Junqiu Wei
Text-to-TrajVis: Enabling Trajectory Data Visualizations from Natural Language Questions
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces the Text-to-TrajVis task, which aims to transform natural language questions into trajectory data visualizations, facilitating the development of natural language interfaces for trajectory visualization systems. As this is a novel task, there is currently no relevant dataset available in the community. To address this gap, we first devised a new visualization language called Trajectory Visualization Language (TVL) to facilitate querying trajectory data and generating visualizations. Building on this foundation, we further proposed a dataset construction method that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) with human efforts to create high-quality data. Specifically, we first generate TVLs using a comprehensive and systematic process, and then label each TVL with corresponding natural language questions using LLMs. This process results in the creation of the first large-scale Text-to-TrajVis dataset, named TrajVL, which contains 18,140 (question, TVL) pairs. Based on this dataset, we systematically evaluated the performance of multiple LLMs (GPT, Qwen, Llama, etc.) on this task. The experimental results demonstrate that this task is both feasible and highly challenging and merits further exploration within the research community.
Training Multilingual Pre-trained Language Model with Byte-level Subwords
Jan 23, 2021



Abstract:The pre-trained language models have achieved great successes in various natural language understanding (NLU) tasks due to its capacity to capture the deep contextualized information in text by pre-training on large-scale corpora. One of the fundamental components in pre-trained language models is the vocabulary, especially for training multilingual models on many different languages. In the technical report, we present our practices on training multilingual pre-trained language models with BBPE: Byte-Level BPE (i.e., Byte Pair Encoding). In the experiment, we adopted the architecture of NEZHA as the underlying pre-trained language model and the results show that NEZHA trained with byte-level subwords consistently outperforms Google multilingual BERT and vanilla NEZHA by a notable margin in several multilingual NLU tasks. We release the source code of our byte-level vocabulary building tools and the multilingual pre-trained language models.
TensorCoder: Dimension-Wise Attention via Tensor Representation for Natural Language Modeling
Aug 12, 2020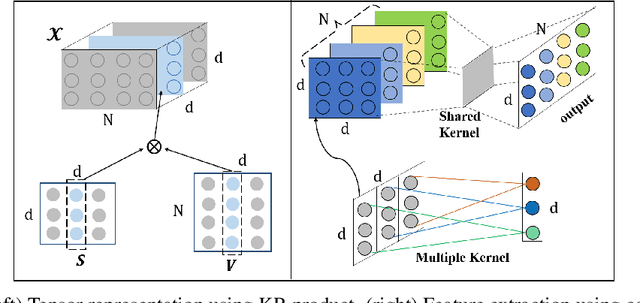
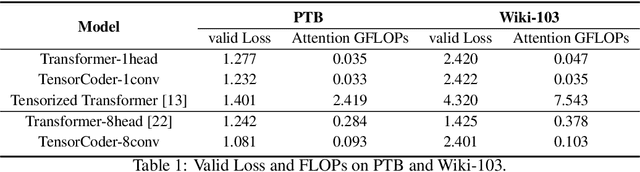
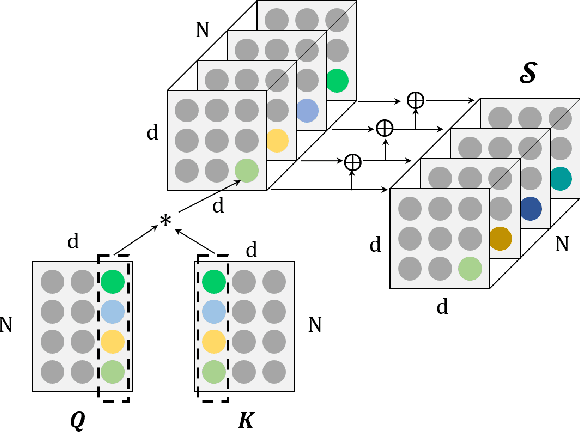
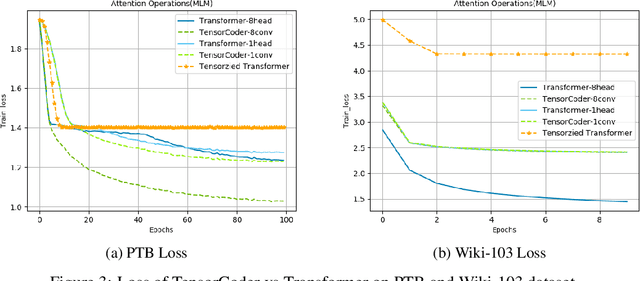
Abstract:Transformer has been widely-used in many Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks and the scaled dot-product attention between tokens is a core module of Transformer. This attention is a token-wise design and its complexity is quadratic to the length of sequence, limiting its application potential for long sequence tasks. In this paper, we propose a dimension-wise attention mechanism based on which a novel language modeling approach (namely TensorCoder) can be developed. The dimension-wise attention can reduce the attention complexity from the original $O(N^2d)$ to $O(Nd^2)$, where $N$ is the length of the sequence and $d$ is the dimensionality of head. We verify TensorCoder on two tasks including masked language modeling and neural machine translation. Compared with the original Transformer, TensorCoder not only greatly reduces the calculation of the original model but also obtains improved performance on masked language modeling task (in PTB dataset) and comparable performance on machine translation tasks.
NEZHA: Neural Contextualized Representation for Chinese Language Understanding
Sep 05, 2019



Abstract:The pre-trained language models have achieved great successes in various natural language understanding (NLU) tasks due to its capacity to capture the deep contextualized information in text by pre-training on large-scale corpora. In this technical report, we present our practice of pre-training language models named NEZHA (NEural contextualiZed representation for CHinese lAnguage understanding) on Chinese corpora and finetuning for the Chinese NLU tasks. The current version of NEZHA is based on BERT with a collection of proven improvements, which include Functional Relative Positional Encoding as an effective positional encoding scheme, Whole Word Masking strategy, Mixed Precision Training and the LAMB Optimizer in training the models. The experimental results show that NEZHA achieves the state-of-the-art performances when finetuned on several representative Chinese tasks, including named entity recognition (People's Daily NER), sentence matching (LCQMC), Chinese sentiment classification (ChnSenti) and natural language inference (XNLI).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge