyo, alongside a global online hub to enable local and virtual collaboration. Overall, the event highlighted significant improvements in LLM capabilities since the previous year's hackathon, suggesting continued expansion of LLMs for applications in materials science and chemistry research. These outcomes demonstrate the dual utility of LLMs as both multipurpose models for diverse machine learning tasks and platforms for rapid prototyping custom applications in scientific research.
From Text to Insight: Large Language Models for Materials Science Data Extraction
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:The vast majority of materials science knowledge exists in unstructured natural language, yet structured data is crucial for innovative and systematic materials design. Traditionally, the field has relied on manual curation and partial automation for data extraction for specific use cases. The advent of large language models (LLMs) represents a significant shift, potentially enabling efficient extraction of structured, actionable data from unstructured text by non-experts. While applying LLMs to materials science data extraction presents unique challenges, domain knowledge offers opportunities to guide and validate LLM outputs. This review provides a comprehensive overview of LLM-based structured data extraction in materials science, synthesizing current knowledge and outlining future directions. We address the lack of standardized guidelines and present frameworks for leveraging the synergy between LLMs and materials science expertise. This work serves as a foundational resource for researchers aiming to harness LLMs for data-driven materials research. The insights presented here could significantly enhance how researchers across disciplines access and utilize scientific information, potentially accelerating the development of novel materials for critical societal needs.
MatText: Do Language Models Need More than Text & Scale for Materials Modeling?
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Effectively representing materials as text has the potential to leverage the vast advancements of large language models (LLMs) for discovering new materials. While LLMs have shown remarkable success in various domains, their application to materials science remains underexplored. A fundamental challenge is the lack of understanding of how to best utilize text-based representations for materials modeling. This challenge is further compounded by the absence of a comprehensive benchmark to rigorously evaluate the capabilities and limitations of these text representations in capturing the complexity of material systems. To address this gap, we propose MatText, a suite of benchmarking tools and datasets designed to systematically evaluate the performance of language models in modeling materials. MatText encompasses nine distinct text-based representations for material systems, including several novel representations. Each representation incorporates unique inductive biases that capture relevant information and integrate prior physical knowledge about materials. Additionally, MatText provides essential tools for training and benchmarking the performance of language models in the context of materials science. These tools include standardized dataset splits for each representation, probes for evaluating sensitivity to geometric factors, and tools for seamlessly converting crystal structures into text. Using MatText, we conduct an extensive analysis of the capabilities of language models in modeling materials. Our findings reveal that current language models consistently struggle to capture the geometric information crucial for materials modeling across all representations. Instead, these models tend to leverage local information, which is emphasized in some of our novel representations. Our analysis underscores MatText's ability to reveal shortcomings of text-based methods for materials design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge