Justin Goodwin
Reducing the Sensitivity of Neural Physics Simulators to Mesh Topology via Pretraining
Jan 16, 2025Abstract:Meshes are used to represent complex objects in high fidelity physics simulators across a variety of domains, such as radar sensing and aerodynamics. There is growing interest in using neural networks to accelerate physics simulations, and also a growing body of work on applying neural networks directly to irregular mesh data. Since multiple mesh topologies can represent the same object, mesh augmentation is typically required to handle topological variation when training neural networks. Due to the sensitivity of physics simulators to small changes in mesh shape, it is challenging to use these augmentations when training neural network-based physics simulators. In this work, we show that variations in mesh topology can significantly reduce the performance of neural network simulators. We evaluate whether pretraining can be used to address this issue, and find that employing an established autoencoder pretraining technique with graph embedding models reduces the sensitivity of neural network simulators to variations in mesh topology. Finally, we highlight future research directions that may further reduce neural simulator sensitivity to mesh topology.
Differentiable Point Scattering Models for Efficient Radar Target Characterization
Jun 05, 2022



Abstract:Target characterization is an important step in many defense missions, often relying on fitting a known target model to observed data. Optimization of model parameters can be computationally expensive depending on the model complexity, thus having models that both describe the data well and that can be efficiently optimized is critical. This work introduces a class of radar models that can be used to represent the radar scattering response of a target at high frequencies while also enabling the use of gradient-based optimization.
Tools and Practices for Responsible AI Engineering
Jan 14, 2022Abstract:Responsible Artificial Intelligence (AI) - the practice of developing, evaluating, and maintaining accurate AI systems that also exhibit essential properties such as robustness and explainability - represents a multifaceted challenge that often stretches standard machine learning tooling, frameworks, and testing methods beyond their limits. In this paper, we present two new software libraries - hydra-zen and the rAI-toolbox - that address critical needs for responsible AI engineering. hydra-zen dramatically simplifies the process of making complex AI applications configurable, and their behaviors reproducible. The rAI-toolbox is designed to enable methods for evaluating and enhancing the robustness of AI-models in a way that is scalable and that composes naturally with other popular ML frameworks. We describe the design principles and methodologies that make these tools effective, including the use of property-based testing to bolster the reliability of the tools themselves. Finally, we demonstrate the composability and flexibility of the tools by showing how various use cases from adversarial robustness and explainable AI can be concisely implemented with familiar APIs.
Principles for Evaluation of AI/ML Model Performance and Robustness
Jul 06, 2021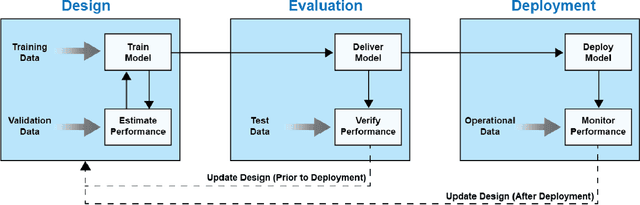
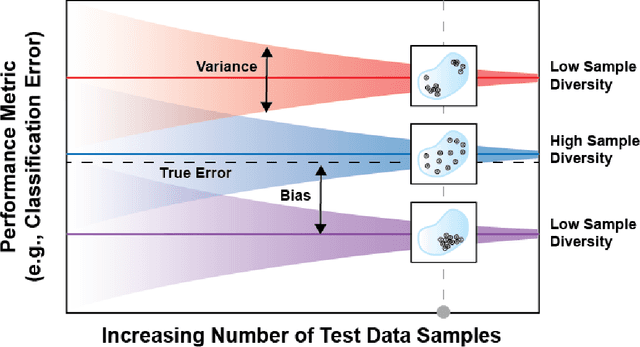
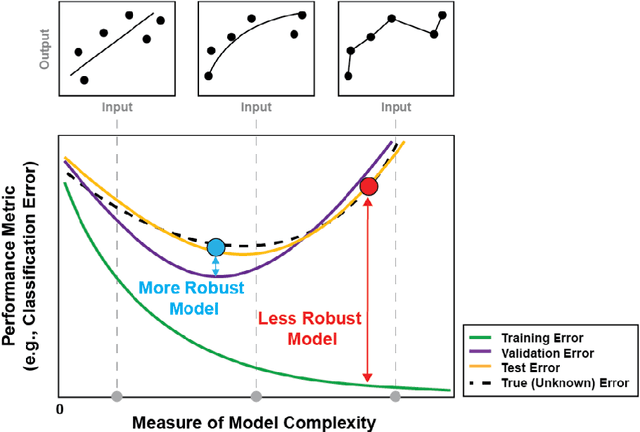
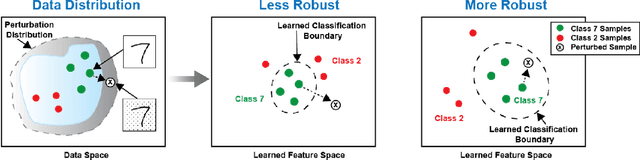
Abstract:The Department of Defense (DoD) has significantly increased its investment in the design, evaluation, and deployment of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) capabilities to address national security needs. While there are numerous AI/ML successes in the academic and commercial sectors, many of these systems have also been shown to be brittle and nonrobust. In a complex and ever-changing national security environment, it is vital that the DoD establish a sound and methodical process to evaluate the performance and robustness of AI/ML models before these new capabilities are deployed to the field. This paper reviews the AI/ML development process, highlights common best practices for AI/ML model evaluation, and makes recommendations to DoD evaluators to ensure the deployment of robust AI/ML capabilities for national security needs.
Fast Training of Deep Neural Networks Robust to Adversarial Perturbations
Jul 08, 2020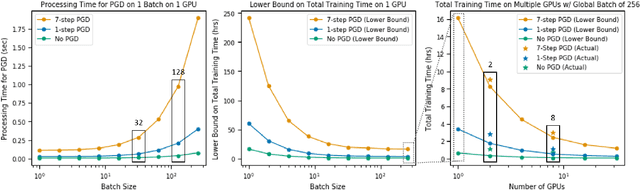
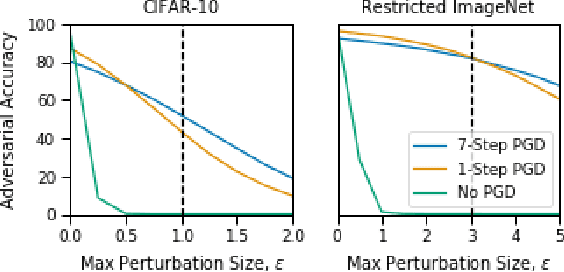


Abstract:Deep neural networks are capable of training fast and generalizing well within many domains. Despite their promising performance, deep networks have shown sensitivities to perturbations of their inputs (e.g., adversarial examples) and their learned feature representations are often difficult to interpret, raising concerns about their true capability and trustworthiness. Recent work in adversarial training, a form of robust optimization in which the model is optimized against adversarial examples, demonstrates the ability to improve performance sensitivities to perturbations and yield feature representations that are more interpretable. Adversarial training, however, comes with an increased computational cost over that of standard (i.e., nonrobust) training, rendering it impractical for use in large-scale problems. Recent work suggests that a fast approximation to adversarial training shows promise for reducing training time and maintaining robustness in the presence of perturbations bounded by the infinity norm. In this work, we demonstrate that this approach extends to the Euclidean norm and preserves the human-aligned feature representations that are common for robust models. Additionally, we show that using a distributed training scheme can further reduce the time to train robust deep networks. Fast adversarial training is a promising approach that will provide increased security and explainability in machine learning applications for which robust optimization was previously thought to be impractical.
Safe Predictors for Enforcing Input-Output Specifications
Jan 29, 2020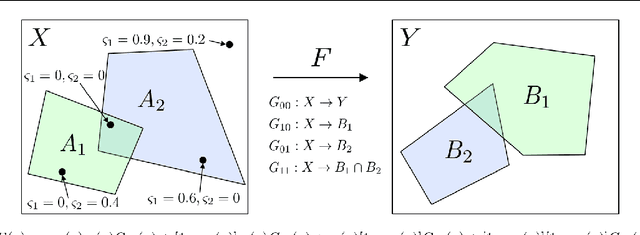


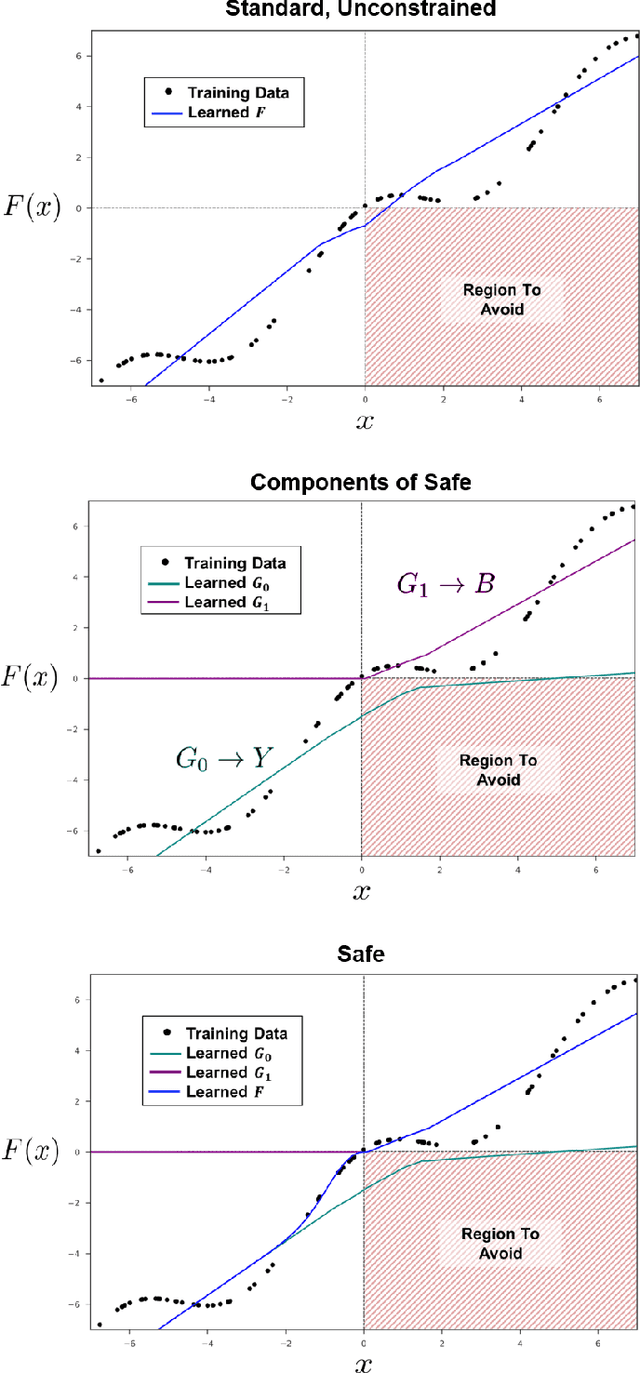
Abstract:We present an approach for designing correct-by-construction neural networks (and other machine learning models) that are guaranteed to be consistent with a collection of input-output specifications before, during, and after algorithm training. Our method involves designing a constrained predictor for each set of compatible constraints, and combining them safely via a convex combination of their predictions. We demonstrate our approach on synthetic datasets and an aircraft collision avoidance problem.
Kernelized Capsule Networks
Jun 07, 2019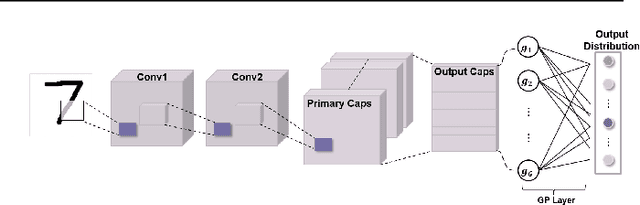
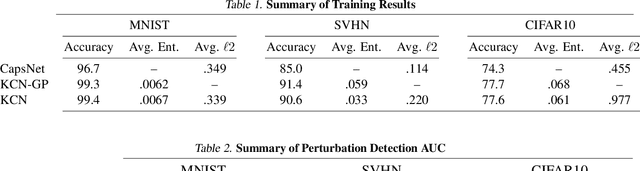
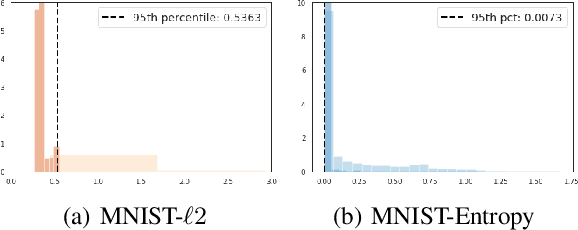
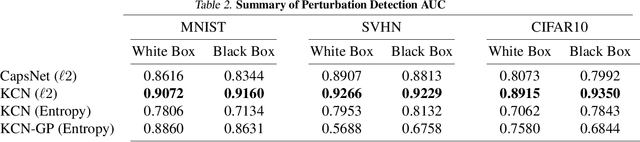
Abstract:Capsule Networks attempt to represent patterns in images in a way that preserves hierarchical spatial relationships. Additionally, research has demonstrated that these techniques may be robust against adversarial perturbations. We present an improvement to training capsule networks with added robustness via non-parametric kernel methods. The representations learned through the capsule network are used to construct covariance kernels for Gaussian processes (GPs). We demonstrate that this approach achieves comparable prediction performance to Capsule Networks while improving robustness to adversarial perturbations and providing a meaningful measure of uncertainty that may aid in the detection of adversarial inputs.
AI Enabling Technologies: A Survey
May 08, 2019



Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the opportunity to revolutionize the way the United States Department of Defense (DoD) and Intelligence Community (IC) address the challenges of evolving threats, data deluge, and rapid courses of action. Developing an end-to-end artificial intelligence system involves parallel development of different pieces that must work together in order to provide capabilities that can be used by decision makers, warfighters and analysts. These pieces include data collection, data conditioning, algorithms, computing, robust artificial intelligence, and human-machine teaming. While much of the popular press today surrounds advances in algorithms and computing, most modern AI systems leverage advances across numerous different fields. Further, while certain components may not be as visible to end-users as others, our experience has shown that each of these interrelated components play a major role in the success or failure of an AI system. This article is meant to highlight many of these technologies that are involved in an end-to-end AI system. The goal of this article is to provide readers with an overview of terminology, technical details and recent highlights from academia, industry and government. Where possible, we indicate relevant resources that can be used for further reading and understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge